|
April 2051 lunar eclipse
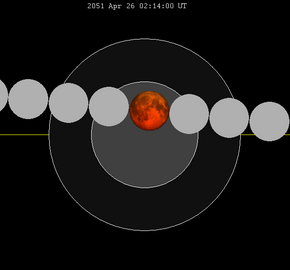
A total lunar eclipse will occur at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit on Wednesday, April 26, 2051,[1] with an umbral magnitude of 1.2034. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. A total lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon's near side entirely passes into the Earth's umbral shadow. Unlike a solar eclipse, which can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world, a lunar eclipse may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth. A total lunar eclipse can last up to nearly two hours, while a total solar eclipse lasts only a few minutes at any given place, because the Moon's shadow is smaller. Occurring about 2.6 days after apogee (on April 23, 2051, at 12:00 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter will be smaller.[2] This lunar eclipse is the third of a tetrad, with four total lunar eclipses in series, the others being on May 6, 2050; October 30, 2050; and October 19, 2051. VisibilityThe eclipse will be completely visible over South America and west Africa, seen rising over North America and the eastern Pacific Ocean and setting over central and east Africa, Europe, and west, central, and south Asia.[3]
Eclipse detailsShown below is a table displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. It describes various parameters pertaining to this eclipse.[4]
Eclipse seasonThis eclipse is part of an eclipse season, a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and repeats just short of six months (173 days) later; thus two full eclipse seasons always occur each year. Either two or three eclipses happen each eclipse season. In the sequence below, each eclipse is separated by a fortnight.
Related eclipsesEclipses in 2051
Metonic
Tzolkinex
Half-Saros
Tritos
Lunar Saros 132
Inex
Triad
Lunar eclipses of 2049–2052This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of lunar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[5] The penumbral lunar eclipse on June 15, 2049 occurs in the previous lunar year eclipse set.
Saros 132Lunar saros series 132, repeating every 18 years and 11 days, has a total of 71 lunar eclipse events including 44 umbral lunar eclipses (32 partial lunar eclipses and 12 total lunar eclipses).
There are 11 series events between 1901 and 2100, grouped into threes (called an exeligmos), each column with approximately the same viewing longitude on earth.
Half-Saros cycleA lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[7] This lunar eclipse is related to two total solar eclipses of Solar Saros 139.
See alsoNotes
External links
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||