|
February 2017 lunar eclipse
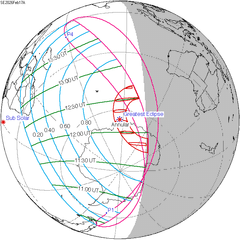
A penumbral lunar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit on Saturday, February 11, 2017,[1] with an umbral magnitude of −0.0342. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. A penumbral lunar eclipse occurs when part or all of the Moon's near side passes into the Earth's penumbra. Unlike a solar eclipse, which can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world, a lunar eclipse may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth. Occurring about 4.6 days before perigee (on February 6, 2017, at 9:00 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.[2] This eclipse occurred the same day as comet 45P/Honda–Mrkos–Pajdušáková made a close approach to Earth (0.08318 AU). It also occurred on the Lantern Festival, the first eclipse to do so since February 9, 2009. VisibilityThe eclipse was completely visible over northeastern North America, eastern South America, Europe, Africa, and west Asia, seen rising over much of North America and western South America and setting over south and east Asia.[3]
Gallery
Eclipse detailsShown below is a table displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. It describes various parameters pertaining to this eclipse.[4]
Eclipse seasonThis eclipse is part of an eclipse season, a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and repeats just short of six months (173 days) later; thus two full eclipse seasons always occur each year. Either two or three eclipses happen each eclipse season. In the sequence below, each eclipse is separated by a fortnight.
Related eclipsesEclipses in 2017
Metonic
Tzolkinex
Half-Saros
Tritos
Lunar Saros 114
Inex
Triad
Lunar eclipses of 2016–2020
Saros 114It is part of Saros cycle 114. Lunar Saros series 114, repeating every 18 years and 11 days, has a total of 71 lunar eclipse events including 13 total lunar eclipses. First Penumbral Lunar Eclipse: 0971 May 13 First Partial Lunar Eclipse: 1115 Aug 07 First Total Lunar Eclipse: 1458 Feb 28 First Central Lunar Eclipse: 1530 Apr 12 Greatest Eclipse of Lunar Saros 114: 1584 May 24 Last Central Lunar Eclipse: 1638 Jun 26 Last Total Lunar Eclipse: 1674 Jul 17 Last Partial Lunar Eclipse: 1890 Nov 26 Last Penumbral Lunar Eclipse: 2233 Jun 22 Half-Saros cycleA lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[5] This lunar eclipse is related to two annular solar eclipses of Solar Saros 121.
See alsoReferences
External linksWikimedia Commons has media related to Lunar eclipse of 2017 February 11.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||