Animals in mammal order Artiodactyla
Various artiodactyls, representing all four suborders. Artiodactyla is an order of placental mammals composed of even-toed ungulates – hooved animals which bear weight equally on two of their five toes with the other toes either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly – as well as their descendants, the aquatic cetaceans . Members of this order are called artiodactyls. The order is sometimes named Cetartiodactyla, in reference to the inclusion of cetaceans in the order beginning in the 1990s.[ 1] extant species, which are grouped into 132 genera . Artiodactyls live on every major landmass and throughout the oceans and in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts. They come in a wide array of body plans in contrasting shapes and sizes, ranging from the 38 cm (15 in) long and 2.5 kg (5.5 lb) royal antelope to the 27 m (89 ft) long and 120 ton blue whale . Some artiodactyls, such as cattle , goats , sheep , pigs , water buffalo , camels , and llamas , have been domesticated , resulting in a worldwide distribution and population sizes for some animals of over one billion.
Artiodactyla is divided into four suborders: Ruminantia , Suina , Tylopoda , and Whippomorpha . The suborders are further subdivided into clades and families . Ruminantia contains six families, Antilocapridae , Bovidae , Cervidae , Giraffidae , Moschidae , and Tragulidae , and includes ruminant animals such as cattle, antelope , deer , and sheep. Suina contains two, Suidae and Tayassuidae , and includes pigs and peccaries ; Tylopoda comprises only Camelidae , the camels and llamas; and Whippomorpha contains fourteen, Balaenidae , Balaenopteridae , Cetotheriidae , Delphinidae , Iniidae , Kogiidae , Lipotidae , Monodontidae , Phocoenidae , Physeteridae , Platanistidae , Pontoporiidae , Ziphiidae , and Hippopotamidae , and includes the aquatic whales and dolphins as well as hippopotamuses . The exact organization of the species is not fixed, with many recent proposals made based on molecular phylogenetic analysis . Three species have gone extinct since 1500 CE: the aurochs and the bluebuck in Bovidae and Schomburgk's deer in Cervidae. Additionally, the red gazelle in Bovidae is considered either extinct or to have never existed; the kouprey in Bovidae is potentially extinct, with no sightings since 1969; and so is the baiji in Lipotidae, last seen in 2002. Several other species are extinct in the wild or critically endangered.
Conventions
Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the collective range of species in that genera is provided. Ranges are based on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species unless otherwise noted. All extinct genera or species listed alongside extant species went extinct after 1500 CE, and are indicated by a dagger symbol "†".
Classification
The order Artiodactyla consists of 349 extant species belonging to 132 genera. This does not include hybrid species or extinct prehistoric species. Modern molecular studies indicate that the 132 genera can be grouped into 23 families; these families are grouped into named suborders and many are further grouped into named clades, and some of these families are subdivided into named subfamilies.
Suborder Ruminantia
Infraorder Pecora
Family Antilocapridae (pronghorn): 1 genus, 1 species
Family Bovidae
Subfamily Aepycerotinae (impala): 1 genus, 1 species
Subfamily Alcelaphinae (wildebeest, hartebeest, bonteboks): 4 genera, 6 species
Subfamily Antilopinae (antelope, gazelles): 15 genera, 37 species
Subfamily Bovinae (cattle, buffalos, bison): 9 genera, 30 species (1 extinct)
Subfamily Caprinae (goats, sheep, ibex, serows): 14 genera, 35 species
Subfamily Cephalophinae (duikers): 3 genera, 20 species
Subfamily Hippotraginae (addax, oryx): 3 genera, 8 species (1 extinct)
Subfamily Nesotraginae (dwarf antelope): 1 genus, 2 species
Subfamily Reduncinae (reedbuck and kob antelope): 3 genera, 9 species
Family Cervidae (deer)
Subfamily Capreolinae (New World deer): 10 genera, 23 species
Subfamily Cervinae (Old World deer): 9 genera, 32 species (1 extinct)
Family Giraffidae (okapi and giraffes): 2 genera, 5 species
Family Moschidae (musk deer): 1 genus, 7 species
Infraorder Tragulina
Family Tragulidae (chevrotains): 3 genera, 10 species Suborder Suina
Family Suidae (pigs): 6 genera, 17 species
Family Tayassuidae (peccaries): 3 genera, 3 species Suborder Tylopoda
Family Camelidae (camels and llamas): 2 genera, 7 species Suborder Whippomorpha
Infraorder Cetacea
Parvorder Mysticeti (baleen whales)
Parvorder Odontoceti (toothed whales)
Family Delphinidae (oceanic dolphins)
Subfamily Delphininae (dolphins): 6 genera, 15 species
Subfamily Lissodelphininae (smooth dolphins): 2 genera, 6 species
Subfamily Globicephalinae (round-headed whales)
Subfamily Orcininae (killer whale): 7 genera, 9 species
Subfamily incertae sedis
Family Iniidae (Amazonian river dolphins): 1 genus, 4 species
Family Kogiidae (dwarf and pygmy sperm whales): 1 genus, 2 species
Family Lipotidae (Chinese river dolphins): 1 genus, 1 species
Family Monodontidae (narwhal and beluga): 2 genera, 2 species
Family Phocoenidae (porpoises): 3 genera, 8 species
Family Physeteridae (sperm whale): 1 genus, 1 species
Family Platanistidae (South Asian river dolphins): 1 genus, 2 species
Family Pontoporiidae (brackish river dolphins): 1 genus, 1 species
Family Ziphiidae (beaked whales)
Subfamily Berardiinae (four-toothed whales): 1 genus, 3 species
Subfamily Hyperoodontinae (bottlenose whales and mesoplodont whales): 3 genera, 18 species
Subfamily Ziphiinae (Cuvier's beaked whale and Shepherd's beaked whale): 2 genera, 2 species
Family Hippopotamidae (hippopotamuses): 2 genera, 2 species
Artiodactyls
The following classification is based on the taxonomy described by Mammal Species of the World molecular phylogenetic analysis .[ 2]
Suborder Ruminantia
Infraorder Pecora
Family Antilocapridae
Members of the Antilocapridae family are called antilocaprids; the family is composed of a single extant species, the pronghorn .
Not assigned to a named subfamily – one genus
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
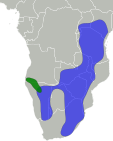
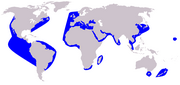
Antilocapra
Ord , 1818
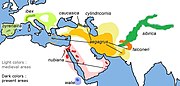
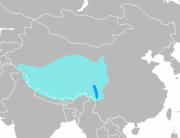
Western North America (former range in yellow)
Size : 130–140 cm (51–55 in) long, plus 9–11 cm (4–4 in) tail[ 3] Habitats : Shrubland, grassland, and desert[ 4] Diet : Shrubs and forbs , as well as grass[ 4]
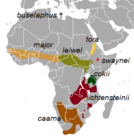
Family Bovidae
Members of the Bovidae family are bovids and include sheep , cattle , goats , antelope , and others. Bovidae comprises 144 extant species, divided into 52 genera. These genera are grouped into eight subfamilies : Aepycerotinae , or the impala; Alcelaphinae , containing the bontebok , hartebeest , wildebeest , and relatives; Antilopinae , containing several antelope , gazelles , and relatives; Bovinae , containing cattle, buffalos , bison , and other antelopes; Caprinae , containing goats, sheep, ibex , serows and relatives; Cephalophinae , or duikers ; Hippotraginae , containing the addax , oryx , and relatives; and Reduncinae , or reedbuck and kob antelopes.
Subfamily Aepycerotinae J. E. Gray , 1872
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
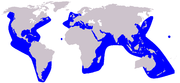
Aepyceros
Sundevall , 1847
Southern Africa (Common impala in green)
Size : 120–160 cm (47–63 in) long, plus 30–45 cm (12–18 in) tail[ 5] Habitats : Savanna, shrubland, and grassland[ 6] Diet : Grass and shrubs[ 6] [ 7]
Subfamily Alcelaphinae Brooke , 1876
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Alcelaphus
Blainville , 1816
Scattered sub-Saharan Africa
Size : 150–245 cm (59–96 in) long, plus 30–70 cm (12–28 in) tail[ 8] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[ 9] Diet : Grass[ 9]
Beatragus
Heller , 1912
Border between Kenya and Somalia
Size : 120–205 cm (47–81 in) long, plus 30–45 cm (12–18 in) tail[ 10] Habitats : Savanna, shrubland, and grassland[ 11] Diet : Grass, as well as forbs[ 10] [ 11]
Connochaetes
Lichtenstein , 1812
Southern Africa
Size range : 170 cm (67 in) long, plus 60 cm (24 in) tail (blue wildebeast) to 242 cm (95 in) long, plus 45 cm (18 in) tail (black wildebeast)[ 12] Habitats : Savanna, shrubland, and grassland[ 13] Diets : Grass[ 13]
Damaliscus
P. L. Sclater , Thomas , 1894
Southern Africa
Size range : 140 cm (55 in) long, plus 30 cm (12 in) tail (bontebok) to 230 cm (91 in) long, plus 42 cm (17 in) tail (common tsessebe)[ 14] Habitats : Savanna, shrubland, and grassland[ 15] Diets : Grass and burnt veldt shrubs[ 15]
Subfamily Antilopinae J. E. Gray , 1821
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Ammodorcas
Thomas , 1891
Horn of Africa
Size : 152–168 cm (60–66 in) long, plus 25–35 cm (10–14 in) tail[ 16] Habitats : Shrubland and grassland[ 17] Diet : Leaves and shoots[ 16] [ 17]
Antidorcas
Sundevall , 1847
Southwestern Africa
Size : 120–150 cm (47–59 in) long, plus 14–28 cm (6–11 in) tail[ 18] Habitats : Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert[ 19] Diet : Shrubs and grass[ 19]
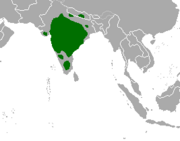
Antilope
Pallas , 1766
India (former range in light green)
Size : Up to 120 cm (47 in) long[ 20] Habitats : Forest, grassland, and desert[ 21] Diet : Grass, as well as leaf litter , flowers, and fruit[ 21]
Dorcatragus
Noack , 1894
Horn of Africa
Size : 76–87 cm (30–34 in) long, plus 5–8 cm (2–3 in) tail[ 22] Habitats : Shrubland, and rocky areas[ 23] Diet : Shrubs[ 23]
Eudorcas
Fitzinger , 1869
Sub-Saharan Africa
Size range : 55 cm (22 in) long, plus 15 cm (6 in) tail (Heuglin's gazelle) to 120 cm (47 in) long, plus 27 cm (11 in) tail (Mongalla gazelle, Red-fronted gazelle, Thomson's gazelle)[ 24] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[ 25] Diets : Grass and shrubs, as well as forbs and fruit[ 25]
Gazella
Blainville , 1816
North Africa, Arabian Peninsula , Asia
Size range : 90 cm (35 in) long, plus 15 cm (6 in) tail (Dorcas gazelle) to 125 cm (49 in) long, plus 20 cm (8 in) tail (Erlanger's gazelle)[ 26] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, grassland, rocky areas, desert, and coastal marine[ 27] Diets : Grass, forbs, leaves, crops, fruit, and low plants[ 27]
Litocranius
Kohl , 1886
Horn of Africa
Size : 140–160 cm (55–63 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail[ 28] Habitats : Savanna and shrubland[ 29] Diet : Shrubs[ 29]
Madoqua
(Ogilby , 1837)
Eastern and southwestern Africa
Size range : 45 cm (18 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (silver dik-dik) to 67 cm (26 in) long, plus 6 cm (2 in) tail (Kirk's dik-dik, Salt's dik-dik)[ 30] Habitats : Forest and shrubland[ 31] Diets : Shrubs, leaves, and grass, as well as flowers, herbs, and sedges [ 31]
Nanger
Lataste , 1885
Eastern Africa and scattered Saharan Desert
Size range : 125 cm (49 in) long, plus 18 cm (7 in) tail (Soemmerring's gazelle) to 168 cm (66 in) long (Dama gazelle)[ 32] Habitats : Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert[ 33] Diets : Leaves, grass, stems, shrubs, and herbs[ 33]
Neotragus
H. Smith , 1827
Sub-Saharan Africa
Size : 38 cm (15 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail[ 34] Habitats : Forest and shrubland[ 35] Diet : Leaves and shoots, as well as fruit and fungi [ 35]
Oreotragus
A. Smith , 1834
Southern and Eastern Africa
Size : 75–115 cm (30–45 in) long[ 36] Habitats : Savanna, shrubland, rocky areas, and desert[ 37] Diet : Shrubs[ 37]
Ourebia
Laurillard , 1842
Sub-Saharan Africa
Size : 92–110 cm (36–43 in) long[ 38] Habitats : Savanna and grassland[ 39] Diet : Grass and shrubs[ 38]
Procapra
Hodgson , 1846
Central Asia
Size range : 91 cm (36 in) long, plus 8 cm (3 in) tail (goa) to 130 cm (51 in) long (Mongolian gazelle)[ 40] Habitats : Grassland, inland wetlands, and desert[ 41] Diets : Grass, onions, forbs, legumes, sedges, and shrubs[ 41]
Raphicerus
H. Smith , 1827
Southern Africa
Size range : 65 cm (26 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (Sharpe's grysbok) to 95 cm (37 in) long, plus 6 cm (2 in) tail (steenbok)[ 42] Habitats : Savanna, shrubland, and grassland[ 43] Diets : Shrubs, grass, geophytes , berries, flowers, and fruit[ 43]
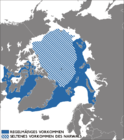
Saiga
J. E. Gray , 1843
Central Asia (historical range in white)
Size : 108–146 cm (43–57 in) long, plus 6–13 cm (2–5 in) tail[ 44] Habitats : Grassland and desert[ 45] Diet : Grass[ 45]
Subfamily Bovinae J. E. Gray , 1821
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Bison
H. Smith , 1827
Scattered North America and Europe
Size range : 210–380 cm (83–150 in) long, plus 43–90 cm (17–35 in) tail (American bison)[ 46] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, and desert[ 47] Diets : Grass, leaves, sedges, herbs, and roots, as well as trees, shrubs, and sagebrush [ 47]
Bos
Linnaeus , 1758
Central, southern, and southeastern Asia, plus worldwide distribution of cattle
Size range : 145 cm (57 in) long, plus 60 cm (24 in) tail (yak), to 385 cm (152 in) long, plus 60 cm (24 in) tail (wild yak)[ 48] Habitats : Forest, savanna, grassland, shrubland, rocky areas, and desert[ 49] Diets : Grass, sedges, shrubs, forbs, herbs, and bamboo, as well as leaves, fruit, flowers, lichen, moss, bark, and young branches of shrubs and trees[ 49]
Boselaphus
Blainville , 1816
Indian subcontinent
Size : 180–200 cm (71–79 in) long[ 50] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, and grassland[ 51] Diet : Grass and shrubs[ 51]
Bubalus
H. Smith , 1827
Scattered southeast Asia, as well as scattered Asia, Egypt, and South America
Size range : 122 cm (48 in) long (mountain anoa) to 300 cm (118 in) long, plus 100 cm (39 in) tail (water buffalo, wild water buffalo)[ 52] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, savanna, grassland, and inland wetlands[ 53] Diets : Grass, shrubs, sedges, and young bamboo shoots, as well as herbs, fruit, and leaves[ 53]
Pseudoryx
Dung , Giao , Chinh , Tuoc , Arctander , MacKinnon , 1993
Annamite Range of Vietnam and Laos Size : 143–150 cm (56–59 in) long, plus up to 25 cm (10 in) tail[ 54] Habitats : Forest[ 55] Diet : Leaves as well as shrubs[ 55]
Syncerus
Hodgson , 1847
Sub-Saharan Africa
Size : 240–340 cm (94–134 in) long, plus 75–110 cm (30–43 in) tail[ 5] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[ 56] Diet : Grass[ 5]
Taurotragus
Wagner , 1855
Sub-Saharan Africa
Size range : 200 cm (79 in) long, plus 50 cm (20 in) tail (common eland), to 345 cm (136 in) long, plus 70 cm (28 in) tail (giant eland)[ 57] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[ 58] Diets : Leaves, shrubs, shoots, herbs, and fruit, as well as grass[ 58]
Tetracerus
Leach , 1825
Indian subcontinent
Size : 80–110 cm (31–43 in) long, plus 10–15 cm (4–6 in) tail[ 59] Habitats : Forest and shrubland[ 60] Diet : Grass and shrubs[ 60]
Tragelaphus
(Blainville , 1816)
Sub-Saharan Africa
Size range : 105 cm (41 in) long, plus 19 cm (7 in) tail (harnessed bushbuck) to 260 cm (102 in) long (mountain nyala)[ 61] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, desert, and inland wetlands[ 62] Diets : Grass, sedges, herbs, leaves, fruit, and shrubs[ 62]
Subfamily Caprinae J. E. Gray , 1821
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Ammotragus
(Blyth , 1840)
Northern Africa
Size : 130–165 cm (51–65 in) long, plus 12–25 cm (5–10 in) tail[ 63] Habitats : Savanna, shrubland, grassland, rocky areas, and desert[ 64] Diet : Grass, shrubs, and forbs[ 64]
Arabitragus
Ropiquet , Hassanin , 2005
Eastern Arabia Size : 93–95 cm (37–37 in) long, plus up to 8–10 cm (3–4 in) tail[ 65] Habitats : Shrubland, rocky areas, and desert[ 66] Diet : Grass, forbs, shrubs, and trees[ 66]
Budorcas
Hodgson , 1850
Eastern Himalayas
Size : 170–220 cm (67–87 in) long, plus 15 cm (6 in) tail[ 67] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, and grassland[ 68] Diet : Grass, bamboo shoots, forbs, and leaves[ 68]
Capra
Linnaeus , 1758
Scattered Europe, Northeast Africa, and western and central Asia
Size range : 100 cm (39 in) long, plus 10 cm (4 in) tail (Iberian ibex) to 185 cm (73 in) long, plus 14 cm (6 in) tail (markhor)[ 69] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, grassland, desert, and rocky areas[ 70] Diets : Grass, shrubs, trees, herbs, lichens, and a variety of other plants[ 70]
Capricornis
Ogilby , 1836
Eastern Asia
Size range : 80 cm (31 in) long, plus 7 cm (3 in) tail (Taiwan serow) to 155 cm (61 in) long, plus 16 cm (6 in) tail (mainland serow)[ 71] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[ 72] Diets : Grass, shoots, leaves, shrubs, acorns, and twigs[ 72]
Hemitragus
(Hodgson , 1841)
Himalayas
Size : 90–140 cm (35–55 in) long[ 73] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[ 74] Diet : Herbaceous plants and shrubs, grass, and sedges[ 74]
Naemorhedus
H. Smith , 1827
Himalayas and Eastern Asia
Size range : 81 cm (32 in) long (long-tailed goral) to 130 cm (51 in) long (Himalayan goral)[ 75] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[ 76] Diets : Grass, herbs, shoots, leaves, nuts, fruit, and lichen[ 76]
Nilgiritragus
Ropiquet , Hassanin , 2005
Southern India
Size : 90–140 cm (35–55 in) long, plus 9–12 cm (4–5 in) tail[ 77] Habitats : Shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[ 78] Diet : Grass and forbs[ 78]
Oreamnos
Rafinesque , 1817
Western North America
Size : 120–160 cm (47–63 in) long, plus 8–20 cm (3–8 in) tail[ 5] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[ 79] Diet : Grass, forbs, sedges, ferns, moss, lichen, twigs, and leaves[ 79]
Ovibos
Blainville , 1816
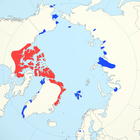
The Arctic (reintroduced in blue)
Size : 190–270 cm (75–106 in) long, plus 7–12 cm (3–5 in) tail[ 5] Habitats : Grassland[ 80] Diet : Sedges and grass, as well as shrubs and some forbs[ 80]
Ovis
Linnaeus , 1758
Asia and western North America, plus worldwide domesticated sheep
Size range : 105 cm (41 in) long, plus 12 cm (5 in) tail (mouflon) to 190 cm (75 in) long (argali)[ 81] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, grassland, rocky areas, savanna, and desert[ 82] Diets : Grass and shrubs, as well as a wide variety of vegetation[ 82]
Pantholops
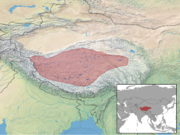
Hodgson , 1834
Tibetan Plateau Size : 120–130 cm (47–51 in) long[ 83] Habitats : Grassland[ 84] Diet : Grass and herbs[ 83]
Pseudois
Hodgson , 1846
Himalayas
Size : 120–140 cm (47–55 in) long[ 85] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, grassland, rocky areas, and desert[ 86] Diet : Grass, alpine herbs, and lichens[ 86]
Rupicapra
Blainville , 1816
Europe and western Asia
Size range : 90 cm (35 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (Pyrenean chamois) to 135 cm (53 in) long (chamois)[ 87] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[ 88] Diets : Grass, herbs, tree leaves, flowers, buds, shoots, and fungi, as well as lichen, moss, and young pine shoots[ 88]
Subfamily Cephalophinae – Gray , 1871
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Cephalophus
H. Smith , 1827
Sub-Saharan Africa
Size range : 60 cm (24 in) long (red-flanked duiker) to 150 cm (59 in) long, plus 16 cm (6 in) tail (Jentink's duiker)[ 89] Habitats : Forest, savanna, and shrubland[ 90] Diets : Leaves, fruit, flowers, twigs, nuts, and tree stems, as well as shrubs, grass, insects, and eggs[ 90]
Philantomba
Blyth , 1840
Sub-Saharan Africa
Size range : 36 cm (14 in) long, plus 14 cm (6 in) tail (Maxwell's duiker) to 72 cm (28 in) long, plus 13 cm (5 in) tail (blue duiker)[ 91] Habitats : Forest and shrubland[ 92] Diets : Leaves, fruit, seeds, flowers, and fungi[ 92]
Sylvicapra
Ogilby , 1837
Sub-Saharan Africa
Size : 70–105 cm (28–41 in) long, plus 10–20 cm (4–8 in) tail[ 93] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert[ 94] Diet : Variety of foliage, herbs, fruit, seeds, and cultivated crops[ 94]
Subfamily Hippotraginae – Sundevall , 1845
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Addax
Laurillard , 1841
Scattered western Africa
Size : 150–170 cm (59–67 in) long, plus 25–35 cm (10–14 in) tail[ 95] Habitats : Savanna, grassland, and desert[ 96] Diet : Grass and shrubs[ 95]
Hippotragus
Sundevall , 1846
Sub-Saharan Africa
Size range : 190 cm (75 in) long, plus 37 cm (15 in) tail (roan antelope) to 300 cm (118 in) long (bluebuck)[ 97] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[ 98] Diets : Grass, as well as forbs and leaves[ 98]
Oryx
Blainville , 1816
Eastern and southern Africa and Arabian Peninsula
Size range : 153 cm (60 in) long, plus 45 cm (18 in) tail (East African oryx) to 235 cm (93 in) long, plus 90 cm (35 in) tail (Arabian oryx)[ 99] Habitats : Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert[ 100] Diets : Grass, shrubs, herbs, roots, and buds, as well as fruit and vegetables[ 100]
Subfamily Nesotraginae von Düben (de ), 1846
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Nesotragus
von Düben (de ), 1846
Sub-Saharan Africa
Size range : 50 cm (20 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (Bates's pygmy antelope) to 62 cm (24 in) long (suni)[ 34] Habitats : Forest, brush and riparian reed scrub[ 35] Diets : Leaves and shoots, as well as fruit and fungi [ 35]
Subfamily Reduncinae – Knottnerus-Meyer , 1907
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Kobus
Smith , 1840
Sub-Saharan Africa
Size range : 126 cm (50 in) long (puku) to 235 cm (93 in) long (waterbuck)[ 101] Habitats : Savanna, shrubland, grassland, forest, and inland wetlands[ 102] Diets : Grass, shrubs, and water plants[ 102]
Pelea
Gray , 1851
Southern Africa
Size : 115–125 cm (45–49 in) long[ 103] Habitats : Savanna and grassland[ 104] Diet : Shrubs and forbs[ 104]
Redunca
H. Smith , 1827
Sub-Saharan Africa
Size range : 100 cm (39 in) long, plus 13 cm (5 in) tail (mountain reedbuck) to 167 cm (66 in) long (southern reedbuck)[ 105] Habitats : Savanna, shrubland, grassland, rocky areas, and inland wetlands[ 106] Diets : Grass, as well as herbs and shrubs[ 106]
Family Cervidae
Members of the Cervidae family are cervids, or colloquially deer. Cervidae comprises 53 extant species, divided into 19 genera. These genera are grouped into two subfamilies : Capreolinae , or New World deer, and Cervinae , or Old World deer.
Subfamily Capreolinae Brookes , 1828
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Alces
J. E. Gray , 1821
North America, Europe, and Asia
Size : 230–340 cm (91–134 in) long, plus 8–12 cm (3–5 in) tail[ 107] Habitats : Forest and inland wetlands[ 108] Diet : Vegetative parts of trees, as well as shrubs, herbs, and aquatic plants[ 108]
Blastocerus
Wagner , 1844
Scattered parts of central South America (former range in red)
Size : 153–191 cm (60–75 in) long, plus 12–16 cm (5–6 in) tail[ 109] Habitats : Savanna, shrubland, and inland wetlands[ 110] Diet : Grasses, reeds and aquatic plants, as well as shrubs and vines[ 110]
Capreolus
J. E. Gray , 1821
Europe and Asia
Size range : 95 cm (37 in) long, plus 20 cm (8 in) tail (Siberian roe deer) to 124 cm (49 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (roe deer)[ 111] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[ 112] Diets : Wide variety of plants[ 112]
Hippocamelus
Leuckart , 1816
Western South America
Size range : 69–77 cm (27–30 in) tall at shoulder (taruca) to 156 cm (61 in) long, plus 13 cm (5 in) tail; 80–90 cm (31–35 in) tall at shoulder (South Andean deer)[ 113] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, rocky areas, and desert[ 114] Diets : Sedges, grass, and other plants[ 114]
Hydropotes
H. Milne-Edwards , 1872
East China and Korean peninsula
Size : 89–103 cm (35–41 in) long, plus 6–7 cm (2–3 in) tail; 45–57 cm (18–22 in) tall at shoulder[ 115] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, and intertidal marine[ 116] Diet : Reeds, coarse grasses, vegetables, and beets[ 116] [ 117]
Mazama
Rafinesque , 1817
South America and Central America
Size range : 70 cm (28 in) long (dwarf brocket) to 146 cm (57 in) long, plus 15 cm (6 in) tail (red brocket)[ 118] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, and rocky areas[ 119] Diets : Wide variety of plants and fruit[ 119]
Odocoileus
Rafinesque , 1832
North America and northern South America
Size range : 105 cm (41 in) long, plus 8 cm (3 in) tail (Yucatan brown brocket) to 203 cm (80 in) long (mule deer)[ 120] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, desert, neritic marine , intertidal marine , and coastal marine[ 121] Diets : Wide variety of vegetation and grasses[ 121]
Ozotoceros
Ameghino , 1891
Scattered central South America
Size : 110–140 cm (43–55 in) long; 70–75 cm (28–30 in) tall at shoulder[ 122] Habitats : Savanna, grassland, and inland wetlands[ 123] Diet : Grasses and shrubs[ 122] [ 123]
Pudu
J. E. Gray , 1852
Western South America
Size range : 60–85 cm (24–33 in) long, plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail[ 124] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, and grassland[ 125] Diets : Leaves of ferns, trees, vines, herbs and shrubs[ 125]
Rangifer
H. Smith , 1827
Arctic North America, Europe, and Asia
Size : 150–230 cm (59–91 in) long; up to 120 cm (47 in) tall at shoulder[ 126] Habitats : Forest and grassland[ 127] Diet : Lichen, forbs, sedges, grasses, and shrubs[ 127]
Subfamily Cervinae Goldfuss , 1820
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Axis
H. Smith , 1827
Southern and southeast Asia
Size range : 70 cm (28 in) long, plus 20 cm (8 in) tail (chital) to 175 cm (69 in) long, plus 38 cm (15 in) tail (Calamian deer)[ 128] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[ 129] Diets : Wide variety of grasses as well as fallen leaves, flowers, and fruit[ 129]
Cervus
Linnaeus , 1758
Southern and southeast Asia
Size range : 95 cm (37 in) long, plus 7 cm (3 in) tail (sika deer) to 280 cm (110 in) long, plus 22 cm (9 in) tail (elk)[ 130] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, grassland, rocky areas, and inland wetlands[ 131] Diets : Shrub and tree shoots and branches, as well as grass, sedges, shrubs, fruit, and seeds[ 131]
Dama
Frisch , 1775
Europe and west Asia; introduced scattered areas worldwide
Size range : 130–175 cm (51–69 in) long, plus 15–23 cm (6–9 in) tail[ 132] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, and grassland[ 133] Diets : Grasses, mast , and shrubs, as well as leaves, buds, shoots, and bark[ 133]
Elaphodus
H. Milne-Edwards , 1872
Central China and northeastern Myanmar
Size : 110–160 cm (43–63 in) long, plus 7–16 cm (3–6 in) tail[ 134] Habitats : Forest and shrubland[ 135] Diet : Grass, as well as shrubs, fruits, bamboo, and herbs[ 135]
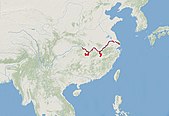
Elaphurus
Milne-Edwards , 1866
China
Size : 183–216 cm (72–85 in) long, plus 22–36 cm (9–14 in) tail[ 136] Habitats : Grassland, inland wetlands, and intertidal marine[ 137] Diet : Grass, reeds, and bush leaves[ 137]
Muntiacus
Rafinesque , 1815
South and southeast Asia; introduced to Britain
Size range : 70 cm (28 in) long, plus 10 cm (4 in) tail (Reeves's muntjac) to 135 cm (53 in) long, plus 23 cm (9 in) tail (Northern red muntjac)[ 138] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, and grassland[ 139] Diets : Fruit and a range of plant materials[ 139]
Panolia
McClelland , 1842
Scattered parts of south and southeast Asia
Size range : 140–170 cm (55–67 in) long, plus 22–25 cm (9–10 in) tail[ 140] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[ 141] Diets : A variety of grass, fruit, and herbaceous and wetland plants[ 141] [ 142]
Rucervus
Hodgson , 1838
Scattered parts of south and southeast Asia
Size range : 140 cm (55 in) long, plus 22 cm (9 in) tail (Eld's deer) to 180 cm (71 in) long (barasingha)[ 143] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[ 144] Diets : A variety of grass, fruit, and herbaceous and wetland plants[ 144]
Rusa
H. Smith , 1827
South and Southeast Asia
Size range : 100 cm (39 in) long (Philippine deer) to 270 cm (106 in) long, plus 30 cm (12 in) tail (sambar deer)[ 145] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[ 146] Diets : Wide variety of plants[ 146]
Family Giraffidae
Members of the Giraffidae family are giraffids, and are the giraffes and the okapi . Giraffidae comprises five extant species in two genera.
Not assigned to a named subfamily – two genera
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Giraffa
Brisson , 1762
Scattered Sub-Saharan Africa (species shown as subspecies)
Size range : 380–470 cm (150–185 in) long, plus 78–100 cm (31–39 in) tail; 600–1,800 kg (1,323–3,968 lb)[ 147] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland[ 148] Diets : Leaves, stems, flowers, and fruit[ 148]
Okapia
Lankester , 1901
Democratic Republic of the Congo in Central AfricaSize : 200–220 cm (79–87 in) long, plus 30–42 cm (12–17 in) tail; 200–350 kg (441–772 lb)[ 147] Habitats : Forest[ 149] Diet : Leaves[ 149]
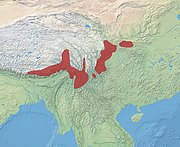
Family Moschidae
Members of the Moschidae family are moschids, or colloquially musk deer. Moschidae contains seven extant species in a single genus.
Not assigned to a named subfamily – one genus
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Moschus
Linnaeus , 1758
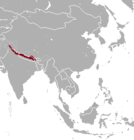
Southern Asia
Size range : 80–100 cm (31–39 in) long, plus 4–6 cm (2–2 in) tail[ 150] [ 151] Habitats : Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[ 152] Diets : Leaves, flowers, shoots, and grass, as well as twigs, moss, and lichen[ 151]
Family Tragulidae
Members of the Tragulidae family are tragulids, or colloquially chevrotains or mouse-deer. Tragulidae contains 10 extant species in 3 genera.
Not assigned to a named subfamily – three genera
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Hyemoschus
Brisson , 1762
Central and western Africa
Size : 45–85 cm (18–33 in) long, plus 7–17 cm (3–7 in) tail[ 153] Habitats : Forest[ 154] Diet : Tree and shrub leaves, fruit, and buds[ 153]
Moschiola
J. E. Gray , 1845
Southern Asia
Size range : 50–56 cm (20–22 in) long, plus 2–3 cm (1–1 in) tail[ 155] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, and marine[ 156] Diets : Herbs, shrubs, and fruit[ 156]
Tragulus
J. E. Gray , 1845
Southeast Asia
Size range : 40–58 cm (16–23 in) long, plus 6–10 cm (2–4 in) tail[ 157] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[ 158] Diets : Fruit, as well as shoots and young leaves[ 158]
Suborder Suina
Family Suidae
Members of the Suidae family are suids, or colloquially pigs, hogs, or boars. Suidae comprises 17 extant species, divided into 6 genera, and is not split into subfamilies.
Not assigned to a named subfamily – six genera
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Babyrousa
Perry , 1811
Indonesia
Size range : 85–110 cm (33–43 in) long, plus 20–32 cm (8–13 in) tail (Buru babirusa and North Sulawesi babirusa)[ 159] Habitats : Forest, inland wetlands, and intertidal marine[ 160] Diets : Fruit and browse , as well as rhizomes , tamarinds , cacao , herbs, and vegetables[ 160]
Hylochoerus
Thomas , 1904
Scattered central Africa
Size : 130–210 cm (51–83 in) long, plus 25–45 cm (10–18 in) tail[ 161] Habitats : Forest[ 162] Diet : Large variety of plants, particularly herbaceous plants [ 162]
Phacochoerus
F. Cuvier , 1826
Sub-saharan Africa
Size range : 90–150 cm (35–59 in) long (common warthog)[ 163] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[ 164] Diets : Grass, shrubs, and tubers, as well as fruit, insects, roots, berries, bark, and carrion[ 164]
Porcula
Hodgson , 1847
Southern Bhutan and northwest India
Size : 55–71 cm (22–28 in) long, plus tail[ 165] Habitats : Grassland[ 166] Diet : Roots, grass, tubers, and invertebrates[ 167] [ 166]
Potamochoerus
J. E. Gray , 1854
Sub-Saharan Africa
Size range : 100–150 cm (39–59 in) long, plus 30–40 cm (12–16 in) tail (red river hog)[ 168] Habitats : Forest and shrubland[ 169] Diets : Roots, tubers, fruit, seeds, invertebrates, small vertebrates, and carrion[ 169]
Sus
Linnaeus , 1758
Southeast Asia, with wild boar in Eurasia and North Africa and introduced to parts of United States, South America, and Oceania
Size range : 80 cm (31 in) long (Celebes warty pig) to 200 cm (79 in) long, plus 40 cm (16 in) tail (wild boar)[ 170] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, neritic marine, intertidal marine, and desert[ 171] Diets : Omnivorous; wide variety of plants and small vertebrates[ 171]
Family Tayassuidae
Members of the Tayassuidae family are tayassuids, or colloquially peccaries. Tayassuidae comprises 3 extant species in 3 genera, and is not split into subfamilies.
Not assigned to a named subfamily – three genera
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Catagonus
Ameghino , 1904
Gran Chaco region of central South AmericaSize : 96–118 cm (38–46 in) long[ 172] Habitats : Savanna and shrubland[ 173] Diet : Cacti, as well as roots, fruit, and forbs[ 173]
Dicotyles
Linnaeus , 1758
South America, Central America, Trinidad in the Caribbean, and southern North America
Size : 80–100 cm (31–39 in) long[ 174] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert[ 175] Diet : Roots, tubers, fruits, seeds, as well as green plants, insects, and small animals[ 175]
Tayassu
Fischer von Waldheim , 1814
South America and Central America
Size : 75–100 cm (30–39 in) long, plus 1–6 cm (0–2 in) tail[ 176] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[ 177] Diet : Fruit, as well as a variety of plants, invertebrates, fungi and fish[ 177]
Suborder Tylopoda
Family Camelidae
Members of the Camelidae family are camelids, and include camels , llamas , and alpacas . Camelidae contains 7 extant species in 2 genera.
Not assigned to a named subfamily – two genera
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Camelus
Linnaeus , 1758
Northern Africa, Middle East, central Asia, central Australia
Size range : 220 cm (87 in) long, plus 20 cm (8 in) tail (dromedary) to 320 cm (126 in) long, plus 25 cm (10 in) tail (wild Bactrian camel)[ 178] Habitats : Desert[ 178] Diets : Wide variety of plants, as well as carrion[ 178]
Lama
Cuvier , 1800
Western and southern South America
Size range : 90 cm (35 in) long, plus 24 cm (9 in) tail (guanaco) to 225 cm (89 in) long, plus 25 cm (10 in) tail (alpaca)[ 179] Habitats : Shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, desert[ 180] Diets : Grass, forbs, shrubs, and lichen[ 180]
Suborder Whippomorpha
Infraorder Cetacea
Parvorder Mysticeti
Family Balaenidae
Members of the Balaenidae family are balaenids, or colloquially right whales. Balaenidae contains four species in two genera.
Family Balaenopteridae
Members of the Balaenopteridae family are balaenopterids, or colloquially rorquals. Balaenopteridae contains eleven species in three genera.
Family Cetotheriidae
Members of the Cetotheriidae family are cetotheriids; the only extant species is the pygmy right whale.
Not assigned to a named subfamily – one genus
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Caperea
J. E. Gray , 1864
Sub-Antarctic oceansSize : 5.5–6.5 m (18–21 ft) long; 3–3.5 tons[ 191] Habitats : Neritic marine and oceanic marine[ 192] Diet : Copepods as well as other zooplankton[ 192]
Parvorder Odontoceti
Family Delphinidae
Members of the Delphinidae family are delphinids, or colloquially oceanic dolphins. Delphinidae contains 37 species in 19 genera, which are grouped into four named subfamilies: Delphininae, Lissodelphininae, Globicephalinae , and Orcininae , as well as one unnamed group.
Subfamily Delphininae – LeDuc , 1997
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Delphinus
Linnaeus , 1758
Tropical and temperate Pacific, Atlantic and Indian OceansSize : 170–240 cm (67–94 in) long; 70–110 kg (154–243 lb)[ 193] Habitats : Neritic marine and oceanic marine[ 194] Diet : Epipelagic and mesopelagic fish as well as squid[ 194]
Lagenodelphis
Fraser , 1956
Tropical and temperate Pacific, Atlantic and Indian Oceans
Size : 200–260 cm (79–102 in) long; 160–210 kg (353–463 lb)[ 195] Habitats : Neritic marine and oceanic marine[ 196] Diet : Mesopelagic fish, cephalopods, and crustaceans[ 196]
Sotalia
J. E. Gray , 1866
Northern and eastern South American coast and Amazon basin rivers
Size range : 130–180 cm (51–71 in) long; 35–45 kg (77–99 lb)[ 197] Habitats : Neritic marine, coastal marine, and inland wetlands[ 198] Diets : Fish, cephalopods, and shrimp[ 198]
Sousa
J. E. Gray , 1866
Western African coast; Indian Ocean coasts; western Pacific Ocean
Size range : 200 cm (79 in) long and 100 kg (220 lb) (Indo-Pacific humpback dolphin) to 280 cm (110 in) long and 200 kg (441 lb) (Atlantic humpback dolphin)[ 199] Habitats : Neritic marine, coastal marine, intertidal marine, oceanic marine, and inland wetlands[ 200] Diets : Wide variety of coastal fish, as well as cephalopods[ 200]
Stenella
J. E. Gray , 1866
Worldwide tropical and temperate oceans
Size range : 130 cm (51 in) long and 45 kg (99 lb) (spinner dolphin) to 250 cm (98 in) long and 150 kg (331 lb) (striped dolphin)[ 201] Habitats : Neritic marine and oceanic marine[ 202] Diets : Small fish, squid, and shrimp[ 202]
Tursiops
Gervais , 1855
Worldwide tropical and temperate oceans
Size range : 190–390 cm (75–154 in) long; 150–650 kg (331–1,433 lb)[ 203] Habitats : Neritic marine, coastal marine, oceanic marine, and inland wetlands[ 204] Diets : Wide variety of fish and cephalopods, as well as shrimp and crustaceans[ 204]
Subfamily Lissodelphininae – Rice , 1984
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Cephalorhynchus
J. E. Gray , 1846
Southern South American coast, southwestern African coast, New Zealand coast, and Kerguelen Islands in Indian Ocean
Size range : 120 cm (47 in) long and 30 kg (66 lb) (Chilean dolphin) to 170 cm (67 in) long and 75 kg (165 lb) (Heaviside's dolphin)[ 205] Habitats : Neritic marine and oceanic marine[ 206] Diets : Small fish, cephalopods, crustaceans, and benthic invertebrates[ 206]
Lissodelphis
Gloger , 1841
Temperate north Pacific Ocean and temperate to sub-Antarctic Pacific and Atlantic Oceans
Size range : 180 cm (71 in) long and 60 kg (132 lb) (southern right whale dolphin) to 300 cm (118 in) long and 100 kg (220 lb) (Northern right whale dolphin)[ 207] Habitats : Neritic marine and oceanic marine[ 208] Diets : Squid and fish[ 208]
Subfamily Globicephalinae LeDuc , 1997
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Feresa
J. E. Gray , 1870
Worldwide tropical and subtropical oceans
Size : 210–260 cm (83–102 in) long; 110–170 kg (243–375 lb)[ 209] Habitats : Oceanic marine[ 210] Diet : Fish and cephalopods[ 210]
Globicephala
Lesson , 1828
Worldwide oceans (short-finned in blue, long-finned in green)
Size range : 360–650 cm (142–256 in) long; 1–4 tons[ 211] Habitats : Oceanic marine[ 212] Diets : Squid, as well as small and medium fish and shrimp[ 212]
Grampus
J. E. Gray , 1828
Worldwide tropical and temperate ocean continental shelves
Size : 260–380 cm (102–150 in) long; 300–500 kg (661–1,102 lb)[ 213] Habitats : Oceanic marine[ 214] Diet : Cephalopods[ 214]
Orcaella
Lesson , 1866
Southeast Asian and northern Australian coasts
Size range : 210–260 cm (83–102 in) long; 90–150 kg (198–331 lb)[ 215] Habitats : Neretic marine, coastal marine, and inland wetlands[ 216] Diets : Fish, as well as squid and shrimp[ 215]
Peponocephala
Nishiwaki , Norris , 1966
Worldwide tropical and subtropical oceans
Size : 210–270 cm (83–106 in) long; about 160 kg (353 lb)[ 217] Habitats : Oceanic marine[ 218] Diet : Mesopelagic fish, squid, and shrimp[ 218]
Pseudorca
Reinhardt , 1862
Worldwide tropical and temperate oceans
Size : 430–600 cm (169–236 in) long; 1.1–2.2 tons[ 219] Habitats : Neritic marine and oceanic marine[ 220] Diet : Large fish and cephalopods[ 220]
Steno
J. E. Gray , 1846
Worldwide tropical and temperate oceans
Size : 210–260 cm (83–102 in) long; 100–150 kg (220–331 lb)[ 221] Habitats : Neritic marine and oceanic marine[ 222] Diet : Fish and cephalopods[ 222]
Subfamily Orcininae Rice , 1967
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Orcinus
Fitzinger , 1860
Worldwide oceans
Size : 550–980 cm (217–386 in) long; 2.6–9 tons[ 223] Habitats : Neritic marine and oceanic marine[ 224] Diet : Wide variety of prey, including marine mammals, seabirds, sea turtles, many species of fish, sharks, rays , and cephalopods[ 224]
Not assigned to a named subfamily – one genus
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Lagenorhynchus
Cope , 1866
Temperate and subarctic northern Atlantic Ocean, Sub-Antarctic Pacific and Atlantic Oceans, temperate north Pacific Ocean, and scattered southern hemisphere coasts
Size range : 150 cm (59 in) long and 50 kg (110 lb) (dusky dolphin) to 270 cm (106 in) long and 275 kg (606 lb) (White-beaked dolphin)[ 225] Habitats : Neritic marine and oceanic marine[ 226] Diets : Wide variety of fish and cephalopods[ 226]
Family Iniidae
Members of the Iniidae family are inniids, and are part of a grouping colloqially termed river dolphins along with Lipotidae , Platanistidae and Pontoporiidae . Iniidae contains four species in one genus.
Not assigned to a named subfamily – one genus
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
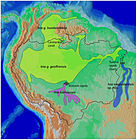
Inia
d'Orbigny , 1834
Amazon rivers in South America (Araguaian river dolphin in blue, Amazon and Orinoco river dolphins in green, and Bolivian river dolphin in purple)
Size range : 180–250 cm (71–98 in) long; 85–160 kg (187–353 lb)[ 227] Habitats : Inland wetlands[ 228] Diets : Fish, as well as shrimp[ 227]
Family Kogiidae
Members of the Kogiidae family are kogiids, and are part of the sperm whale superfamily Physeteroidea ; the family contains two species in one genus.
Not assigned to a named subfamily – one genus
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Kogia
G. R. Gray , 1864
Worldwide tropical and temperate oceans
Size range : 210 cm (83 in) long and 135 kg (298 lb) (dwarf sperm whale) to 340 cm (134 in) long and 400 kg (882 lb) (pygmy sperm whale)[ 229] Habitats : Oceanic marine[ 230] Diets : Cephalopods, as well as fish, shrimp, and crabs[ 230]
Family Lipotidae
Members of the Lipotidae family are lipotids and are part of the river dolphin grouping along with Iniidae, Platanistidae and Pontoporiidae; the only extant species is the baiji .
Not assigned to a named subfamily – one genus
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Lipotes
Miller , 1918
Yangtze river in ChinaSize : 140–250 cm (55–98 in) long; 100–160 kg (220–353 lb)[ 231] Habitats : Inland wetlands[ 232] Diet : Fish[ 232]
Family Monodontidae
Members of the Monodontidae family are monodontids and comprises two living whale species in two genera, the narwhal and the beluga whale .
Family Phocoenidae
Members of the Phocoenidae family are phocoenids, or colloquially porpoises. Phocoenidae contains eight species in three genera.
Not assigned to a named subfamily – three genera
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Neophocaena
Palmer , 1899
Asian coasts
Size range : 120–190 cm (47–75 in) long; 30–45 kg (66–99 lb)[ 237] Habitats : Inland wetlands, neritic marine, oceanic marine, intertidal marine, and coastal marine[ 238] Diets : Small fish, cephalopods, and crustaceans[ 238]
Phocoena
Cuvier , 1816
North Atlantic, North Pacific, and Antarctic oceans, Black Sea , and South American coast
Size range : 130–220 cm (51–87 in) long; 60–84 kg (132–185 lb) (spectacled porpoise)[ 239] Habitats : Neritic marine and oceanic marine[ 240] Diets : Fish, shrimp, squid, and crustaceans[ 240]
Phocoenoides
(Andrews , 1911)
North Pacific ocean
Size : 170–220 cm (67–87 in) long; 135–220 kg (298–485 lb) (spectacled porpoise)[ 241] Habitats : Neritic marine and oceanic marine[ 242] Diet : Wide variety of fish, squid[ 242]
Family Physeteridae
Members of the Physeteridae family are physeterids, and are part of the sperm whale superfamily Physeteroidea; the only extant species is the sperm whale .
Not assigned to a named subfamily – one genus
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
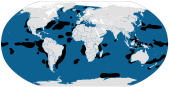
Physeter
Linnaeus , 1758
Worldwide oceans (concentrations in black)
Size : 11–18 m (36–59 ft) long; 20–50 tons[ 243] Habitats : Neritic marine and oceanic marine[ 244] Diet : Deep-water squid[ 244]
Family Platanistidae
Members of the Platanistidae family are platanistids, and are part of a grouping colloqially termed river dolphins along with Iniidae, Lipotidae, and Pontoporiidae. Platanistidae contains two species in one genus.
Not assigned to a named subfamily – one genus
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
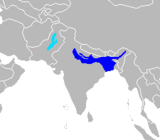
Platanista
Wagler , 1830
Ganges river (dark blue) and Indus river (light blue)Size range : 150–250 cm (59–98 in) long; 70–90 kg (154–198 lb)[ 245] Habitats : Neritic marine and inland wetlands[ 246] Diets : Fish and shrimp[ 245]
Family Pontoporiidae
Members of the Pontoporiidae family are pontoporiids, and are part of a grouping colloqially termed river dolphins along with Iniidae, Lipotidae, and Platanistidae. The only extant species is the La Plata dolphin .
Not assigned to a named subfamily – one genus
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Pontoporia
J. E. Gray , 1846
Southeastern South American coast
Size : 130–170 cm (51–67 in) long; 30–53 kg (66–117 lb)[ 247] Habitats : Neritic marine and oceanic marine[ 248] Diet : Fish, cephalopods, and crustaceans[ 248]
Family Ziphiidae
Members of the Ziphiidae family are ziphiids, or colloquially beaked whales. Ziphiidae contains 23 species in 6 genera, which are grouped into three named subfamilies: Berardiinae, Hyperoodontinae, and Ziphiinae.
Subfamily Berardiinae – Moore , 1968
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Berardius
Duvernoy , 1851
Antarctic, subantarctic, and north Pacific oceans
Size range : 7.8 m (26 ft) long and 7 tons (Arnoux's beaked whale) to 12.8 m (42 ft) long and 16 tons (Baird's beaked whale)[ 249] Habitats : Oceanic marine[ 250] Diets : Deepwater and pelagic fish, cephalopods, and crustaceans[ 250]
Subfamily Hyperoodontinae – J. E. Gray , 1846
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Hyperoodon
Lacépède , 1804
Antarctic, subantarctic, and north Atlantic oceans
Size range : 6–9 m (20–30 ft) long; 5.8–8 tons[ 251] Habitats : Oceanic marine[ 252] Diets : Squid, as well as fish, sea cucumbers, starfish, and prawns[ 252]
Indopacetus
Moore , 1968
Small ocean regions near Horn of Africa and Australia
Size : 7–7.5 m (23–25 ft) long[ 253] Habitats : Oceanic marine[ 254] Diet : Squid[ 254]
Mesoplodon
Gervais , 1850
Worldwide tropical and temperate oceans
Size range : 3.4 m (11 ft) long (pygmy beaked whale) to 6.2 m (20 ft) long and 3 tons (strap-toothed whale)[ 255] Habitats : Oceanic marine[ 256] Diets : Squid, fish, and crustaceans[ 256]
Family Hippopotamidae
Members of the Hippopotamidae family are hippopotamids, or colloquially hippopotamuses or hippos. Hippopotamidae contains 2 species in 2 genera.
Not assigned to a named subfamily – two genera
Name
Authority and species
Range
Size and ecology
Choeropsis
Leidy , 1853
Scattered western Africa
Size : 150–175 cm (59–69 in) long, plus a tail of about 20 cm (8 in); 160–275 kg (353–606 lb)[ 261] Habitats : Forest, savanna, inland wetlands[ 262] Diet : Variety of terrestrial and semi-aquatic plants[ 262]
Hippopotamus
Linnaeus , 1758
Sub-Saharan Africa and Nile River (current range in green, historical in red)
Size : 209–505 cm (82–199 in) long, including a tail of about 35 cm (14 in); 1,300–3,200 kg (2,866–7,055 lb)[ 263] Habitats : Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, neritic marine, coastal marine[ 264] Diet : Grass[ 264]
See also
References
^ Graur, Dan; Higgins, Desmond G. (1994). "Molecular Evidence for the Inclusion of Cetaceans within the Order Artiodactyla" . Molecular Biology and Evolution 11 (3): 357– 364. doi :10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040118 PMID 8015431 . ^ Wilson, Reeder , pp. 637–743^ Burnie , p. 227^ a b IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2017) [errata version of 2016 assessment]. "Antilocapra americana " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T1677A50181848. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T1677A50181848.en ^ a b c d e Harris , pp. 122–131^ a b IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2016). "Aepyceros melampus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T550A50180828. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T550A50180828.en ^ Lundrigan, Barbara; Sproull, Karen (2000). "Aepyceros melampus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved April 30, 2021 . ^ Batty, Kristin (2002). "Alcelaphus buselaphus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved May 27, 2021 . ^ a b IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2019) [amended version of 2016 assessment]. "Alcelaphus buselaphus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019 : e.T811A143160967. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T811A143160967.en ^ a b Olney, Hannah (2002). "Beatragus hunteri " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 27, 2021 . ^ a b IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2017). "Beatragus hunteri " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T6234A50185297. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T6234A50185297.en ^ Connochaetes sizes:
^ a b Connochaetes habitats and diets:
^ Damaliscus sizes:
^ a b Damaliscus habitats and diets:
^ a b Derrig, Jim Bob (2003). "Ammodorcas clarkei " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 27, 2021 . ^ a b Heckel, J.; Wilhelmi, F.; Kaariye, X.; Amir, O. (2016). "Ammodorcas clarkei " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T1141A50181613. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T1141A50181613.en ^ Kingdon 2013 , ch. Springbok^ a b IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2017) [errata version of 2016 assessment]. "Antidorcas marsupialis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T1676A50181753. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T1676A50181753.en ^ "Blackbuck (Antilope cervicapra )" . ARKive Wildscreen . Archived from the original on February 1, 2019. Retrieved September 5, 2021 .^ a b IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2017). "Antilope cervicapra " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T1681A50181949. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T1681A50181949.en ^ Kingdon 2020 , ch. Beira^ a b IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2016). "Dorcatragus megalotis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T6793A50185898. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T6793A50185898.en ^ Eudorcas sizes:
^ a b Eudorcas habitats and diets:
^ Gazella sizes:
Arabian gazelle : Castelló , p. 132Chinkara : McCart, Dylan (2012). "Gazella bennettii " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved May 11, 2021 . Cuvier's gazelle : Kingdon 2020 , ch. Cuvier's gazelleDorcas gazelle : Kingdon 2020 , ch. Dorcas gazelleErlanger's gazelle : Castelló , p. 134Mountain gazelle : Castelló , p. 128Rhim gazelle : Castelló , p. 146Arabian sand gazelle : Castelló , p. 156Speke's gazelle : Kingdon 2013 , ch. Speke's gazelleGoitered gazelle : Castelló , p. 150^ a b Gazella habitats and diets:
^ Payne, Jamie (2003). "Litocranius walleri " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved May 21, 2021 . ^ a b IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2016). "Litocranius walleri " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T12142A50190292. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T12142A50190292.en ^ Madoqua sizes:
^ a b Madoqua habitats and diets:
^ Nanger sizes:
^ a b Nanger habitats and diets:
^ a b Neotragus sizes:
^ a b c d Neotragus habitats and diets:
^ Ewacha, Michelle (2013). "Oreotragus oreotragus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved May 24, 2021 . ^ a b IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2016). "Oreotragus oreotragus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T15485A50191264. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T15485A50191264.en ^ a b Frey, Dayna (2000). "Ourebia ourebi " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved June 18, 2021 . ^ IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2016). "Ourebia ourebi " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T15730A50192202. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T15730A50192202.en ^ Procapra sizes:
^ a b Procapra habitats and diets:
^ Raphicerus sizes:
^ a b Raphicerus habitats and diets:
^ Castelló , p. 170^ a b IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2018). "Saiga tatarica " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T19832A50194357. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T19832A50194357.en ^ Bison sizes:
American bison : Harris , pp. 122–131European bison : Semenov, U. A. (2014). "The Wisents of Karachay-Cherkessia". Proceedings of the Sochi National Park . KMK Scientific Press. pp. 23– 24. ISBN 978-5-87317-984-8 ^ a b Bison habitats and diets:
^ Bos sizes:
Gayal : Lundrigan, Barbara; Zachariah, Trevor (2000). "Bos frontalis " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved June 19, 2021 . Gaur : Castelló , p. 624Yak : Castelló , p. 638Banteng : Saari, Jason (2002). "Bos javanicus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 27, 2021 . Wild yak : Castelló , p. 636Kouprey : Winker, Jill (2004). "Bos sauveli " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved June 19, 2021 . Cattle : Castelló , p. 642^ a b Bos habitats and diets:
Gayal : Lundrigan, Barbara; Zachariah, Trevor (2000). "Bos frontalis " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved June 19, 2021 . Gaur : Duckworth, J. W.; Sankar, K.; Williams, A. C.; Samba Kumar, N.; Timmins, R. J. (2016). "Bos gaurus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T2891A46363646. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T2891A46363646.en Yak : Oliphant, Matthew (2003). "Bos grunniens " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved September 6, 2021 . Banteng : Gardner, P.; Hedges, S.; Pudyatmoko, S.; Gray, T. N. E.; Timmins, R. J. (2016). "Bos javanicus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T2888A46362970. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T2888A46362970.en Wild yak : Buzzard, P.; Berger, J. (2016). "Bos mutus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T2892A101293528. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T2892A101293528.en Kouprey : Timmins, R. J.; Burton, J.; Hedges, S. (2016). "Bos sauveli " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T2890A46363360. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T2890A46363360.en Cattle : Dewey, Tanya; Ng, Jessica (2001). "Bos taurus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved September 6, 2021 . ^ Benton, Melody (2000). "Boselaphus tragocamelus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved July 7, 2021 . ^ a b IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2017) [errata version of 2016 assessment]. "Boselaphus tragocamelus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T2893A50182076. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T2893A50182076.en ^ Bubalus sizes:
^ a b Bubalus habitats and diets:
Wild water buffalo : Kaul, R.; Williams, A. C.; Rithe, K.; Steinmetz, R.; Mishra, R. (2019). "Bubalus arnee " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019 : e.T3129A46364616. doi :10.2305/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T3129A46364616.en Water buffalo : Roth, Jason (2004). "Bubalus bubalis " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 27, 2021 . Lowland anoa : Burton, J.; Wheeler, P.; Mustari, A. (2016). "Bubalus depressicornis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T3126A46364222. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T3126A46364222.en Tamaraw : Boyles, R.; Schutz, E.; de Leon, J. (2016). "Bubalus mindorensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T3127A50737640. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T3127A50737640.en Mountain anoa : Burton, J.; Wheeler, P.; Mustari, A. (2016). "Bubalus quarlesi " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T3128A46364433. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T3128A46364433.en ^ Castelló , p. 648^ a b Timmins, R. J.; Hedges, S.; Robichaud, W. (2020) [amended version of 2016 assessment]. "Pseudoryx nghetinhensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T18597A166485696. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-1.RLTS.T18597A166485696.en ^ IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2019). "Syncerus caffer " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019 : e.T21251A50195031. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T21251A50195031.en ^ Taurotragus sizes:
^ a b Taurotragus habitats and diets:
^ Lundeen, Brooks (2003). "Tetracerus quadricornis " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved August 18, 2021 . ^ a b IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2017). "Tetracerus quadricornis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T21661A50195368. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T21661A50195368.en ^ Tragelaphus sizes:
Nyala : Kingdon 2013 , ch. NyalaMountain nyala : Aleman, Maria (2003). "Tragelaphus buxtoni " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved August 18, 2021 . Bongo : "Bongo (Tragelaphus eurycerus )" . ARKive Wildscreen . Archived from the original on February 1, 2019. Retrieved September 5, 2021 .Lesser kudu : Paschka, Nick (2000). "Tragelaphus imberbis " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved August 18, 2021 . Harnessed bushbuck : Kingdon 2020 , ch. BushbuckSitatunga : Kingdon 2013 , ch. SitatungaGreater kudu : Harris , pp. 122–131^ a b Tragelaphus habitats and diets:
IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2017) [errata version of 2016 assessment]. "Tragelaphus angasii " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T22052A50196443. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22052A50196443.en ^ "Barbary sheep (Ammotragus lervia )" . ARKive Wildscreen . Archived from the original on February 1, 2019. Retrieved September 5, 2021 .^ a b Cassinello, J.; Cuzin, F.; Jdeidi, T.; Masseti, M.; Nader, I.; de Smet, K. (2008). "Ammotragus lervia " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2008 : e.T1151A3288917. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T1151A3288917.en ^ Castelló , p. 310^ a b Ross, S.; Al-Rawahi, H.; Al-Jahdhami, M. H.; Spalton, J. A.; Mallon, D.; Al-Shukali, A.; Al-Fazari, W.; Chreiki, M. K. (2019) [errata version of 2019 assessment]. "Arabitragus jayakari " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019 : e.T9918A156925170. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T9918A156925170.en ^ Marceau, Jonathan (2000). "Budorcas taxicolor " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved August 19, 2021 . ^ a b Song, Y.-L.; Smith, A. T.; MacKinnon, J. (2008). "Budorcas taxicolor " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2008 : e.T3160A9643719. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T3160A9643719.en ^ Capra sizes:
Wild goat : Mileski, Adam (2004). "Capra hircus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved August 19, 2021 . West Caucasian tur : Castelló , p. 326East Caucasian tur : Eule, David (2002). "Capra cylindricornis " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved August 19, 2021 . Alpine ibex : Sippl, John (2003). "Capra ibex " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved August 19, 2021 . Markhor : Cothran, Nora (2005). "Capra falconeri " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved August 19, 2021 . Nubian ibex : Tomsen, Jan (2007). "Capra nubiana " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved August 19, 2021 . Iberian ibex : Blaha, Dillon (2003). "Capra pyrenaica " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved August 19, 2021 . Siberian ibex : Williams, Jeffrey (2007). "Capra sibirica " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved August 19, 2021 . Walia ibex : Kingdon 2020 , ch. Walia ibex^ a b Capra habitats and diets:
Wild goat : Weinberg, P.; Ambarli, H. (2020). "Capra aegagrus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T3786A22145942. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T3786A22145942.en West Caucasian tur : Weinberg, P. (2020). "Capra caucasica " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T3794A22143809. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T3794A22143809.en East Caucasian tur : Lortkipanidze, B.; Weinberg, P. (2020). "Capra cylindricornis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T3795A91287260. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T3795A91287260.en Alpine ibex : Toïgo, C.; Brambilla, A.; Grignolio, S.; Pedrotti, L. (2020). "Capra ibex " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T42397A161916377. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T42397A161916377.en Markhor : Michel, S.; Rosen Michel, T. (2016) [errata version of 2015 assessment]. "Capra falconeri " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T3787A82028427. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T3787A82028427.en Nubian ibex : Ross, S.; Elalqamy, H.; Al Said, T.; Saltz, D. (2020). "Capra nubiana " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T3796A22143385. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T3796A22143385.en Iberian ibex : Herrero, J.; Acevedo, P.; Arnal, M. C.; Fernández de Luco, D.; Fonseca, C.; García-González, R.; Pérez, J. M.; Sourp, E. (2021) [amended version of 2020 assessment]. "Capra pyrenaica " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2021 : e.T3798A195855497. Siberian ibex : Reading, R.; Michel, S.; Suryawanshi, K.; Bhatnagar, Y. V. (2020). "Capra sibirica " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T42398A22148720. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T42398A22148720.en Walia ibex : Ejigu, D. (2020) [errata version of 2020 assessment]. "Capra walie " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T3797A178652661. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T3797A178652661.en "Walia ibex (Capra walie )" . ARKive Wildscreen . Archived from the original on May 17, 2018. Retrieved September 6, 2021 .^ Capricornis sizes:
^ a b Capricornis habitats and diets:
^ Kennedy, Sara (2002). "Hemitragus jemlahicus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved August 26, 2021 . ^ a b Ale, S. B.; Sathyakumar, S.; Forsyth, D. M.; Lingyun, X.; Bhatnagar, Y. V. (2020). "Hemitragus jemlahicus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T9919A22152905. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T9919A22152905.en ^ Naemorhedus sizes:
^ a b Naemorhedus habitats and diets:
Red goral : Nijhawan, S. (2020) [amended version of 2020 assessment]. "Naemorhedus baileyi " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T14294A179947455. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T14294A179947455.en Long-tailed goral : Bragina, E.; Kim, S.; Zaumyslova, O.; Park, Y.-S.; Lee, W. (2020). "Naemorhedus caudatus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T14295A22150540. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T14295A22150540.en Himalayan goral : Duckworth, J. W.; MacKinnon, J. (2008). "Naemorhedus goral " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2008 : e.T14296A4430073. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T14296A4430073.en Chinese goral : Duckworth, J. W.; Steinmetz, R.; Chaiyarat, R. (2008). "Naemorhedus griseus (This concept is no longer recognised)" . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2008 : e.T14303A4430834. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T14303A4430834.en ^ Herman, Adam (2004). "Hemitragus hylocrius " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved August 26, 2021 . ^ a b Alempath, M.; Rice, C. (2008). "Nilgiritragus hylocrius " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2008 : e.T9917A13026736. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T9917A13026736.en ^ a b Festa-Bianchet, M. (2020). "Oreamnos americanus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T42680A22153133. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T42680A22153133.en ^ a b Gunn, A.; Forchhammer, M. (2016) [errata version of 2008 assessment]. "Ovibos moschatus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2008 : e.T29684A9526203. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T29684A9526203.en ^ Ovis sizes:
Argali : Tonda, John (2002). "Ovis ammon " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved September 3, 2021 . Sheep : Reavill, Chris (2000). "Ovis aries " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved September 3, 2021 . Bighorn sheep : Dewey, Tanya; Ballenger, Liz (1999). "Ovis canadensis " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved September 3, 2021 . Dall sheep : Gozdzik, Agnes (2001). "Ovis dalli " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved September 3, 2021 . Mouflon : Castelló , p. 397Snow sheep : Castelló , p. 367Urial : Castelló , pp. 390, 391^ a b Ovis habitats and diets:
Argali : Reading, R.; Michel, S.; Amgalanbaatar, S. (2020). "Ovis ammon " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T15733A22146397. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T15733A22146397.en Sheep : Reavill, Chris (2000). "Ovis aries " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved September 3, 2021 . Bighorn sheep : Festa-Bianchet, M. (2020). "Ovis canadensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T15735A22146699. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T15735A22146699.en Dall sheep : Festa-Bianchet, M. (2020). "Ovis dalli " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T39250A22149895. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T39250A22149895.en Mouflon : Michel, S.; Ghoddousi, A. (2020). "Ovis gmelini " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T54940218A22147055. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T54940218A22147055.en Snow sheep : Harris, R. B.; Tsytsulina. K. (2008). "Ovis nivicola " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2008 : e.T15740A5076357. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T15740A5076357.en Urial : Michel, S.; Ghoddousi, A. (2021) [errata version of 2020 assessment]. "Ovis vignei " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T54940655A195296049. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T54940655A195296049.en ^ a b Castelló , pp. 405, 407^ IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2016). "Pantholops hodgsonii " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T15967A50192544. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T15967A50192544.en ^ Smith, Mary Alice (2000). "Pseudois nayaur " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved September 3, 2021 . ^ a b Harris, R. B. (2014). "Pseudois nayaur " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2014 : e.T61513537A64313015. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2014-3.RLTS.T61513537A64313015.en ^ Rupicapra sizes:
^ a b Rupicapra habitats and diets:
Pyrenean chamois : Herrero, J.; Lovari, S.; Nores, C.; Toigo, C. (2020). "Rupicapra pyrenaica " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T19771A171131310. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T19771A171131310.en Chamois : Anderwald, P.; Ambarli, H.; Avramov, S.; Ciach, M.; Corlatti, L.; Farkas, A.; Jovanovic, M.; Papaioannou, H.; Peters, W.; Sarasa, M.; Šprem, N.; Weinberg, P.; Willisch, C. (2021) [amended version of 2020 assessment]. "Rupicapra rupicapra " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2021 : e.T39255A195863093. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-1.RLTS.T39255A195863093.en ^ Cephalophus sizes:
Aders's duiker : "Aders' duiker (Cephalophus adersi )" . ARKive Wildscreen . Archived from the original on February 1, 2019. Retrieved September 5, 2021 .Brooke's duiker : Castelló , p. 269Peters's duiker : Kingdon 2020 , ch. Peters's duikerWhite-legged duiker : Kingdon 2020 , ch. Ogilby's duikerBay duiker : "Bay duiker (Cephalophus dorsalis )" . ARKive Wildscreen . Archived from the original on February 1, 2019. Retrieved September 5, 2021 .Jentink's duiker : Kingdon 2013 , ch. Jentink's duikerWhite-bellied duiker : Kingdon 2013 , ch. White-bellied duikerRed forest duiker : Kingdon 2020 , ch. Red duikerBlack duiker : Milich, Krista (2002). "Cephalophus niger " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved September 3, 2021 . Black-fronted duiker : "Black-fronted duiker (Cephalophus nigrifrons )" . ARKive Wildscreen . Archived from the original on February 2, 2019. Retrieved September 5, 2021 .Ogilby's duiker : Kingdon 2020 , ch. Ogilby's duikerRed-flanked duiker : Hanson, Benjamin (2006). "Cephalophus rufilatus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved September 3, 2021 . Yellow-backed duiker : DeWitt, Kristina (2006). "Cephalophus silvicultor " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved September 3, 2021 . Abbott's duiker : "Abbott's duiker (Cephalophus spadix )" . ARKive Wildscreen . Archived from the original on February 1, 2019. Retrieved September 5, 2021 .Weyns's duiker : Kingdon 2020 , ch. Weyns's duikerZebra duiker : Kingdon 2020 , ch. Zebra duiker^ a b Cephalophus habitats and diets:
^ Philantomba sizes:
^ a b Philantomba habitats and diets:
^ Castelló , p. 244^ a b IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2016). "Sylvicapra grimmia " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T21203A50194717. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T21203A50194717.en ^ a b Altan, Berke (2000). "Addax nasomaculatus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved September 5, 2021 . ^ IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2016). "Addax nasomaculatus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T512A50180603. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T512A50180603.en ^ Hippotragus sizes:
^ a b Hippotragus habitats and diets:
^ Oryx sizes:
^ a b Oryx habitats and diets:
^ Kobus sizes:
^ a b Kobus habitats and diets:
^ Dewey, Stephen (2002). "Pelea capreolus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved September 5, 2021 . ^ a b Taylor, A.; Cowell, C.; Drouilly, M. (2017). "Pelea capreolus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T16484A50192715. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T16484A50192715.en ^ Redunca sizes:
^ a b Redunca habitats and diets:
^ De Bord, Daniel (2009). "Alces alces " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved February 24, 2021 . ^ a b Hundertmark, K. (2016). "Alces alces " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T56003281A22157381. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T56003281A22157381.en ^ Eisenberg, Redford, Reid, Bonner (vol. 3) , p. 340^ a b Duarte, J. M. B; Varela, D.; Piovezan, U.; Beccaceci, M. D.; Garcia, J. E. (2016). "Blastocerus dichotomus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T2828A22160916. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T2828A22160916.en ^ Capreolus sizes:
^ a b Capreolus habitats and diets:
^ Hippocamelus sizes:
^ a b Hippocamelus habitats and diets:
Taruca : Barrio, J.; Nuñez, A.; Pacheco, L.; Regidor, H. A.; Fuentes-Allende, N. (2017). "Hippocamelus antisensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T10053A22158621. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T10053A22158621.en South Andean deer : Black-Decima, P. A.; Corti, P.; Díaz, N.; Fernandez, R.; Geist, V.; Gill, R.; Gizejewski, Z.; Jiménez, J.; Pastore, H.; Saucedo, C.; Wittmer, H. (2016). "Hippocamelus bisulcus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T10054A22158895. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T10054A22158895.en ^ Smith, Xie , p. 359^ a b Harris, R. B.; Duckworth, J. W. (2015). "Hydropotes inermis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T10329A22163569. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T10329A22163569.en ^ Katopodes, Demetra (1999). "Hydropotes inermis " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 12, 2021 . ^ Mazama sizes:
Red brocket : Kossel, Kyle (2013). "Mazama americana " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved February 25, 2021 . Dwarf brocket : "Dwarf brocket (Mazama chunyi )" . ARKive Wildscreen . Archived from the original on August 11, 2010. Retrieved March 17, 2021 .Pygmy brocket, Little red brocket : Eisenberg, Redford, Reid, Bonner (vol. 3) , p. 346Mérida brocket, Small red brocket, Gray brocket, Amazonian brown brocket, Central American red brocket : Wilson, Mittermeier , p. 441–443^ a b Mazama habitats and diets:
Red brocket : Duarte, J. M. B; Vogliotti, A. (2016). "Mazama americana " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T29619A22154827. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T29619A22154827.en Mérida brocket : Lizcano, D. J.; Alvarez, S. J. (2016). "Mazama bricenii " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T136301A22165039. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T136301A22165039.en Small red brocket : Vogliotti, A.; Oliveira, M. L.; Duarte, J. M. B. (2016). "Mazama bororo " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T41023A22155086. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41023A22155086.en Dwarf brocket : Rumiz, D. I.; Barrio, J. (2016). "Mazama chunyi " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T12913A22165860. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T12913A22165860.en Gray brocket : Black-Decima, P. A.; Vogliotti, A. (2016). "Mazama gouazoubira " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T29620A22154584. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T29620A22154584.en Pygmy brocket : Duarte, J. M. B; Vogliotti, A.; Cartes, J. L.; Oliveira, M. L. (2015). "Mazama nana " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T29621A22154379. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T29621A22154379.en Amazonian brown brocket : Rossi, R. V.; Duarte, J. M. B (2016). "Mazama nemorivaga " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T136708A22158407. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T136708A22158407.en Little red brocket : Lizcano, D. and Alvarez; S. J. (2016). "Mazama rufina " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T12914A22165586. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T12914A22165586.en Central American red brocket : Bello, J.; Reyna, R.; Schipper, J. (2016). "Mazama temama " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T136290A22164644. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T136290A22164644.en ^ Odocoileus sizes:
^ a b Odocoileus habitats and diets:
^ a b D'Elia, Guillermo (1999). "Ozotoceros bezoarticus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 5, 2021 . ^ a b González, S.; Jackson, III; J. J., Merino; M. L. (2016). "Ozotoceros bezoarticus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T15803A22160030. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T15803A22160030.en ^ Pudu sizes:
^ a b Pudu habitats and diets:
^ Joly, Kyle C.; Shefferly, Nancy (2000). "Rangifer tarandus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 5, 2021 . ^ a b Gunn, A. (2016). "Rangifer tarandus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T29742A22167140. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T29742A22167140.en ^ Axis sizes:
^ a b Axis habitats and diets:
Chital : Duckworth, J. W.; Kumar, N. S.; Anwarul Islam, M.; Sagar Baral, H.; Timmins, R. (2015). "Axis axis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T41783A22158006. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41783A22158006.en Calamian deer : Widmann, P.; Lastica, E. (2015). "Axis calamianensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T2446A22156678. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T2446A22156678.en Bawean deer : Semiadi, G.; Duckworth, J. W.; Timmins, R. (2015). "Axis kuhlii " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T2447A73071875. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T2447A73071875.en Indian hog deer : Timmins, R.; Duckworth, J. W.; Samba Kumar, N.; Anwarul Islam, M.; Sagar Baral, H.; Long, B.; Maxwell, A. (2015). "Axis porcinus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T41784A22157664. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41784A22157664.en ^ Cervus sizes:
Thorold's deer : Smith, Xie , p. 356Elk : Armstrong, Fitzgerald, Meaney , p. 446; Burt , p. 149Red deer : Senseman, Rachel Lesley (2002). "Cervus elaphus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 5, 2021 . Sika deer : Landesman, Nathan (1999). "Cervus nippon " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 5, 2021 . ^ a b Cervus habitats and diets:
Thorold's deer : Harris, R. B. (2015). "Cervus albirostris " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T4256A61976756. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T4256A61976756.en Elk : Brook, S. M.; Pluháček, J.; Lorenzini, R.; Lovari, S.; Masseti, M.; Pereladova, O.; Mattioli, S. (2019) [errata version of 2018 assessment]. "Cervus canadensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T55997823A142396828. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T55997823A142396828.en Red deer : Lovari, S.; Lorenzini, R.; Masseti, M.; Pereladova, O.; Carden, R. F.; Brook, S. M.; Mattioli, S. (2019) [errata version of 2018 assessment]. "Cervus elaphus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T55997072A142404453. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T55997072A142404453.en Central Asian red deer : Brook, S. M.; Donnithorne-Tait, D.; Lorenzini, R.; Lovari, S.; Masseti, M.; Pereladova, O.; Ahmad, K.; Thakur, M. (2017) [amended version of 2017 assessment]. "Cervus hanglu " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T4261A120733024. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T4261A120733024.en Sika deer : Harris, R. B. (2015). "Cervus nippon " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T41788A22155877. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T41788A22155877.en ^ Dama sizes:
^ a b Dama habitats and diets:
^ Lundrigan, Barbara; Oas, Rebecca (2003). "Elaphodus cephalophus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 5, 2021 . ^ a b Harris, R. B.; Jiang, Z. (2015). "Elaphodus cephalophus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T7112A22159620. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T7112A22159620.en ^ Jacobson, Erin (2003). "Elaphurus davidianus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 11, 2021 . ^ a b Jiang, Z.; Harris, R. B. (2016). "Elaphurus davidianus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T7121A22159785. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T7121A22159785.en ^ Muntiacus sizes:
Bornean yellow muntjac : Jetzer, Ashley (2007). "Muntiacus atherodes " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 11, 2021 . Hairy-fronted muntjac : Wood, Aaron (2006). "Muntiacus crinifrons " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 11, 2021 . Fea's muntjac : Wilson, Mittermeier , p. 409–412Gongshan muntjac : Smith, Xie , p. 355Indian muntjac : Jackson, Adria (2002). "Muntiacus muntjak " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 11, 2021 . Pu Hoat muntjac : Wilson, Mittermeier , p. 409–412Leaf muntjac : Gigliotti, Deanna (2013). "Muntiacus putaoensis " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 11, 2021 . Reeves's muntjac : Deuling, Sara (2004). "Muntiacus reevesi " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 11, 2021 . Roosevelt's muntjac : Wilson, Mittermeier , p. 409–412Truong Son muntjac : Wilson, Mittermeier , p. 409–412Giant muntjac : Wilson, Mittermeier , p. 409–412^ a b Muntiacus habitats and diets:
Bornean yellow muntjac : Timmins, R. J.; Belden, G.; Brodie, J.; Ross, J.; Wilting, A.; Duckworth, J. W. (2016). "Muntiacus atherodes " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T42189A22166396. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T42189A22166396.en Hairy-fronted muntjac : Timmins, R.; Chan, B. (2016). "Muntiacus crinifrons " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T13924A22160753. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T13924A22160753.en Fea's muntjac : Timmins, R.; Steinmetz, R.; Chutipong, W. (2016). "Muntiacus feae " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T13927A22160266. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T13927A22160266.en Gongshan muntjac : Timmins, R.; Duckworth, J. W. (2016). "Muntiacus gongshanensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T13926A22160596. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T13926A22160596.en Indian muntjac : Timmins, R. J.; Duckworth, J. W.; Hedges, S. (2016). "Muntiacus muntjak " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T42190A56005589. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T42190A56005589.en Pu Hoat muntjac : Timmins, J; Duckworth, J. W. (2016). "Muntiacus puhoatensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T136293A22164930. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T136293A22164930.en Leaf muntjac : Timmins, R. J.; Duckworth, J. W. (2016). "Muntiacus putaoensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T136479A22159478. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T136479A22159478.en Reeves's muntjac : Timmins, J; Chan, B. (2020) [errata version of 2016 assessment]. "Muntiacus reevesi " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T42191A170905827. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T42191A170905827.en Roosevelt's muntjac : Timmins, R.; Duckworth, J. W. (2016). "Muntiacus rooseveltorum " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T13928A22160435. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T13928A22160435.en Truong Son muntjac : Timmins, R.; Duckworth, J. W. (2016). "Muntiacus truongsonensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T44704A22154056. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T44704A22154056.en Giant muntjac : Timmins, R. J.; Duckworth, J. W.; Robichaud, W.; Long, B.; Gray, T. N. E.; Tilker, A. (2016). "Muntiacus vuquangensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T44703A22153828. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T44703A22153828.en ^ Wilson, Mittermeier , p. 425–426^ a b Gray, T. N. E.; Brook, S. M.; McShea, W. J.; Mahood, S.; Ranjitsingh, M. K.; Miyunt, A.; Hussain, S. A.; Timmins, R. (2015). "Rucervus eldii " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T4265A22166803. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T4265A22166803.en ^ "Eld's deer (Cervus eldii )" . ARKive Wildscreen . Archived from the original on February 26, 2013. Retrieved March 17, 2021 .^ Rucervus sizes:
^ a b Rucervus habitats and diets:
^ Rusa sizes:
^ a b Rusa habitats and diets:
Visayan spotted deer : Brook, S. M. (2016). "Rusa alfredi " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T4273A22168782. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T4273A22168782.en Philippine deer : MacKinnon, J. R.; Ong, P.; Gonzales, J. (2015). "Rusa marianna " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T4274A22168586. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T4274A22168586.en Javan deer : Hedges, S.; Duckworth, J. W.; Timmins, R.; Semiadi, G.; Dryden, G. (2015). "Rusa timorensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T41789A22156866. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T41789A22156866.en Sambar deer : Timmins, R.; Kawanishi, K.; Giman, B; Lynam, A.; Chan, B.; Steinmetz, R.; Sagar Baral, H.; Samba Kumar, N. (2015) [errata version of 2015 assessment]. "Rusa unicolor " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T41790A22156247. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T41790A22156247.en ^ a b Burnie , p. 228^ a b Muller, Z.; Bercovitch, F.; Brand, R.; Brown, D.; Brown, M.; Bolger, D.; Carter, K.; Deacon, F.; Doherty, J. B.; Fennessy, J.; Fennessy, S.; Hussein, A. A.; Lee, D.; Marais, A.; Strauss, M.; Tutchings, A.; Wube, T. (2018) [amended version of 2016 assessment]. "Giraffa camelopardalis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T9194A136266699. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T9194A136266699.en ^ a b Mallon, D.; Kümpel, N.; Quinn, A.; Shurter, S.; Lukas, J.; Hart, J. A.; Mapilanga, J.; Beyers, R.; Maisels, F. (2015). "Okapia johnstoni " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T15188A51140517. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T15188A51140517.en ^ Burnie , p. 225^ a b Macdonald , p. 518^ Moschus habitats and diets:
Anhui musk deer : Wang, Y.; Harris, R. B. (2015). "Moschus anhuiensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T136643A61979276. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T136643A61979276.en Dwarf musk deer : Wang, Y.; Harris, R. (2016) [errata version of 2015 assessment]. "Moschus berezovskii " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T13894A61976926. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T13894A61976926.en Alpine musk deer : Harris, R. (2016). "Moschus chrysogaster " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T13895A61977139. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T13895A61977139.en Kashmir musk deer : Timmins, R. J.; Duckworth, J. W. (2015). "Moschus cupreus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T136750A61979453. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T136750A61979453.en Black musk deer : Wang, Y.; Harris, R. (2015). "Moschus fuscus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T13896A61977357. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T13896A61977357.en White-bellied musk deer : Timmins, R. J.; Duckworth, J. W. (2015). "Moschus leucogaster " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T13901A61977764. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T13901A61977764.en Siberian musk deer : Nyambayar, B.; Mix, H.; Tsytsulina, K. (2015). "Moschus moschiferus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T13897A61977573. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T13897A61977573.en ^ a b Edwards, Helen (2000). "Hyemoschus aquaticus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved September 21, 2021 . ^ IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group. (2016). "Hyemoschus aquaticus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T10341A50188841. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T10341A50188841.en ^ Wijeyeratne , ch. White-spotted mouse deer^ a b
^ Francis , pp. 340–341^ a b Tragulus habitats and diets:
Java mouse-deer : Duckworth, J. W.; Timmins, R.; Semiadi, G. (2015). "Tragulus javanicus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T41780A61978138. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T41780A61978138.en Lesser mouse-deer : Timmins, R.; Duckworth, J. W. (2015). "Tragulus kanchil " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T136297A61978576. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T136297A61978576.en Greater mouse-deer : Timmins, R.; Duckworth, J. W. (2015). "Tragulus napu " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T41781A61978315. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T41781A61978315.en Philippine mouse-deer : Widmann, P. (2015). "Tragulus nigricans " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T22065A61977991. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T22065A61977991.en Vietnam mouse-deer : Timmins, R.; Duckworth, J. W.; Meijaard, E. (2015). "Tragulus versicolor " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T136360A61978789. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T136360A61978789.en Williamson's mouse-deer : Timmins, R.; Duckworth, J. W.; Meijaard, E. (2015). "Tragulus williamsoni " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T136533A61978926. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T136533A61978926.en ^ Babyrousa sizes:
Bola Batu babirusa : Meijaard, E.; Groves, C. (2002). "Upgrading three subspecies of babirusa (Babyrousa sp.) to full species level". Asian Wild Pig News (2): 33– 39. North Sulawesi babirusa : Burnie , p. 219Togian babirusa : Wilson, Mittermeier , pp. 275–276; Melletti, Meijaard , p. 77^ a b Babyrousa habitats and diets:
Bola Batu babirusa : Meijaard, E.; Groves, C. (2002). "Upgrading three subspecies of babirusa (Babyrousa sp.) to full species level". Asian Wild Pig News (2): 33– 39. North Sulawesi babirusa : Leus, K.; Macdonald, A.; Burton, J.; Rejeki, I. (2016). "Babyrousa celebensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T136446A44142964. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T136446A44142964.en Togian babirusa : Macdonald, A.; Leus, K.; Masaaki, I.; Burton, J. (2016). "Babyrousa togeanensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T136472A44143172. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T136472A44143172.en ^ Melletti, Meijaard , p. 115^ a b d'Huart, J.; Reyna, R. (2016) [errata version of 2016 assessment]. "Hylochoerus meinertzhageni " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T41769A44140722. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41769A44140722.en ^ Phacochoerus sizes:
^ a b Phacochoerus habitats and diets:
^ Oliver , pp. 108–109^ a b Meijaard, E.; Narayan, G.; Deka, P. (2019). "Porcula salvania " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019 : e.T21172A44139115. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T21172A44139115.en ^ Saha, Mazumdar , p. 18^ Potamochoerus sizes:
^ a b Potamochoerus habitats and diets:
^ Sus sizes:
Palawan bearded pig : Wilson, Mittermeier , pp. 283–290; Melletti, Meijaard , p. 171–172Bornean bearded pig : Knibbe, Nicole (2000). "Sus barbatus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 26, 2021 . Visayan warty pig : Melletti, Meijaard , p. 151–153Celebes warty pig : Noel, Nicole (2004). "Sus celebensis " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 26, 2021 . Oliver's warty pig : Melletti, Meijaard , p. 163Philippine warty pig : Melletti, Meijaard , p. 159Javan warty pig : McMahon, Sara (2002). "Sus verrucosus " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 26, 2021 . Wild boar : "Eurasian Wild Pig (Sus scrofa )" . IUCN Wild Pig Specialist Group . International Union for Conservation of Nature . Archived from the original on September 10, 2016. Retrieved March 27, 2021 .^ a b Sus habitats and diets:
Palawan bearded pig : Meijaard, E.; Widmann, P. (2017). "Sus ahoenobarbus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T21177A44140029. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T21177A44140029.en Bornean bearded pig : Luskin, M.; Ke, A.; Meijaard, E.; Gumal, M.; Kawanishi, K. (2018) [errata version of 2017 assessment]. "Sus barbatus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T41772A44141317. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T41772A44141317.en Visayan warty pig : Meijaard, E.; Oliver, W. R. T.; Leus, K. (2017). "Sus cebifrons " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T21175A44139575. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T21175A44139575.en Celebes warty pig : Burton, J.; Mustari, A.; Rejeki, I. (2020). "Sus celebensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T41773A44141588. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T41773A44141588.en Oliver's warty pig : Schütz, E. (2016). "Sus oliveri " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T136340A44142784. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T136340A44142784.en Philippine warty pig : Heaney, L.; Meijaard, E. (2017). "Sus philippensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T21176A44139795. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T21176A44139795.en Javan warty pig : Semiadi, G.; Rademaker, M.; Meijaard, E. (2016). "Sus verrucosus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T21174A44139369. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T21174A44139369.en Wild boar : Keuling, O.; Leus, K. (2019). "Sus scrofa " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019 : e.T41775A44141833. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T41775A44141833.en ^ "Catagonus Wagneri – Chacoan Peccary" . Vertebrate Collection . University of Wisconsin–Stevens Point . Retrieved March 27, 2021 .^ a b Altrichter, M.; Taber, A.; Noss, A.; Maffei, L.; Campos, J. (2015). "Catagonus wagneri " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T4015A72587993. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T4015A72587993.en ^ ^ a b Gongora, J.; Reyna-Hurtado, R.; Beck, H.; Taber, A.; Altrichter, M.; Keuroghlian, A. (2011). "Pecari tajacu " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2011 : e.T41777A10562361. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2011-2.RLTS.T41777A10562361.en ^ Csomos, Rebecca Ann (2001). "Tayassu pecari " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved March 26, 2021 . ^ a b Keuroghlian, A.; Desbiez, A.; Reyna-Hurtado, R.; Altrichter, M.; Beck, H.; Taber, A.; Fragoso, J. M. V. (2013). "Tayassu pecari " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2013 : e.T41778A44051115. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2013-1.RLTS.T41778A44051115.en ^ a b c Burnie , p. 222^ Lama sizes:
^ a b Lama habitats and diets:
Llama : Portman, Charles (2004). "Lama glama " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved September 23, 2021 . Guanaco : Baldi, R. B.; Acebes, P.; Cuéllar, E.; Funes, M.; Hoces, D.; Puig, S.; Franklin, W. L. (2016). "Lama guanicoe " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T11186A18540211. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T11186A18540211.en Alpaca : Castillo-Ruiz, Alexandra (2007). "Lama pacos " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved September 23, 2021 . Vicuña : Acebes, P.; Wheeler, J.; Baldo, J.; Tuppia, P.; Lichtenstein, G.; Hoces, D.; Franklin, W. L. (2019) [errata version of 2018 assessment]. "Vicugna vicugna " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T22956A145360542. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22956A145360542.en ^ Burnie , p. 247^ a b Cooke, J. G.; Reeves, R. (2018). "Balaena mysticetus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T2467A50347659. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T2467A50347659.en ^ Perrin; Wursig; Thewissen , pp. 962–969^ a b Eubalaena habitats and diets:
^ a b Carwardine , pp. 57–75^ Balaenoptera habitats and diets:
Common minke whale : Cooke, J. G. (2018). "Balaenoptera acutorostrata " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T2474A50348265. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T2474A50348265.en Antarctic minke whale : Cooke, J. G.; Zerbini, A. N.; Taylor, B. L. (2018). "Balaenoptera bonaerensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T2480A50350661. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T2480A50350661.en Sei whale : Cooke, J. G. (2018). "Balaenoptera borealis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T2475A130482064. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T2475A130482064.en Eden's whale , Bryde's whale , Rice's whale : Cooke, J. G.; Brownell Jr., R. L. (2018). "Balaenoptera edeni " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T2476A50349178. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T2476A50349178.en Blue whale : Cooke, J. G. (2019) [errata version of 2018 assessment]. "Balaenoptera musculus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T2477A156923585. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T2477A156923585.en Fin whale : Cooke, J. G. (2018). "Balaenoptera physalus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T2478A50349982. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T2478A50349982.en Omura's whale : Cooke, J. G.; Brownell Jr., R. L. (2019) [amended version of 2018 assessment]. "Balaenoptera omurai " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019 : e.T136623A144790120. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T136623A144790120.en ^ Carwardine , p. 51^ a b Cooke, J. G. (2018). "Eschrichtius robustus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T8097A50353881. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T8097A50353881.en ^ Carwardine , p. 77^ a b Cooke, J. G. (2018). "Megaptera novaeangliae " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T13006A50362794. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T13006A50362794.en ^ Carwardine , p. 49^ a b Cooke, J. G. (2018). "Caperea marginata " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T3778A50351626. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T3778A50351626.en ^ Carwardine , p. 165^ a b Braulik, G.; Jefferson, T. A.; Bearzi, G. (2021) [amended version of 2021 assessment]. "Delphinus delphis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2021 : e.T134817215A199893039. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-2.RLTS.T134817215A199893039.en ^ Carwardine , p. 209^ a b Kiszka, J.; Braulik, G. (2018). "Lagenodelphis hosei " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T11140A50360282. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T11140A50360282.en ^ Carwardine , p. 173^ a b Sotalia habitats and diets:
^ Carwardine , pp. 175–177^ a b Sousa habitats and diets:
Indo-Pacific humpback dolphin : Jefferson, T. A.; Smith, B. D.; Braulik, G. T.; Perrin, W. (2018) [errata version of 2017 assessment]. "Sousa chinensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T82031425A123794774. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T82031425A50372332.en Indian Ocean humpback dolphin : Braulik, G. T.; Findlay, K.; Cerchio, S.; Baldwin, R.; Perrin, W. (2017). "Sousa plumbea " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T82031633A82031644. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T82031633A82031644.en Australian humpback dolphin : Parra, G.; Cagnazzi, D.; Perrin, W.; Braulik, G. T. (2017). "Sousa sahulensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T82031667A82031671. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T82031667A82031671.en Atlantic humpback dolphin : Collins, T.; Braulik, G. T.; Perrin, W. (2018) [errata version of 2017 assessment]. "Sousa teuszii " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T20425A123792572. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T20425A50372734.en ^ Carwardine , pp. 179–187^ a b Stenella habitats and diets:
^ Carwardine , p. 193^ a b Tursiops habitats and diets:
^ Carwardine , pp. 199–205^ a b Cephalorhynchus habitats and diets:
Commerson's dolphin : Crespo, E.; Olavarria, C.; Dellabianca, N.; Iñíguez, M.; Ridoux, V.; Reeves, R. (2018) [errata version of 2017 assessment]. "Cephalorhynchus commersonii " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T4159A128963283. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T4159A128963283.en Chilean dolphin : Heinrich, S.; Reeves, R. (2017). "Cephalorhynchus eutropia " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T4160A50351955. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T4160A50351955.en Heaviside's dolphin : Elwen, S.; Gopal, K. (2018). "Cephalorhynchus heavisidii " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T4161A50352086. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T4161A50352086.en Hector's dolphin : Reeves, R. R.; Dawson, S. M.; Jefferson, T. A.; Karczmarski, L.; Laidre, K.; O’Corry-Crowe, G.; Rojas-Bracho, L.; Secchi, E. R.; Slooten, E.; Smith, B. D.; Wang, J. Y.; Zhou, K. (2013). "Cephalorhynchus hectori " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2013 : e.T4162A44199757. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2013-1.RLTS.T4162A44199757.en ^ Carwardine , pp. 169–171^ a b Lissodelphis habitats and diets:
^ Carwardine , pp. 147^ a b Braulik, G. (2018). "Feresa attenuata " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T8551A50354433. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T8551A50354433.en ^ Carwardine , pp. 149–151^ a b Globicephala habitats and diets:
^ Carwardine , p. 207^ a b Kiszka, J.; Braulik, G. (2018). "Grampus griseus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T9461A50356660. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T9461A50356660.en ^ a b Carwardine , p. 223^ Orcaella habitats:
^ Carwardine , p. 157^ a b Kiszka, J.; Brownell Jr., R. L.; Beasley, I. (2019). "Peponocephala electra " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019 : e.T16564A50369125. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T16564A50369125.en ^ Carwardine , p. 159^ a b Baird, R. W. (2019) [errata version of 2018 assessment]. "Pseudorca crassidens " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T18596A145357488. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T18596A145357488.en ^ Carwardine , p. 191^ a b Kiszka, J.; Baird, R.; Braulik, G. (2020) [errata version of 2019 assessment]. "Steno bredanensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019 : e.T20738A178929751. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T20738A178929751.en ^ Carwardine , p. 153^ a b Reeves, R.; Pitman, R. L.; Ford, J. K. B. (2017). "Orcinus orca " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T15421A50368125. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T15421A50368125.en ^ Carwardine , pp. 211–221^ a b Lagenorhynchus habitats and diets:
^ a b Carwardine , p. 227^ da Silva, V.; Trujillo, F.; Martin, A.; Zerbini, A. N.; Crespo, E.; Aliaga-Rossel, E.; Reeves, R. (2018). "Inia geoffrensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T10831A50358152. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T10831A50358152.en ^ Carwardine , pp. 83–85^ a b Kogia habitats and diets:
^ Carwardine , p. 229^ a b Smith, B. D.; Wang, D.; Braulik, G. T.; Reeves, R.; Zhou, K.; Barlow, J.; Pitman, R. L. (2017). "Lipotes vexillifer " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T12119A50362206. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T12119A50362206.en ^ Carwardine , p. 93^ a b Lowry, L.; Reeves, R.; Laidre, K. (2017). "Delphinapterus leucas " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T6335A50352346. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T6335A50352346.en ^ Carwardine , p. 97^ a b Lowry, L.; Laidre, K.; Reeves, R. (2017). "Monodon monoceros " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T13704A50367651. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T13704A50367651.en ^ Carwardine , p. 239^ a b Neophocaena habitats and diets:
^ Carwardine , pp. 241–247^ a b Phocoena habitats and diets:
Spectacled porpoise : Dellabianca, N.; Pitman, R. L.; Braulik, G. (2018). "Phocoena dioptrica " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T41715A50381544. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T41715A50381544.en Harbour porpoise : Braulik, G.; Minton, G.; Amano, M.; Bjørge, A. (2020). "Phocoena phocoena " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T17027A50369903. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T17027A50369903.en Vaquita : Rojas-Bracho, L.; Taylor, B. L. (2017). "Phocoena sinus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T17028A50370296. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T17028A50370296.en Burmeister's porpoise : Félix, F.; Alfaro, J.; Reyes, J.; Mangel, J.; Dellabianca, N.; Heinrich, S.; Crespo, E. (2018). "Phocoena spinipinnis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T17029A50370481. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T17029A50370481.en ^ Carwardine , p. 249^ a b Jefferson, T. A.; Braulik, G. (2018). "Phocoenoides dalli " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T17032A50370912. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T17032A50370912.en ^ Carwardine , p. 87^ a b Taylor, B. L.; Baird, R.; Barlow, J.; Dawson, S. M.; Ford, J.; Mead, J. G.; Notarbartolo di Sciara, G.; Wade, P.; Pitman, R. L. (2019) [amended version of 2008 assessment]. "Physeter macrocephalus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019 : e.T41755A160983555. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T41755A160983555.en ^ a b Carwardine , p. 231^ Platanista habitats and diets:
^ Carwardine , p. 235^ a b Zerbini, A. N.; Secchi, E.; Crespo, E.; Danilewicz, D.; Reeves, R. (2018) [errata version of 2017 assessment]. "Pontoporia blainvillei " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T17978A123792204. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T17978A50371075.en ^ Carwardine , pp. 105–107^ a b Berardius habitats and diets:
^ Carwardine , pp. 109–111^ a b Hyperoodon habitats and diets:
Northern bottlenose whale : Whitehead, H.; Reeves, R.; Feyrer, L.; Brownell Jr., R. L. (2021). "Hyperoodon ampullatus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2021 : e.T10707A50357742. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-1.RLTS.T10707A50357742.en Southern bottlenose whale : Taylor, B. L.; Baird, R.; Barlow, J.; Dawson, S. M.; Ford, J.; Mead, J. G.; Notarbartolo di Sciara, G.; Wade, P.; Pitman, R. L. (2008). "Hyperoodon planifrons " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2008 : e.T10708A3208830. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T10708A3208830.en ^ Carwardine , p. 135^ a b Pitman, R. L.; Brownell Jr., R. L. (2020). "Indopacetus pacificus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T40635A50380449. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T40635A50380449.en ^ Carwardine , pp. 113–139^ a b Mesoplodon habitats and diets:
Sowerby's beaked whale : Pitman, R. L.; Brownell Jr., R. L. (2020). "Mesoplodon bidens " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T13241A50363686. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T13241A50363686.en Andrews' beaked whale : Pitman, R. L.; Brownell Jr., R. L. (2020). "Mesoplodon bowdoini " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T13242A50363892. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T13242A50363892.en Hubbs' beaked whale : Pitman, R. L.; Brownell Jr., R. L. (2020). "Mesoplodon carlhubbsi " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T13243A50364109. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T13243A50364109.en Blainville's beaked whale : Pitman, R. L.; Brownell Jr., R. L. (2020). "Mesoplodon densirostris " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T13244A50364253. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T13244A50364253.en Gervais' beaked whale : Pitman, R. L.; Brownell Jr., R. L. (2020). "Mesoplodon europaeus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T13245A50365198. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T13245A50365198.en Ginkgo-toothed beaked whale : Pitman, R. L.; Brownell Jr., R. L. (2020). "Mesoplodon ginkgodens " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T127827012A127827154. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T127827012A127827154.en Gray's beaked whale : Pitman, R. L.; Taylor, B. L. (2020). "Mesoplodon grayi " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T13247A50366236. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T13247A50366236.en Hector's beaked whale : Pitman, R. L.; Brownell Jr., R. L. (2020). "Mesoplodon hectori " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T13248A50366525. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T13248A50366525.en Deraniyagala's beaked whale : Pitman, R. L.; Brownell Jr., R. L. (2020). "Mesoplodon hotaula " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T127826787A182525770. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T127826787A182525770.en Strap-toothed whale : Pitman, R. L.; Brownell Jr., R. L. (2020). "Mesoplodon layardii " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T13249A50366790. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T13249A50366790.en True's beaked whale : Pitman, R. L.; Brownell Jr., R. L. (2020). "Mesoplodon mirus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T13250A50367095. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T13250A50367095.en Perrin's beaked whale : Pitman, R. L.; Taylor, B. L.; Barlow, J.; Cooke, J. G. (2020). "Mesoplodon perrini " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T41759A50383813. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T41759A50383813.en Pygmy beaked whale : Pitman, R. L.; Taylor, B. L. (2020). "Mesoplodon peruvianus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T13251A50367335. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T13251A50367335.en Stejneger's beaked whale : Pitman, R. L.; Brownell Jr., R. L. (2020). "Mesoplodon stejnegeri " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T13252A50367496. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T13252A50367496.en Spade-toothed whale : Pitman, R. L.; Taylor, B. L. (2020). "Mesoplodon traversii " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T41760A50383956. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T41760A50383956.en ^ Carwardine , p. 141^ a b Braulik, G. (2018). "Tasmacetus shepherdi " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T21500A50377701. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T21500A50377701.en ^ Carwardine , p. 143^ a b Baird, R. W.; Brownell Jr., R. L.; Taylor, B. L. (2020). "Ziphius cavirostris " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T23211A50379111. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T23211A50379111.en ^ Fredrickson, Daniel (2009). "Hexaprotodon liberiensis " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved October 8, 2021 . ^ a b Ransom, C; Robinson, P. T.; Collen, B. (2015). "Choeropsis liberiensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015 : e.T10032A18567171. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T10032A18567171.en ^ Mason, Kassandra (2013). "Hippopotamus amphibius " . Animal Diversity Web University of Michigan . Retrieved October 8, 2021 . ^ a b Lewison, R.; Pluháček, J. (2017). "Hippopotamus amphibius " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T10103A18567364. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T10103A18567364.en
Sources
Armstrong, David M.; Fitzgerald, James P.; Meaney, Carron A. (2011). Mammals of Colorado (2nd ed.). University Press of Colorado . ISBN 978-1-60732-048-7 Burnie, David (2017). Animal: The Definitive Visual Guide . DK . ISBN 978-1-4654-7086-7 Burt, William Henry (1957). Mammals of the Great Lakes Region . University of Michigan Press . ISBN 978-0-472-06183-9 Carwardine, Mark (2002). Whales, Dophins, and Porpoises . DK . ISBN 978-0-7894-8990-6 Castelló, José R. (2016). Bovids of the World: Antelopes, Gazelles, Cattle, Goats, Sheep, and Relatives . Princeton University Press . ISBN 978-0-691-16717-6 Eisenberg, John F.; Redford, Kent H.; Reid, Fiona; Bonner, Sigrid James (1989). Mammals of the Neotropics . Vol. 2: The Southern Cone: Chile, Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay. University of Chicago Press . ISBN 978-0-226-19542-1 Eisenberg, John F.; Redford, Kent H.; Reid, Fiona; Bonner, Sigrid James (1989). Mammals of the Neotropics . Vol. 3: Ecuador, Bolivia, Brazil. University of Chicago Press . ISBN 978-0-226-19542-1 Emanoil, Mary, ed. (1994). Encyclopedia of Endangered Species . Vol. 1. Gale Research . ISBN 978-0-8103-8857-4 Francis, Charles (2019). Field Guide to the Mammals of South-East Asia (2nd ed.). Bloomsbury Publishing . ISBN 978-1-4729-3499-4 Geist, Valerius (1998). Deer of the World: Their Evolution, Behaviour, and Ecology . Stackpole Books . ISBN 978-0-8117-0496-0 Harris, Tim (2018). The Encyclopedia of Animals . Chartwell Books . ISBN 978-0-7858-3646-9 Kingdon, Jonathan (2013). The Kingdon Field Guide to African Mammals (1st ed.). Bloomsbury Publishing . ISBN 978-1-4081-7481-4 Kingdon, Jonathan (2020). The Kingdon Pocket Guide to African Mammals (2nd ed.). Bloomsbury Publishing . ISBN 978-1-4729-8320-6 Long, John L. (2003). Introduced Mammals of the World: Their History, Distribution and Influence . CABI Publishing . ISBN 978-0-643-06714-1 Macdonald, David W. (1984). The Encyclopedia of Mammals . Equinox. ISBN 978-0-87196-871-5 Melletti, Mario; Meijaard, Erik, eds. (2017). Ecology, Conservation and Management of Wild Pigs and Peccaries . Cambridge University Press . ISBN 978-1-316-95340-2 IUCN/SSC Hippo Specialist Group; IUCN/SSC Pigs and Peccaries Specialist Group (1993). Oliver, William L. R. (ed.). Pigs, Peccaries, and Hippos: Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan . International Union for Conservation of Nature . ISBN 978-2-8317-0141-7 Perrin, W. F.; Wursig, B.; Thewissen, J. G. M., eds. (2008). Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals . Elsevier Science . ISBN 978-0-12-373553-9 Reid, Fiona (2009). A Field Guide to the Mammals of Central America and Southeast Mexico (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press . ISBN 978-0-19-534322-9 Saha, Goutam Kumar; Mazumdar, Subhendu (2008). Threatened Mammals of India: Ecology and Management . Daya Publishing House. ISBN 978-81-7035-546-5 Schaller, George B. (2009). The Deer and the Tiger: Study of Wild Life in India . University of Chicago Press . ISBN 978-0-226-73657-0 Smith, Andrew T.; Xie, Yan, eds. (2013). Mammals of China . Princeton University Press . ISBN 978-1-4008-4688-7 Wijeyeratne, Gehan de Silva (2016). Mammals of Sri Lanka . Bloomsbury Publishing . ISBN 978-1-4729-3289-1 Wilson, Don E.; Mittermeier, Russell A., eds. (2011). Handbook of the Mammals of the World . Vol. 2 (Hoofed Mammals). Lynx Edicions . ISBN 978-84-96553-77-4 Grubb, Peter (2005). Wilson, Don E.; Reeder, DeeAnn M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World Johns Hopkins University Press . ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0