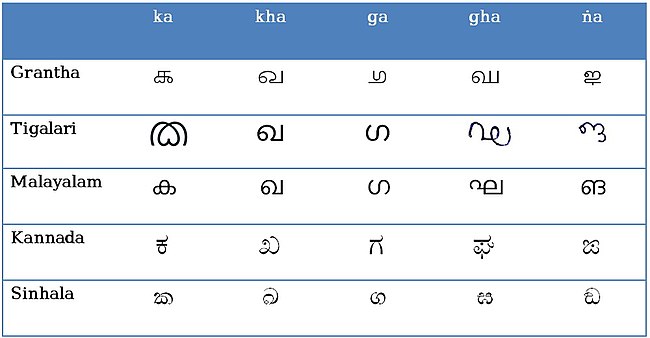
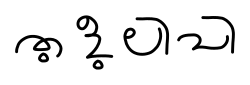Tigalari script
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Brazilian judoka (born 1983) This article is about the Brazilian judoka born in 1983. For the Brazilian judoka born in 1994, see Eduardo Yudy Santos. Eduardo SantosPersonal informationBorn (1983-04-22) 22 April 1983 (age 41)São Paulo, BrazilOccupationJudokaHeight1.82 m (6 ft 0 in)SportCountry BrazilSportJudoWeight class–90 kgAchievements and titlesOlympic Games7th (2008)World Champ.R64 (2013)Pan American Champ. (2008) Medal record Men's judo Rep…

Sexual violence in India Rape Types Acquaintance rape Campus rape Child sexual abuse Corrective rape LGBT victims Cybersex trafficking Drug-facilitated rape Date rape Gang rape Genocidal rape Gray rape Live streaming rape Marital rape Prison rape Rape chant Serial rape Sexual abuse Sexual assault Statutory rape Unacknowledged rape Rape by deception Effects and motivations Effects and aftermath Factors involved Pregnancy from rape Rape crisis movement Rape trauma syndrome Causes Post-assault trea…

Questa voce sugli argomenti arene di pallacanestro e palazzetti di pallavolo è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Ginásio do MaracanãzinhoMaracanãzinho, Ginásio Gilberto Cardoso Informazioni generaliStato Brasile UbicazioneRua Professor Rabelo20271-111 Rio de Janeiro Inizio lavori24 settembre 1954 Inaugurazione1954 Chiusuraottobre 2003 Ristrutturazione2003-2007 Costi di ricostr.R$ 97 000 000 ProprietarioSoprintendenza delle s…

Breakfast soup made from a beer-based roux Beer soupTypeSoupMain ingredientsRoux, beer, cheeseVariationsUse of potato as an ingredient and thickener Media: Beer soup Beer soup (German: Biersuppe, Alsatian: Biersupp, Czech: Pivní polévka) is a soup which is usually roux-based and made with beer.[1] In medieval Europe, it was served as a breakfast soup,[2] sometimes poured over bread. Variations on the recipe use the starchiness of potato as a thickener.[3] The …

Dommartin-sous-HanscomuneDommartin-sous-Hans – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Francia RegioneGrand Est Dipartimento Marna ArrondissementSainte-Menehould CantoneArgonne Suippe et Vesle TerritorioCoordinate49°07′N 4°47′E / 49.116667°N 4.783333°E49.116667; 4.783333 (Dommartin-sous-Hans)Coordinate: 49°07′N 4°47′E / 49.116667°N 4.783333°E49.116667; 4.783333 (Dommartin-sous-Hans) Superficie6,63 km² Abitanti55[1] (2009) Densità8…
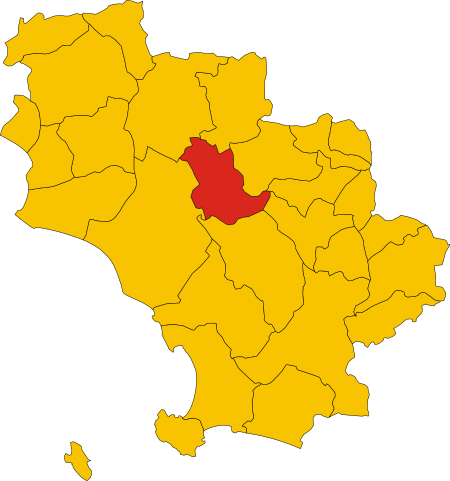
Campagnatico Apse of the بيفي of San Giovanni Battista. شعار Campagnaticoشعار Campagnaticoشعار الاسم الرسمي Comune di Campagnatico الإحداثيات 42°53′04″N 11°16′17″E / 42.884444444444°N 11.271388888889°E / 42.884444444444; 11.271388888889 [1] تقسيم إداري البلد إيطاليا[2] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة غروسيتو خصائص جغرافية …

Part of a series onPurinergic signallingSimplified illustration of extracellular purinergic signalling Concepts Purinergic signalling Receptors Pannexins Ectonucleotidases Metabolism Membrane transporters Nucleoside transporters Concentrative Equilibrative vte PannexinIdentifiersSymbolPannexinInterProIPR039099TCDB1.A.25 pannexin 1IdentifiersSymbolPANX1NCBI gene24145HGNC8599OMIM608420RefSeqNM_015368UniProtQ96RD7Other dataLocusChr. 11 q14-q21Search forStructuresSwiss-modelDomainsInterPro pannexin …

British architect (1858-1937) Sir Philip Sidney StottBtBorn(1858-02-20)20 February 1858Wykeham Place, Chadderton, Lancashire, EnglandDied31 March 1937(1937-03-31) (aged 79)NationalityBritishOccupation(s)Architect, civil engineer, surveyor Sir Philip Sidney Stott, 1st Baronet (20 February 1858 – 31 March 1937), usually known by his full name[1] or as Sidney Stott, was an English architect, civil engineer and surveyor. Early life and career Stott was born in Chadderton, Lancashire, …

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁地�…

坐标:43°11′38″N 71°34′21″W / 43.1938516°N 71.5723953°W / 43.1938516; -71.5723953 此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2017年5月21日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:新罕布什尔州 — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(…

H. M. Pulham, Esq.Poster Film TeatrikalSutradaraKing VidorProduserKing VidorSkenarioKing VidorElizabeth Hill VidorBerdasarkanH. M. Pulham, Esq.Novel tahun 1941oleh John P. MarquandPemeranHedy LamarrRobert YoungRuth HusseyCharles CoburnPenata musikBronislau KaperSinematograferRay JunePenyuntingHarold KressDistributorMetro-Goldwyn MayerTanggal rilis 18 Desember 1941 (1941-12-18) (Amerika Serikat) Durasi120 menitNegaraAmerika SerikatBahasaInggris H. M. Pulham, Esq. adalah sebuah film…
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)[2…

莎拉·阿什頓-西里洛2023年8月,阿什頓-西里洛穿著軍服出生 (1977-07-09) 1977年7月9日(46歲) 美國佛羅里達州国籍 美國别名莎拉·阿什頓(Sarah Ashton)莎拉·西里洛(Sarah Cirillo)金髮女郎(Blonde)职业記者、活動家、政治活動家和候選人、軍醫活跃时期2020年—雇主內華達州共和黨候選人(2020年)《Political.tips》(2020年—)《LGBTQ國度》(2022年3月—2022年10月)烏克蘭媒體�…

Night Fighters redirects here. For the 1960 film also known as The Night Fighters, see A Terrible Beauty (film). Fighter aircraft adapted or designed for use at night Night fighter / All-weather fighterTop left: Swedish de Havilland Venom NF.51 (J 33), during night operation 1954Top right: The nose of a German Lichtenstein radar-equipped Messerschmitt Bf 110 G-4 night fighterBottom left: American Northrop P-61 Black Widow night fighter with a radome nose for its radarBottom right: A de Havilland…

R1SEAsalTiongkokGenreC-popMandopopTahun aktif2019–2021LabelTencent Penguin PictureWajijiwa EntertainmentAnggota Zhou Zhennan He Luoluo Yan Xujia Xia Zhiguang Yao Chen Zhai Xiaowen Zhang Yanqi Liu Ye Ren Hao Zhao Lei Zhao Rang R1SE adalah sebuah grup vokal laki-laki idola Tiongkok bentukan Tencent lewat acara realitas tahun 2019 Produce Camp 2019 di Tencent Video. Grup tersebut terdiri dari sebelas anggota: Zhou Zhennan, He Luoluo, Yan Xujia, Xia Zhiguang, Yao Chen, Zhai Xiaowen, Zhang Yanqi, L…

Emoia caeruleocauda Status konservasi Risiko Rendah (IUCN 3.1)[1] Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Chordata Subfilum: Vertebrata Kelas: Reptilia Ordo: Squamata Subordo: Sauria Infraordo: Scincomorpha Famili: Scincidae Subfamili: Eugongylinae[2] Genus: Emoia Spesies: E. caeruleocauda Nama binomial Emoia caeruleocauda(De Vis, 1892) Sinonim Mocoa caeruleocauda De Vis, 1892 Lygosoma cyanurum werneri T. Vogt, 1912 Lygosoma werneri triviale Schüz, 1929 Emoia tri…

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Steyr (entreprise) et AUG. Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Certaines informations figurant dans cet article ou cette section devraient être mieux reliées aux sources mentionnées dans les sections « Bibliographie », « Sources » ou « Liens externes » (septembre 2018). Vous pouvez améliorer la vérifiabilité en associant ces informations à des références à l'aide d'appels …

Concept of continued life after death The Ladder of Divine Ascent is an important icon kept and exhibited at Saint Catherine's Monastery, Sinai, situated at the base of Mount Sinai in Egypt. The gold ground is typical of icons such as this, which was manufactured in the 12th century after a manuscript written by the 6th century monk John Climacus who based it on the biblical description of Jacob's ladder. It depicts the ascent to Heaven by monks, some of whom fall and are dragged away by black d…

Houses with higher-than-average price and quality Part of a series onLiving spaces MainHouse (detached) • Apartment • Housing projects • Human outpost • Tenement • Condominium • Mixed-use development (live-work) • Hotel • Hostel (travellers' hotel) • Castles • Public housing • Squat • Flophouse • Green home • Shack • Slum • Shanty town IssuesAffordability • Executive housing • Environmental planning • Eviction • Fair housing • Healthiness • Homelessnes…

Bomba lacrimógena rebotando recién explotada, lanzada contra estudiantes de Grecia. Un gas lacrimógeno es un tipo de arma química. Fueron utilizados en la Primera Guerra Mundial (1914-1918) y en la actualidad son armas antidisturbios y pueden llegar a ser disparados para provocar lagrimeo, irritación y ceguera temporal. Los compuestos químicos utilizados más habitualmente son el bromuro de bencilo o el gas CS (o-clorobenzilideno malononitrilo).[1] Función Cualquier compuesto quím…