List of recently extinct mammals
Biodiversity of large mammal species per continent before and after humans' arrival Mammalian species (IUCN, 2020-1)
5850 extant species have been evaluated
4978 of those are fully assessed[ a]
3651 are not threatened at present[ b]
1244 to 2116 are threatened[ c]
81 to 83 are extinct or extinct in the wild:
81 extinct (EX) species[ d]
2 extinct in the wild (EW)
0 possibly extinct [CR(PE)]
0 possibly extinct in the wild [CR(PEW)]
^ excludes data deficient evaluations.
^ NT and LC.
^ Threatened comprises CR, EN and VU. Upper estimate additionally includes DD.
^ Chart omits extinct (EX) species
Recently extinct mammals are defined by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as any mammals that have become extinct since the year 1500 CE .[ 1] [ 2]
Extinction of taxa is difficult to confirm, as a long gap without a sighting is not definitive, but before 1995 a threshold of 50 years without a sighting was used to declare extinction.[ 1]
One study found that extinction from habitat loss is the hardest to detect, as this might only fragment populations to the point of concealment from humans. Some mammals declared as extinct may very well reappear .[ 1] [ 3]
As of June 2023, the IUCN listed 233 mammalian species as critically endangered , while 27% of all mammalian species were threatened with extinction.[ 4]
Conventions
All species listed here as extinct International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Species which are extinct in the wild possibly extinct are classified as being critically endangered , as it is unknown whether or not these species are extinct.[ 5] subspecies such as the Javan tiger (Panthera tigris sondaica )[ 6] Panthera tigris extant . The IUCN Redlist classification for each species serves as a citation, and the superscripted "IUCN" by the date is a link to that species' page. A range map is provided where available, and a description of their former or current range is given if a range map is not available.
Causes of extinction
Anthropogenic (human caused) habitat degradation is the main cause of species extinctions now. The main cause of habitat degradation worldwide is agriculture, with urban sprawl , logging, mining and some fishing practices close behind. The physical destruction of a habitat, both directly (deforestation for land development or lumber ) and indirectly (burning fossil fuels ), is an example of this.[ 7] [ 8]
Also, increasing toxicity, through media such as pesticides , can kill off a species very rapidly, by killing all living members through contamination or sterilizing them. Persistent organic pollutants (POPs), for example, can bioaccumulate to hazardous levels, getting increasingly dangerous further up the food chain .[ 9]
Disease can also be a factor: white nose syndrome in bats , for example, is causing a substantial decline in their populations and may even lead to the extinction of some species.[ 10]
Overhunting also has an impact. Terrestrial mammals, such as the tiger and deer, are mainly hunted for their pelts and in some cases meat, and marine mammals can be hunted for their oil and leather. Specific targeting of one species can be problematic to the ecosystem because the sudden demise of one species can inadvertently lead to the demise of another (coextinction ) especially if the targeted species is a keystone species . Sea otters , for example, were hunted in the maritime fur trade , and their drop in population led to the rise in sea urchins —their main food source—which decreased the population of kelp—the sea urchin's and Steller's sea cow 's main food source—leading to the extinction of the Steller's sea cow.[ 11] bluebuck whose range was confined to 1,700 square miles (4,400 km2 ) and which was hunted into extinction soon after discovery by European settlers.[ 12]
Australia
Island creatures are usually endemic to only that island, and that limited range and small population can leave them vulnerable to sudden changes.[ 13] unique fauna has suffered an extreme decline in mammal species, 10% of its 273 terrestrial mammals, since European settlement (a loss of one to two species per decade); in contrast, only one species in North America has become extinct since European settlement .[citation needed Furthermore, 21% of Australia's mammals are threatened , and unlike in most other continents, the main cause is predation by feral species , such as cats .[ 14]
Extinct species
A species is declared extinct after exhaustive surveys of all potential habitats eliminate all reasonable doubt that the last individual of a species, whether in the wild or in captivity, has died.[ 15] CE .[ 1]
Common name
Binomial name
Order
Date of extinction
Former range
Picture
Broad-faced potoroo
Potorous platyops Gould , 1844Diprotodontia
1875 1
Australia
Eastern hare wallaby
Lagorchestes leporides Gould , 1841Diprotodontia
1889 1
Australia
Lake Mackay hare-wallaby
Lagorchestes asomatus Finlayson, 1943
Diprotodontia
1932 1
Australia
Desert rat-kangaroo
Caloprymnus campestris Gould , 1843Diprotodontia
1935 1
Australia
Thylacine Thylacinus cynocephalus Harris , 1808Dasyuromorphia
1936 1
Australia, Tasmania
Toolache wallaby
Macropus greyi Waterhouse , 1846Diprotodontia
1939 1
Australia
Desert bandicoot
Perameles eremiana Spencer , 1837Peramelemorphia
1943 1
Australia
New South Wales barred bandicoot[ 16]
Perameles fasciata Gray , 1841Peramelemorphia
mid-19th century
Australia
Southwestern barred bandicoot[ 16]
Perameles myosuros Wagner , 1841Peramelemorphia
mid-19th century
Australia
Southern barred bandicoot[ 16]
Perameles notina Thomas , 1922Peramelemorphia
mid-19th century
Australia
Nullarbor barred bandicoot [ 16] Perameles papillon Travouillon & Phillips, 2018
Peramelemorphia
early 20th century
Australia
Lesser bilby Macrotis leucura Thomas , 1887Peramelemorphia
1960s 1
Australia
Southern pig-footed bandicoot
Chaeropus ecaudatus Ogilby , 1838Peramelemorphia
1950s 1
Australia
Northern pig-footed bandicoot
Chaeropus yirratji Travouillon et al. , 2019
Peramelemorphia
1950s
Crescent nail-tail wallaby
Onychogalea lunata Gould , 1841Diprotodontia
1956 1
Australia (western and central)
Red-bellied gracile opossum Cryptonanus ignitus Díaz, Flores and Barquez, 2002
Didelphimorphia
1962 1
Argentina
Nullarbor dwarf bettong
Bettongia pusilla McNamara, 1997
Diprotodontia
1 Australia (Nullarbor Plain )
Steller's sea cow
Hydrodamalis gigas von Zimmermann , 1780Sirenia
1768 1
Commander Islands (Russia , United States )
Bramble Cay melomys
Melomys rubicola Thomas , 1924Rodentia
2016 1
Australia (Bramble Cay )
Oriente cave rat
Boromys offella Miller , 1916Rodentia
1 Cuba
Torre's cave rat
Boromys torrei Allen , 1917Rodentia
1 Cuba
Imposter hutia
Hexolobodon phenax Miller , 1929Rodentia
1 Hispaniola (currently Haiti and the Dominican Republic )
Montane hutia
Isolobodon montanus Miller , 1922Rodentia
1 Hispaniola
Dwarf viscacha
Lagostomus crassus Thomas , 1910Rodentia
1 Peru
Galápagos giant rat
Megaoryzomys curioi Niethammer, 1964
Rodentia
1 Santa Cruz Island (Galápagos)
Cuban coney
Geocapromys columbianus Chapman , 1892Rodentia
1 Cuba
Hispaniolan edible rat
Brotomys voratus Miller , 1916Rodentia
1536–1546 1
Hispaniola
Puerto Rican hutia
Isolobodon portoricensis Allen , 1916Rodentia
1 Hispaniola; introduced to Puerto Rico , Saint Thomas Island , Saint Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands and Mona Island
Big-eared hopping mouse
Notomys macrotis Thomas , 1921Rodentia
1843 1
Australia (central Western Australia )
Darling Downs hopping mouse
Notomys mordax Thomas , 1921Rodentia
1846 1
Australia (Darling Downs , Queensland )
White-footed rabbit-rat
Conilurus albipes Lichtenstein , 1829Rodentia
1 Australia (eastern coast)
Capricorn rabbit rat
Conilurus capricornensis Cramb and Hocknull, 2010
Rodentia
1 Australia (Queensland )
Short-tailed hopping mouse
Notomys amplus Brazenor, 1936
Rodentia
1896 1
Australia (Great Sandy Desert )
Long-tailed hopping mouse
Notomys longicaudatus Gould , 1844Rodentia
1901 1
Australia
Great hopping mouse
Notomys robustus Mahoney, Smith and Medlin, 2008
Rodentia
1 Australia (Flinders Ranges and Davenport Ranges)
Desmarest's pilorie Megalomys desmarestii Fischer, 1829
Rodentia
1902 1
Martinique
Saint Lucia pilorie Megalomys luciae Major, 1901
Rodentia
1881 1
Saint Lucia
Bulldog rat
Rattus nativitatis Thomas , 1888Rodentia
1903 1
Christmas Island
Maclear's rat
Rattus macleari Thomas , 1887Rodentia
1903 1
Christmas Island
Darwin's Galápagos mouse
Nesoryzomys darwini Osgood , 1929Rodentia
1930 1
Galápagos Islands
Gould's mouse
Pseudomys gouldii Waterhouse , 1839Rodentia
1930 1
Australia (southern half)
Plains rat Pseudomys auritus Thomas , 1910Rodentia
1 Australia (Kangaroo Island and the Younghusband Peninsula )
Pemberton's deer mouse
Peromyscus pembertoni Burt , 1932Rodentia
1931 1
San Pedro Nolasco Island , Mexico
Samaná hutia
Plagiodontia ipnaeum Johnson, 1948
Rodentia
[ a] 1 Hispaniola
Hispaniola monkey
Antillothrix bernensis MacPhee, Horovitz, Arredondo, & Jimenez Vasquez, 1995
Primates
early 16th century
Hispaniola (currently Dominican Republic)
Lesser stick-nest rat Leporillus apicalis John Gould , 1854Rodentia
1933 1
Australia (west-central)
Indefatigable Galápagos mouse
Nesoryzomys indefessus Thomas , 1899Rodentia
1934 1
Galápagos Islands
Little Swan Island hutia
Geocapromys thoracatus True , 1888Rodentia
1955 1
Swan Islands, Honduras
Blue-gray mouse
Pseudomys glaucus Thomas , 1910Rodentia
1956 1
Australia (Queensland , New South Wales )
Buhler's coryphomys Coryphomys buehleri Schaub, 1937
Rodentia
1 West Timor , Indonesia
Insular cave rat
Heteropsomys insulans Anthony, 1916
Rodentia
1 Vieques Island , Puerto Rico
Candango mouse
Juscelinomys candango Moojen , 1965Rodentia
1960 1
Central Brazil
Anthony's woodrat
Neotoma anthonyi Allen , 1898Rodentia
1926 1
Isla Todos Santos , Mexico
Bunker's woodrat
Neotoma bunkeri Burt, 1932
Rodentia
1931 1
Coronado Islands , Mexico
Vespucci's rodent
Noronhomys vespuccii Carleton and Olson , 1999
Rodentia
1500 1
Fernando de Noronha , Brazil
St. Vincent colilargo Oligoryzomys victus Thomas , 1898Rodentia
1892 1
Saint Vincent
Jamaican rice rat
Oryzomys antillarum Thomas , 1898Rodentia
1877 1
Jamaica
Nelson's rice rat
Oryzomys nelsoni Merriam , 1889Rodentia
1897 1
Islas Marías , Mexico
Nevis rice rat ,Pennatomys nivalis Turvey, Weksler, Morris & Nokkert, 2010
Rodentia
[ b] 1 Sint Eustatius and Saint Kitts and Nevis
Christmas Island pipistrelle
Pipistrellus murrayi Andrews , 1900Chiroptera
2009 1
Christmas Island
Sardinian pika
Prolagus sardus Wagner , 1832Lagomorpha
1774 1
Corsica and Sardinia
Marcano's solenodon
Solenodon marcanoi Patterson , 1962Eulipotyphla
1 Dominican Republic
Puerto Rican nesophontes
Nesophontes edithae Anthony, 1916
Eulipotyphla
1 Puerto Rico, Vieques Island, Saint John, U.S. Virgin Islands and Saint Thomas, U.S. Virgin Islands
Atalaye nesophontes
Nesophontes hypomicrus Miller , 1929Eulipotyphla
1 Hispaniola
Greater Cuban nesophontes
Nesophontes major Arredondo, 1970
Eulipotyphla
1 Cuba
Western Cuban nesophontes
Nesophontes micrus Allen , 1917Eulipotyphla
1 Cuba (including Isla de la Juventud )
St. Michel nesophontes
Nesophontes paramicrus Miller , 1929Eulipotyphla
1 Hispaniola
Haitian nesophontes
Nesophontes zamicrus Miller , 1929Eulipotyphla
1 Haiti
Lesser Mascarene flying fox Pteropus subniger kerr , 1792Chiroptera
1864 1
Réunion , Mauritius
Guam flying fox Pteropus tokudae Tate , 1934Chiroptera
1968 1
Guam
Dusky flying fox Pteropus brunneus Dobson , 1878Chiroptera
1870 1
Percy Islands (Australia)
Large Palau flying fox
Pteropus pilosus Andersen , 1908Chiroptera
1874 1
Palau
Large sloth lemur
Palaeopropithecus ingens Grandidier , 1899Primates
1620 1
In green
Aurochs
Bos primigenius Bojanus , 1827Artiodactyla
1627 1
Bluebuck
Hippotragus leucophaeus Pallas , 1766Artiodactyla
1800 1
Red gazelle
Eudorcas rufina Thomas , 1894Artiodactyla
1 Algeria
Schomburgk's deer
Rucervus schomburgki Blyth , 1863Artiodactyla
1932 1
Thailand
Queen of Sheba's gazelle Gazella bilkis Grover and Lay, 1985
Artiodactyla
1951 1
Yemen
Madagascan dwarf hippopotamus
Hippopotamus lemerlei Milne-Edwards , 1868Artiodactyla
[ c] 1 Madagascar
Falkland Islands wolf or warrah
Dusicyon australis Kerr , 1792Carnivora
1876 1
Falkland Islands
Dusicyon avus
Dusicyon avus Burmeister , 1866Carnivora
1 Argentina , Chile , Brazil , Uruguay , Paraguay
Sea mink
Neogale macrodon Prentiss, 1903
Carnivora
1894 1
United States (Maine , Massachusetts ) and Canada (New Brunswick , Newfoundland )
Japanese sea lion
Zalophus japonicus Peters , 1866Carnivora
1970s 1
Japan , Korea , Russia
Caribbean monk seal
Neomonachus tropicalis Gray , 1850Carnivora
1952 1
Caribbean Sea
Giant fossa
Cryptoprocta spelea Grandidier , 1902Carnivora
1
Lord Howe long-eared bat
Nyctophilus howensis McKean , 1975Chiroptera
prior to 1972 1
Lord Howe Island , Australia
Japanese otter
Lutra nippon
Imaizumi & Yoshiyuki, 1989
Carnivora
1990s [ 19]
Japan
Extinct subspecies
Common name
Binomial name
Species
Order
Date of extinction
Former range
Picture
Mississippi Valley wolf
Canis rufus gregoryi Goldman, 1937
Red wolf (Canis rufus )
Carnivora
1980
North America
Caucasian wisent
Bison bonasus caucasicus Turkin and Satunin, 1904
European bison (Bison bonasus )
Artiodactyla
1927
Europe
Carpathian wisent
Bison bonasus hungarorum Kretzoi, 1946
European bison (Bison bonasus )
Artiodactyla
1852
Europe
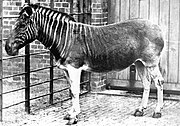
Quagga
Equus quagga quagga Boddaert, 1785
Plains zebra (Equus quagga )
Perissodactyla
1883
Africa
Japanese wolf
Canis lupus hodophilax Temminick 1839
Grey wolf (Canis lupus )
Carnivora
1905
Asia
Hokkaido wolf
Canis lupus hattai Kishida, 1931
Grey wolf (Canis lupus )
Carnivora
1889
Asia
Atlas bear
Ursus arctos crowtheri Schinz, 1844
Brown bear (Ursus arctos )
Carnivora
1890
Africa
Bali tiger
Panthera tigris sondaica Shwarz,1912
Tiger (Panthera tigris )
Carnivora
1950s
Asia
Caspian tiger
Panthera tigris tigris Illiger, 1815
Tiger (Panthera tigris )
Carnivora
1970s
Asia
Javan tiger
Panthera tigris sondaica Temminick, 1844
Tiger (Panthera tigris )
Carnivora
1980s
Asia
Bubal hartebeest
Alcelaphus buselaphus buselaphus Pallas 1766
Hartebeest (Alcephalus buselaphus )
Artiodactyla
1925
Africa
Portuguese ibex
Capra pyrenaica lusitanica Schlegel, 1872
Iberian ibex (Capra pyrenaica )
Artiodactyla
1892
Europe
Pyrenean ibex
Capra pyrenaica pyreneica Schinz, 1838
Iberian ibex (Capra pyrenaica )
Artiodactyla
2000
Europe
Western black rhinoceros
Diceros bicornis longipes Zukowsky, 1999
Black rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis )
Artiodactyla
2011
Africa
Cape lion
Panthera leo melanochaita Smith, 1842
Lion (Panthera leo )
Carnivora
mid 19th century
Africa
Barbary lion
Panthera leo leo Linnaeus, 1758
Lion (Panthera leo )
Carnivora
1960s
Africa
Southern Rocky Mountain wolf
Canis lupus nubilus Nowak, 1995
Grey wolf (Canis lupus )
Carnivora
1935
North America
Kenai Peninsula wolf
Canis lupus occidentalis Nowak, 1995
Grey wolf (Canis lupus )
Carnivora
1925
North America
Banks Island wolf
Canis lupus arctos Nowak, 1995
Grey wolf (Canis lupus )
Carnivora
1952
North America
Newfoundland wolf
Canis lupus nubilus Nowak, 1995
Grey wolf (Canis lupus )
Carnivora
1911
North America
Florida black wolf
Canis rufus floridanus Miller, 1912
Red wolf (Canis rufus )
Carnivora
1934
North America
Cascade Mountains wolf
Canis lupus nubilus Nowak, 1995
Grey wolf (Canis lupus )
Carnivora
1944
North America
Mogollon mountain wolf
Canis lupus nubilus Nowak, 1995
Grey wolf (Canis lupus )
Carnivora
1970s
North America
Texas wolf
Canis lupus nubilus Nowak, 1995
Grey wolf (Canis lupus )
Carnivora
19th century
North America
Sicilian wolf
Canis lupus cristaldii Angelici and Rossi, 2018
Grey wolf (Canis lupus )
Carnivora
1924
Europe
Mexican grizzly bear
Ursus arctos nelsoni Merriam, 1914
Brown bear (Ursus arctos )
Carnivora
1965
North America
California grizzly bear
Ursus arctos californicus Merriam, 1896
Brown bear (Ursus arctos )
Carnivora
1924
North America
Tarpan
Equus ferus ferus Boddaert, 1785
Wild horse (Equus ferus )
Perissodactyla
1909
Europe
A species that is extinct in the wild is one which has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as only known by living members kept in captivity or as a naturalized population outside its historic range due to massive habitat loss . A species is declared extinct in the wild after thorough surveys have inspected its historic range and failed to find evidence of a surviving individual.[ 15]
Possibly extinct
Extinction of taxa is difficult to detect, as a long gap without a sighting is not definitive. Some mammals declared as extinct may very well reappear .[ 1] [ 3] [ 4]
Common name
Binomial name
Order
Last confirmed sighting
Range
Picture
Kouprey Bos sauveliUrbain , 1937
Artiodactyla
1988 1
Garrido's hutia
Capromys garridoi Varona, 1970
Rodentia
1989 1 [dead link ]
Cayo Maja , Cuba
Christmas Island shrew
Crocidura trichura Dobson , 1889Eulipotyphla
1985 1
Wimmer's shrew
Crocidura wimmeri de Balsac and Aellen , 1958Eulipotyphla
1976 1
Baiji Lipotes vexillifer Miller , 1918Artiodactyla
2002 [ d] 1
Zuniga's dark rice rat
Melanomys zunigae Sanborn Rodentia
1949 1
Peru
Dwarf hutia
Mesocapromys nanus Allen , 1917Rodentia
1937 1
Ciénaga de Zapata ,
San Felipe hutia Mesocapromys sanfelipensis Varona & Garrido, 1970
Rodentia
1978 1
Cuba
One-striped opossum
Monodelphis unistriata Wagner , 1842Didelphimorphia
1899 1
Gloomy tube-nosed bat
Murina tenebrosa Yoshiyuki , 1970Chiroptera
1962 1
Tsushima Island and possibly Yaku Island ,
New Zealand greater short-tailed bat
Mystacina robusta Dwyer , 1962Chiroptera
1967 1
Taukihepa / Big South Cape Island , New Zealand
Ethiopian amphibious rat Nilopegamys plumbeus Osgood , 1928Rodentia
1920s 1
Mouth of the Lesser Abay River ,
Angel Island mouse
Peromyscus guardia Townsend , 1912Rodentia
1991 1
Isla Ángel de la Guarda ,
Puebla deer mouse
Peromyscus mekisturus Merriam , 1898Rodentia
1950s 1
Ciudad Serdan and Tehuacán ,
Telefomin cuscus
Phalanger matanim Flannery , 1987Diprotodontia
1997 1
Montane monkey-faced bat
Pteralopex pulchra Flannery , 1991Chiroptera
1990s 1
Aru flying fox
Pteropus aruensis Peter , 1867Chiroptera
1877 1
Emma's giant rat
Uromys emmae Groves and Flannery , 1994
Rodentia
1990s 1
Papua Province ,
Emperor rat
Uromys imperator Thomas , 1888Rodentia
1888 1
Guadalcanal ,
Guadalcanal rat
Uromys porculus Thomas , 1904Rodentia
1888 1
Guadalcanal,
Malabar large-spotted civet Viverra civettina Blyth , 1862Carnivora
late 1900s [ e] 1
See also
Notes
^ A 1985 study suggested they may have survived into the 1900s based on local legends of the "comadreja"
^ There were reports of unusual rats on Nevis being eaten by islanders in the 1930s.[ 17]
^ Although, 14 C dating[ 18]
^ The species may be functionally extinct .[ 20]
^ The last confirmed sighting is unknown and their range in the wild is unconfirmed. Camera traps in Karnataka , their presumed habitat, found no individuals after 1,084 nights in 2006.[ 21]
References
^ a b c d e Fisher, Diana O.; Blomberg, Simon P. (2011). "Correlates of rediscovery and the detectability of extinction in mammals" . Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences . 278 (1708): 1090– 1097. doi :10.1098/rspb.2010.1579 . PMC 3049027 PMID 20880890 . ^ Ceballos, G.; Ehrlich, A. H.; Ehrlich, P. R. (2015). The Annihilation of Nature: Human Extinction of Birds and Mammals . Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-1421417189 ^ a b Macphee, Ross D. E.; Flemming, Clare (1999). "Requiem Æternam: the last five hundred years of mammalian species extinctions" . In MacPhee, Ross D. E.; Sues, Hans-Dieter (eds.). Extinctions in Near Time . Advances in Vertebrate Paleobiology. Vol. 2. ISBN 978-1-4419-3315-7 ^ a b "IUCN Red List version 2022.2" . The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species . International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN). Retrieved 21 June 2023 .^ "Possibly Extinct and Possibly Extinct in the Wild Species" (PDF) . IUCN Redlist of Threatened Species . 2016. Retrieved 29 August 2016 .^ Jackson, P.; Nowell, K. (2008). "Panthera tigris ssp. sondaica " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2008 : e.T41681A10509194. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T41681A10509194.en . Retrieved 12 November 2021 . ^ Primack, R. B. (2006). "Habitat destruction". Essentials of Conservation Biology (4th ed.). Sunderland, MA.: Sinauer Associates. pp. 177– 188. ISBN 978-0-87893-720-2 ^ Winkelmann, Ricarda ; Levermann, Anders; Ridgwell, Andy; Caldeira, Ken (2015). "Combustion of available fossil fuel resources sufficient to eliminate the Antarctic Ice Sheet" . Science Advances . 1 (8): e1500589. Bibcode :2015SciA....1E0589W . doi :10.1126/sciadv.1500589 . PMC 4643791 PMID 26601273 .^ Kelly, B. C.; Ikonomou, M. G.; Blair, J. D.; Morin, A. E.; Gobas, F. A. P. C. (2007). "Food Web-Specific Biomagnification of Persistent Organic Pollutants". Science . 317 (5835): 236– 239. Bibcode :2007Sci...317..236K . doi :10.1126/science.1138275 . PMID 17626882 . S2CID 52835862 . ^ Langwig, K.E.; W.F. Frick; J.T. Bried; A.C. Hicks; T.H. Kunz; A.M. Kilpatrick (2012). "Sociality, density-dependence and microclimates determine the persistence of populations suffering from a novel fungal disease, white-nose syndrome". Ecology Letters . 15 (1): 1050– 1057. Bibcode :2012EcolL..15.1050L . doi :10.1111/j.1461-0248.2012.01829.x . PMID 22747672 . ^ Estes, James A.; Burdin, Alexander; Doak, Daniel F. (2016). "Sea otters, kelp forests, and the extinction of Steller's sea cow" . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 113 (4): 880– 885. Bibcode :2016PNAS..113..880E . doi :10.1073/pnas.1502552112 PMC 4743786 PMID 26504217 . ^ Husson, A. M.; Holthuis, L. B. (1969). "On the type of Antilope leucophaea preserved in the collection of the Rijksmuseum van Natuurlijke Historie Leiden". Zoologische Mededelingen . 44 : 147– 157. ^ van der Geer, Alexandra; Lyras, George; de Vos, John; Dermitzakis, Michael (2010). Evolution of Island Mammals: Adaptation and Extinction of Placental Mammals on Islands 225– 227. ISBN 978-1-4051-9009-1 ^ Woinarskia, John C. Z.; Burbidge, Andrew A.; Harrison, Peter L. (2015). "Ongoing unraveling of a continental fauna: Decline and extinction of Australian mammals since European settlement" (PDF) . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 112 (5): 4531– 4540. Bibcode :2015PNAS..112.4531W . doi :10.1073/pnas.1417301112 PMC 4403217 PMID 25675493 . ^ a b IUCN Redlist Categories and Criteria (PDF) (2nd ed.). Gland, Switzerland: IUCN Species Survival Commission. 2012. ISBN 978-2-8317-1435-6 ^ a b c d TRAVOUILLON, KENNY J.; PHILLIPS, MATTHEW J. (7 February 2018). "Total evidence analysis of the phylogenetic relationships of bandicoots and bilbies (Marsupialia: Peramelemorphia): reassessment of two species and description of a new species" . Zootaxa . 4378 (2): 224– 256. doi :10.11646/zootaxa.4378.2.3 . ISSN 1175-5334 . PMID 29690027 . ^ Turvey, Samuel T.; Weksler, Marcelo; Morris, Elaine L.; Nokkert, Mark (2010). "Taxonomy, phylogeny, and diversity of the extinct Lesser Antillean rice rats (Sigmodontinae: Oryzomyini), with description of a new genus and species" . Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society . 160 (4): 748– 772. doi :10.1111/j.1096-3642.2009.00628.x ^ MacPhee, R. D. E.; Burney, David A. (1991). "Dating of modified femora of extinct dwarf Hippopotamus from Southern Madagascar: Implications for constraining human colonization and vertebrate extinction events" . Journal of Archaeological Science . 18 (6): 695– 706. Bibcode :1991JArSc..18..695M . doi :10.1016/0305-4403(91)90030-S ^ "Japanese river otter declared extinct" . Mainichi jp . Japan: The Mainichi Newspapers. 28 August 2012. Archived from the original on 1 September 2012. Retrieved 28 August 2012 .^ Turvey, Samuel T.; Pitman, Robert L.; Taylor, Barbara L.; Barlow, Jay; Akamatsu, Tomonari; Barrett, Leigh A.; Zhao, Xiujiang; Reeves, Randall R.; Stewart, Brent S.; Kexiong, Wang; Zhuo, Wei; Zhang, Xianfeng; Pusser, L. T.; Richlen, Michael; Brandon, John R.; Wang, Ding (2007). "First human-caused extinction of a cetacean species?" . Biology Letters . 3 (5): 537– 540. doi :10.1098/rsbl.2007.0292 . PMC 2391192 PMID 17686754 . ^ Rao, S.; Ashraf, N. V. K.; Nixon, A. M. A. (2007). "Search for the Malabar Civet Viverra civettina in Karnataka and Kerala, India, 2006–2007". Small Carnivore Conservation . 37 : 6– 10.
Yinotheria
Theria
Metatheria (Marsupial inclusive)
Eutheria (Placental inclusive)
Atlantogenata
Boreoeutheria
Laurasiatheria
Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, shrews, moles and relatives) Chiroptera (bats) Pholidota (pangolins) Carnivora (dogs, cats and relatives) Perissodactyla (horses, zebras, donkeys, rhinoceroses and tapirs) Artiodactyla (pigs, camels, hippos, deer, buffalo, gazelles, giraffes, whales, dolphins and relatives) Euarchontoglires
Rodentia (rats, mice, guinea pigs, squirrels, beavers, chinchillas, porcupines, capybaras and relatives) Lagomorpha (rabbits, hares and pikas) Scandentia (treeshrews) Dermoptera (colugos) Primates (lorises, lemurs, tarsiers, monkeys, apes (including humans) and relatives)