List of genetic disorders
The following is a list of genetic disorders and if known, type of mutation and for the chromosome involved. Although the parlance "disease-causing gene" is common, it is the occurrence of an abnormality in the parents that causes the impairment to develop within the child. There are over 6,000 known genetic disorders in humans .
Most common
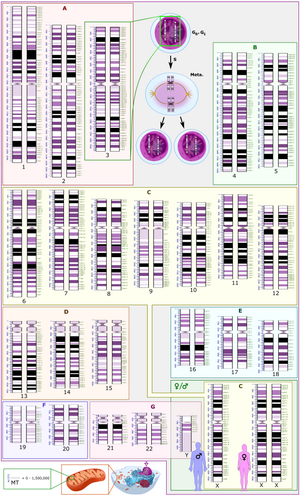
Human karyotype with annotated bands and sub-bands as used for the nomenclature of chromosome abnormalities . It shows dark and white regions as seen on G banding . Each row is vertically aligned at centromere level. It shows 22 homologous autosomal chromosome pairs, both the female (XX) and male (XY) versions of the two sex chromosomes , as well as the mitochondrial genome (at bottom left). Duchenne muscular dystrophy Craniosynostosis can be found in several disorders, like Carpenter Syndrome
Full genetic disorders list
Disorder
Chromosome or gene
Type
Reference
Prevalence
1p36 deletion syndrome
1
D
1:7,500
1q21.1 deletion syndrome
1q21.1
D
2q37 deletion syndrome
2q37
D
5q deletion syndrome
5q
D
5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate synthetase deficiency
MTHFS
[ 2]
7p22.1 microduplication syndrome
7p22.1
17q12 microdeletion syndrome
17q12
[ 3] [ 4] 1:14,000-62,500
17q12 microduplication syndrome
17q12
[ 5]
18p deletion syndrome
18p
D
1:50,000
21-hydroxylase deficiency
6p21.3
recessive
1:15,000
Alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency
14q32
co-dominant ,
1:2,500-5,000
AAA syndrome (achalasia–addisonianism–alacrima syndrome)
AAAS
recessive
[ 6] 1:1,000,000
Aarskog–Scott syndrome
FGD1
X-linked recessive
1:25,000
ABCD syndrome
EDNRB
recessive
1:18,000-20,000
Absence deformity of leg-cataract syndrome
Aceruloplasminemia
CP (3p26.3)
recessive
1:2,000,000
Acheiropodia
LMBR1
recessive
Achondrogenesis type II
COL2A1 (12q13.11)
dominant
1:40,000-60,000
Achondroplasia FGFR3 (4p16.3)dominant
1:27,500
Acute intermittent porphyria HMBS dominant and recessive forms
1:500-50,000
Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency ADSL
recessive
Adrenoleukodystrophy ABCD1 (X)recessive
1:17,000
Alagille syndrome JAG1 , NOTCH2
dominant
[ 7] 1:30,000-50,000
ADULT syndrome
TP63
dominant
Aicardi–Goutières syndrome TREX1 , RNASEH2A , RNASEH2B , RNASEH2C , SAMHD1 , ADAR , IFIH1
1:19,500,000
Albinism
1:18,000-20,000
Alexander disease GFAP
1:15,600,000
Alfi's syndrome
9p
monosomy
1:50,000
Alkaptonuria HGD
1:250,000-1,000,000
Alport syndrome 10q26.13 COL 4A3COL4A4 COL4A5
1:5,000-10,000
Alternating hemiplegia of childhood
ATP1A3
1:1,000,000
Aortic arch anomaly - peculiar facies - intellectual disability
dominant
Amish lethal microcephaly
SLC25A19
recessive
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis – Frontotemporal dementia C9orf72 , SOD1 , FUS , TARDBP , CHCHD10 , MAPT
1:100,000
Angel-shaped phalango-epiphyseal dysplasia
GDF5
dominant
Alström syndrome ALMS1
1:8,600,000
Alzheimer's disease PSEN1 , PSEN2 , APP , APOEε4
1:177
Amelogenesis imperfecta
1:14,000
Aminolevulinic acid dehydratase deficiency porphyria
ALAD
1:780,000,000
Androgen insensitivity syndrome
1:20,000-50,000
Angelman syndrome UBE3A
1:12,000-20,000
Aphalangy-syndactyly-microcephaly syndrome
dominant
Apert syndrome
FGFR2
1:65,000-80,000
Arthrogryposis–renal dysfunction–cholestasis syndrome VPS33B
1:78,000,000
Ataxia telangiectasia ATM
1:40,000-1,000,000
Axenfeld syndrome
PITX2 , FOXO1 A, FOXC1 , PAX6
1:200,000
Bainbridge–Ropers syndrome
ASXL3
de novo
Beare–Stevenson cutis gyrata syndrome 10q26, FGFR2
1:390,000,000
Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome
IGF-2 , CDKN1C , H19 , KCNQ1OT1
1:15,000
Benjamin syndrome
1:20,000,000
biotinidase deficiency BTD
1:110,000,000
Björnstad syndrome
BCS1L
1:260,000,000
Blepharophimosis intellectual disability syndromes
Bloom syndrome 15q26.1
1:480,000
Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome 17 FLCN
1:19,500,000
Brody myopathy
ATP2A1
1:10,000,000
Brunner syndrome
MAOA
1:500,000,000
CADASIL syndrome NOTCH3 P
1:156,000,000
Cat eye syndrome
22
1:74,000
CATSHL syndrome
FGFR3
dominant/recessive
[ 8]
CRASIL syndrome
HTRA1
1:156,000,000
Chronic granulomatous disorder
1:200,000
Campomelic dysplasia X 17q24.3–q25.1
C
1:40,000-200,000
Camptodactyly-taurinuria syndrome
dominant
Canavan disease ASPA
1:6,400-13,500
Carpenter syndrome
RAB23
1:1,000,000
CDKL5 deficiency disorder
CDKL5
[ 9] 1:40,000-60,000[ 9]
Cerebral dysgenesis–neuropathy–ichthyosis–keratoderma syndrome (CEDNIK)SNAP29
<1:1,000,000[ 10]
Cleft palate short stature vertebral anomalies syndrome
Combined malonic and methylmalonic aciduria (CMAMMA)
ACSF3
recessive
[ 11] [ 12] 1:30,000[ 11]
Combined malonic and methylmalonic aciduria (CMAMMA)
MLYCD
recessive
Congenital muscular dystrophy-infantile cataract-hypogonadism syndrome
recessive
Cystic fibrosis CFTR (7q31.2)D or S
[ 13] 1:100,000
Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease PMP22 , MFN2
1:2,500
CHARGE syndrome CHD7
1:8,500-10,000
Chédiak–Higashi syndrome LYST recessive
1:39,000,000
Chondrodysplasia, Grebe type
GDF5
autosomal recessive
[ 14]
Cleidocranial dysostosis
RUNX2
1:7,800
Cockayne syndrome ERCC6 , ERCC8
1:2,600-3,900
Coffin–Lowry syndrome X RPS6KA3
1:40,000-50,000
Cohen syndrome COH1
1:7,800,000
Collagenopathy, types II and XI COL11A1 , COL11A2 , COL2A1
Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis (CIPA)
NTRK1
Congenital muscular dystrophy
multiple
dominant or recessive
[ 15]
Corneal dystrophy-perceptive deafness syndrome
SLC4A11
autosomal recessive
[ 16]
Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CDLS)
HDAC8 , SMC1A , NIPBL , SMA3 , RAD21
1:10,000-30,000
Cowden syndrome PTEN
1:200,000
CPO deficiency (coproporphyria )
CPOX
Cranio-lenticulo-sutural dysplasia 14q13–q21
Cri du chat 5p15.2
D
[ 17] [ 18] 1:37,000-50,000
Crohn's disease 16q12
P
Crouzon syndrome FGFR2 , FGFR3
1.6:100,000
Crouzonodermoskeletal syndrome (Crouzon syndrome with acanthosis nigricans)FGFR3
1:1,000,000
Currarino syndrome
HLXB9
dominant
1:100,000
Darier's disease
ATP2A2
1:30,000-100,000
Dent's disease (Genetic hypercalciuria)Xp11.22 CLCN5 , OCRL
Denys–Drash syndrome
WT1
De Grouchy syndrome 18q
D
Dolichonychia
Down syndrome
21
C
1:1,000-1,100U.S. )
DiGeorge syndrome 22q11.2
D
1:4,000
Distal hereditary motor neuropathies , multiple typesHSPB8 , HSPB1 , HSPB3 , GARS , REEP1 , IGHMBP2 , SLC5A7 , DCTN1 , TRPV4 , SIGMAR1
Distal muscular dystrophy
Dysferlin , TIA1 , GNE (gene) , MYH7 , Titin , MYOT , MATR3 , unknown
Dominant or recessive
[ 19]
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Dystrophin
X-linked recessive
[ 20]
Dravet syndrome SCN1A , SCN2A
1:20,000-40,000
Ectrodactyly-polydactyly syndrome
Edwards syndrome
18
trisomy
1:5,000
Ehlers–Danlos syndrome COL1A1 , COL1A2 , COL3A1 , COL5A1 , COL5A2 , TNXB , ADAMTS2 , PLOD1 , B4GALT7 , DSE
dominant
1:5,000
Emanuel syndrome
11, 22
partial trisomy
Emery–Dreifuss syndrome
EMD , LMNA , SYNE1 , SYNE2 , FHL1 , TMEM43
Epidermolysis bullosa
KRT5 , KRT14 , DSP , PKP1 , JUP , PLEC1 , DST , EXPH5 , TGM5 , LAMA3 , LAMB3 , LAMC2 , COL17A1 , ITGA6 , ITGA4 , ITGA3 , COL7A1 , FERMT1
dominant or recessive
[ 21] [ 22] 11.08:1,000,000
Erythropoietic protoporphyria
FECH
1:75,000-200,000
Fanconi anemia (FA)
FANCA , FANCB , FANCC , FANCD1 , FANCD2 , FANCE , FANCF , FANCG , FANCI , FANCJ , FANCL , FANCM , FANCN , FANCP , FANCS , RAD51C , XPF
1:130,000
Fabry disease GLA (Xq22.1)P
1:117,000-476,000
Factor V Leiden thrombophilia
Fatal familial insomnia
PRNP
dominant
Familial adenomatous polyposis APC
1:10,000-15,000
Familial dysautonomia IKBKAP
Familial Creutzfeld–Jakob disease
PRNP
dominant
Familial episodic pain syndrome
TRPA1 , SCN10A , SCN11A
dominant
Familial thoracic aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection
FOXE3 , SMAD2 , LOX , MAT2A , ELN , HEY2 , TGFB3 , TGFBR1 , TGFBR2 , FBN1 , ACTA2 , MYLK , SMAD3 , PRKG1 , MFAP5 , TGFB2 , SMAD4 , MYH11
dominant
Feingold syndrome
MYCN
FG syndrome MED12
FBXW7 neurodevelopmental syndrome
FBXW7
Fibular aplasia-ectrodactyly syndrome
dominant
Fine-Lubinsky syndrome
MAF
recessive
Fragile X syndrome
FMR1
T
1:4,000 males
1:8,000 females
Friedreich's ataxia FXN T
1:50,000 (U.S.)
G6PD deficiency X-linked recessive
[ 23]
Galactosemia GALT , GALK1 , GALE
Gaucher disease GBA (1)
1:20,000
Gerstmann–Sträussler–Scheinker syndrome
PRNP
dominant
Gillespie syndrome
PAX6
Glutaric aciduria, type I and type 2
GCDH , ETFA , ETFB , ETFDH
recessive
GRACILE syndrome
BCS1L
GRIN2B-related neurodevelopmental disorder
GRIN2B
Griscelli syndrome MYO5A , RAB27A , MLPH
Gustavson syndrome
Hailey–Hailey disease
ATP2C1 (3)
Harlequin type ichthyosis ABCA12
Hemochromatosis type 1 HFE (chromosome 6)recessive
.
1:200 (Northern Europe ), 1:300 (Northern America )
Hemochromatosis type 2A HJV (or HFE2A) (chromosome 1)recessive
Hemochromatosis type 2B HAMP (or HFE2B) (chromosome 19)recessive
Haemochromatosis type 3 TFR2 (or HFE3) (chromosome 7)recessive
Hemochromatosis type 4 SLC40A1 (or HFE4) (chromosome 2)dominant
Hemochromatosis type 5FTH1 (chromosome 11)dominant
Hemophilia FVIII
1:7,500 males (hemophilia A)
1:40,000 males (hemophilia B)
Hepatoerythropoietic porphyria UROD
Hereditary coproporphyria 3q12
P
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler–Weber–Rendu syndrome)ENG , ACVRL1 , MADH4
1:5,000 [ 24]
Hereditary inclusion body myopathy GNE , MYHC2A , VCP , HNRPA2B1 , HNRNPA1
Hereditary multiple exostoses EXT1 , EXT2 , EXT3
1:50,000
Hereditary spastic paraplegia (infantile-onset ascending hereditary spastic paralysis)AP4M1 , AP4S1 , AP4B1 , AP4E1
autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive or X-linked recessive
2-6:100,000
Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome HPS1 , HPS3 , HPS4 , HPS5 , HPS6 , HPS7 , AP3B1
1:500,000
Hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies (HNPP)PMP22
Heterotaxy
NODAL , NKX2-5 , ZIC3 , CCDC11 , CFC1 , SESN1
Homocystinuria CBS (gene)
recessive
[ 25]
Huntington's disease
chromosome 4 HTT gene
autosomal dominant
1:10,000 in US
Hunter syndrome
IDS
1:100,000-150,000 males
Hurler syndrome
IDUA
1:100,000
Hutchinson–Gilford progeria syndrome LMNA
1:18,000,000
Hyperlysinemia
AASS
recessive
Hyperoxaluria, primary AGXT , GRHPR , DHDPSL
Hyperphenylalaninemia 12q
Hypoalphalipoproteinemia (Tangier disease)
ABCA1
Hypochondrogenesis COL2A1
Hypochondroplasia
FGFR3 (4p16.3)
Immunodeficiency–centromeric instability–facial anomalies syndrome (ICF syndrome)20q11.2
Incontinentia pigmenti IKBKG (Xq28)P
Infantile cerebral and cerebellar atrophy with postnatal progressive microcephaly
MED17
recessive
Ischiopatellar dysplasia TBX4 dominant
Isodicentric 15 15q11–14
Inv dup
1:30,000 [ 26]
PRICKLE1-related progressive myoclonus epilepsy with ataxia
PRICKLE1
dominant or recessive
Jackson–Weiss syndrome FGFR2
Jacobsen syndrome
11
1:100,000
Joubert syndrome INPP5E , TMEM216 , AHI1 , NPHP1 , CEP290 , TMEM67 , RPGRIP1L , ARL13B , CC2D2A , OFD1 , TMEM138 , TCTN3 , ZNF423 , AMRC9
Juvenile-onset dystonia
ACTB , IMPDH2
dominant
Juvenile primary lateral sclerosis (JPLS)ALS2
Keloid disorder
KIF1A-Associated neurological disorder
KIF1A (2q37.3)
Dominant negative
Kleefstra syndrome
9q34
D
Kniest dysplasia COL2A1
1:1,000,000
Kosaki overgrowth syndrome PDGFRB
Krabbe disease GALC
1:100,000
Kufor–Rakeb syndrome
ATP13A2
LCAT deficiency
LCAT
Lesch–Nyhan syndrome HPRT (X)
1:380,000
Li–Fraumeni syndrome TP53
Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy
Multiple
dominant or recessive
[ 27] [ 28] 1:14,500-123,000
Lynch syndrome MSH2 , MLH1 , MSH6 , PMS2 , PMS1 , TGFBR2 , MLH3
1:279
lipoprotein lipase deficiency recessive
1:1,000,000
Malignant hyperthermia
RYR1 (19q13.2)
dominant
1:5,000-100,000
Maple syrup urine disease
BCKDHA , BCKDHB , DBT , DLD
recessive
Marfan syndrome 15q
dominant
1:5,000-10,000
Maroteaux–Lamy syndrome
ARSB
recessive
1:43,261-1,505,160
McCune–Albright syndrome 20 q13.2–13.3
1:100,000-1,000,000
McLeod syndrome XK (X)
0.5-1:100,000
MEDNIK syndrome AP1S1 D
[ 29] [ 30]
Mediterranean fever, familial MEFV
Menkes disease ATP7A (Xq21.1)
1:100,000-250,000
Methemoglobinemia
Methylmalonic acidemia MMAA , MMAB , MMACHC , MMADHC , LMBRD1 , MUT
recessive
1:48,000
Micro syndrome RAB3GAP (2q21.3)
Microcephaly ASPM (1q31)P
Miller-Dieker syndrome
17p13.3
D
1:100,000
Morquio syndrome GALNS , GLB1
1:200,000-300,000
Mowat–Wilson syndrome ZEB2 (2)
Muenke syndrome FGFR3
1:30,000
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (Wermer's syndrome)MEN1 dominant
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2
RET
dominant
Muscular dystrophy multiple
AR, AD, X-linked
Muscular dystrophy, Duchenne and Becker type
Myostatin-related muscle hypertrophy MSTN
Myotonic dystrophy DMPK , CNBP dominant or T
1:8,000
Natowicz syndrome
HYAL1
<1:1,000,000
Neurofibromatosis type I 17q11.2
Neurofibromatosis type II NF2 (22q12.2)
Niemann–Pick disease SMPD1 , NPA , NPB , NPC1 , NPC2
1:250,000 (types A and B)
1:150,000 (type C)
Nonketotic hyperglycinemia GLDC , AMT , GCSH
recessive
1:60,000
Nonsyndromic deafness
Noonan syndrome PTPN11 , KRAS , SOS1 , RAF1 , NRAS , HRAS , BRAF , SHOC2 , MAP2K1 , MAP2K2 , CBL dominant
1:1,000
Norman–Roberts syndrome
RELN
recessive
Ogden syndrome
X
P
Omenn syndrome
RAG1 , RAG2
recessive
Osteogenesis imperfecta COL1A1 , COL1A2 , IFITM5
dominant
1:15,000-20,000
Ostravik-Lindemann-Solberg syndrome
2p15
autosomal recessive
[ 31]
Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration PANK2 (20p13–p12.3)recessive
1-3:1,000,000
Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13)13
trisomy
PCC deficiency (propionic acidemia)PC recessive
1:250,000
Porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT)UROD dominant
1:10,000
Pendred syndrome PDS (7)
recessive
Peutz–Jeghers syndrome STK11
dominant
1:25,000-300,000
Pfeiffer syndrome FGFR1 , FGFR2 dominant
1:100,000
Phelan-McDermid syndrome
22q13
D
Phenylketonuria PAH recessive
1:12,000
Pipecolic acidemia
AASDHPPT
recessive
Pitt–Hopkins syndrome
TCF4 (18)
dominant, de novo
1:11,000-41,000
Polycystic kidney disease
PKD1 (16) or PKD2 (4)
P
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Porphyria
1-100:50,000
Prader–Willi syndrome 15
paternal imprinting
1:10,000-30,000
Primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD)DNAI1 , DNAH5 , TXNDC3 , DNAH11 , DNAI2 , KTU , RSPH4A , RSPH9 , LRRC50
recessive
1:32,000
Primary pulmonary hypertension
Protein C deficiency PROC
dominant
[ 32] 1:20,000
Protein S deficiency PROS1
dominant
Proximal 18q deletion syndrome
18q
D
Pseudo-Gaucher disease
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum ABCC6
recessive
1:25,000
Retinitis pigmentosa
RP1, RP2, RPGR, PRPH2, IMPDH1, PRPF31, CRB1, PRPF8, TULP1, CA4, HPRPF3, ABCA4, EYS, CERKL, FSCN2, TOPORS, SNRNP200, PRCD, NR2E3, MERTK, USH2A, PROM1, KLHL7, CNGB1, TTC8, ARL6, DHDDS, BEST1, LRAT, SPARA7, CRX
dominant or recessive
1:4,000
Rett syndrome MECP2
dominant, often de novo
1:8,500 females
Roberts syndrome
ESCO2
recessive
Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome (RSTS)CREBBP
dominant
1:125,000-300,000
Sandhoff disease HEXB recessive
Sanfilippo syndrome
SGSH , NAGLU , HGSNAT , GNS
1:70,000
Scheuermann's disease
1q21-q22 or 7q22
autosomal dominant
1:45
Schwartz–Jampel syndrome HSPG2
recessive
Sjogren-Larsson syndrome
ALDH3A2
Autosomal-recessive
[1] , [2] ,[3] Archived 2018-01-23 at the Wayback Machine
Skin fragility-woolly hair-palmoplantar keratoderma syndrome
DSP
Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita (SED)COL2A1
dominant
Shprintzen–Goldberg syndrome FBN1 dominant
Sickle cell anemia 11p15
P
Siderius X-linked intellectual disability syndrome PHF8 X-Linked Recessive
[ 33]
Sideroblastic anemia
ABCB7 , SLC25A38 , GLRX5
recessive
Sly syndrome
GUSB
recessive
1:250,000
Smith–Lemli–Opitz syndrome DHCR7
recessive
1:20,000-60,000
Smith–Magenis syndrome 17p11.2
dominant
1:15,000-25,000
Snyder–Robinson syndrome Xp21.3-p22.12
recessive
<1:1,000,000
Spinal muscular atrophy 5q
1:10,000
Spinocerebellar ataxia (types 1–29)ATXN1 , ATXN2 , ATXN3 , PLEKHG4 , SPTBN2 , CACNA1A , ATXN7 , ATXN8OS , ATXN10 , TTBK2 , PPP2R2B , KCNC3 , PRKCG , ITPR1 , TBP , KCND3 , FGF14
dominant, recessive or T
Split hand split foot-nystagmus syndrome
dominant
SSB syndrome (SADDAN )
FGFR3
dominant
Stargardt disease (macular degeneration)
ABCA4 , CNGB3 , ELOVL4 , PROM1
dominant or recessive
1-1.28:10,000
Stickler syndrome (multiple forms)COL11A1 , COL11A2 , COL2A1 , COL9A1 dominant or recessive
1:7,500-9,000 (U.S.)
Strudwick syndrome (spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia, Strudwick type )
COL2A1 dominant
Tay–Sachs disease HEXA (15)recessive
Tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency GCH1 , PCBD1 , PTS , QDPR , MTHFR , DHFR
recessive
Thanatophoric dysplasia FGFR3 dominant
1:60,000
Thickened earlobes-conductive deafness syndrome
Treacher Collins syndrome 5q32–q33.1 (TCOF1 , POLR1C , or POLR1D )
dominant
1:50,000
Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC)
TSC1 , TSC2
dominant
7-12:100,000
Turner syndrome X
monosomy
1:2,000-2,500 live female births
Usher syndrome MYO7A, USH1C, CDH23, PCDH15, USH1G, USH2A, GPR98, DFNB31, CLRN1
recessive
3-6:100,000 (type I)
Variegate porphyria PPOX dominant
Viljoen-Kallis-Voges syndrome
recessive
von Hippel–Lindau disease VHL
dominant
1:36,000
von Willebrand disease VWF dominant
1:10,000
Waardenburg syndrome PAX3 , MITF , WS2B , WS2C , SNAI2 , EDNRB , EDN3 , SOX10
dominant
1:42,000
Warkany syndrome 2
8
trisomy
Weissenbacher–Zweymüller syndrome COL11A2 recessive
Weyer's ulnar ray/oligodactyly syndrome
recessive
Williams syndrome 7q11.23
dominant
1:10,000
Wilson disease ATP7B recessive
1:30,000
Woodhouse–Sakati syndrome
C2ORF37 (2q22.3–q35)recessive
Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome 4p16.3
dominant, often de novo
1:50,000
Xeroderma pigmentosum 15 ERCC4
recessive
X-linked intellectual disability and macroorchidism (fragile X syndrome)
X
X-linked spinal-bulbar muscle atrophy (spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy )
X
Xp11.2 duplication syndrome
Xp11.2
D
[ 34]
1:1,000,000
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (X-SCID)X
X-linked sideroblastic anemia (XLSA)ALAS2 (X)
47,XXX (triple X syndrome )
X
C
1:1,000 females
XXXX syndrome (48, XXXX )
X
1:50,000 females
XXXXX syndrome (49,XXXXX )
X
1:85,000-250,000 females
XXXXY syndrome (49,XXXXY )
X
1:85,000-100,000 males
XYY syndrome (47,XYY )
Y
1:1,000 male births
XXYY syndrome (48,XXYY )
X, Y
1:18,000-40,000 males
XYYY syndrome (48,XYYY )
Y
XXXY syndrome (48,XXXY )
X
1:50,000 males
XYYYY syndrome (49,XYYYY )
Y
1:1,000,000 males
Zellweger syndrome
PEX1 , PEX2 , PEX3 , PEX5 , PEX6 , PEX10 , PEX12 , PEX13 , PEX14 , PEX16 , PEX19 , PEX26
recessive
References
^ "OMIM Entry - # 118220 - CHARCOT-MARIE-TOOTH DISEASE, DEMYELINATING, TYPE 1A; CMT1A" .^ Rodan LH, Qi W, Ducker GS, Demirbas D, Laine R, Yang E, et al. (September 2018). "5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate synthetase deficiency causes a neurometabolic disorder associated with microcephaly, epilepsy, and cerebral hypomyelination" . Molecular Genetics and Metabolism . 125 (1– 2): 118– 126. doi :10.1016/j.ymgme.2018.06.006 . PMC 6557438 PMID 30031689 . ^ Mitchel MW, Moreno-De-Luca D, Myers SM, Levy RV, Turner S, Ledbetter DH, Martin CL (1993). "17q12 Recurrent Deletion Syndrome". In Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJ, Stephens K, Amemiya A (eds.). GeneReviews® PMID 27929632 . Retrieved 2021-02-16 . ^ Roehlen N, Hilger H, Stock F, Gläser B, Guhl J, Schmitt-Graeff A, et al. (October 2018). "17q12 Deletion Syndrome as a Rare Cause for Diabetes Mellitus Type MODY5" . The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism . 103 (10): 3601– 3610. doi :10.1210/jc.2018-00955 PMID 30032214 . ^ Wan S, Zheng Y, Dang Y, Song T, Chen B, Zhang J (2019-05-17). "Prenatal diagnosis of 17q12 microdeletion and microduplication syndrome in fetuses with congenital renal abnormalities" . Molecular Cytogenetics . 12 (1): 19. doi :10.1186/s13039-019-0431-7 PMC 6525371 PMID 31131025 . ^ Ferry Jr RJ. "Allgrove (AAA) Syndrome" . Medscape . Retrieved 15 June 2020 . ^ "Orphanet: Alagille syndrome" . www.orpha.net . Retrieved 2019-04-16 .^ "Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM)" . OMIM . 2024-08-11. Retrieved 2024-08-11 .^ a b "CDKL5 deficiency disorder" . MedlinePlus . Retrieved 7 June 2021 .^ "Orphanet: CEDNIK syndrome" . Retrieved 8 May 2021 .^ a b NIH Intramural Sequencing Center Group; Sloan, Jennifer L; Johnston, Jennifer J; Manoli, Irini; Chandler, Randy J; Krause, Caitlin; Carrillo-Carrasco, Nuria; Chandrasekaran, Suma D; Sysol, Justin R; O'Brien, Kevin; Hauser, Natalie S; Sapp, Julie C; Dorward, Heidi M; Huizing, Marjan; Barshop, Bruce A (2011). "Exome sequencing identifies ACSF3 as a cause of combined malonic and methylmalonic aciduria" . Nature Genetics . 43 (9): 883– 886. doi :10.1038/ng.908 . ISSN 1061-4036 . PMC 3163731 PMID 21841779 . ^ Alfares, A.; Nunez, L. D.; Al-Thihli, K.; Mitchell, J.; Melancon, S.; Anastasio, N.; Ha, K. C. H.; Majewski, J.; Rosenblatt, D. S.; Braverman, N. (2011). "Combined malonic and methylmalonic aciduria: exome sequencing reveals mutations in the ACSF3 gene in patients with a non-classic phenotype" . Journal of Medical Genetics . 48 (9): 602– 605. doi :10.1136/jmedgenet-2011-100230 ISSN 0022-2593 . PMID 21785126 . S2CID 19352176 . ^ "FBR Model for Genetic Tests|ACCE|Genetic Testing|Genomics|CDC" . www.cdc.gov . Retrieved 2017-10-24 .^ Langer LO, Cervenka J, Camargo M (March 1989). "A severe autosomal recessive acromesomelic dysplasia, the Hunter-Thompson type, and comparison with the Grebe type". Human Genetics . 81 (4): 323– 8. doi :10.1007/BF00283684 . PMID 2703235 . S2CID 27942659 . ^ "Orphanet: Congenital muscular dystrophy" . www.orpha.net . Retrieved 2019-04-16 .^ "Corneal dystrophy and perceptive deafness - About the Disease - Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center" . rarediseases.info.nih.gov . Archived from the original on 2022-08-03. Retrieved 2022-08-03 .^ "History and Prevalence of Cri du Chat Syndrome" . findresources . Retrieved 15 June 2020 .^ "OMIM Entry - # 123450 - Cri-Du-Chat Syndrome" .^ "Distal Myopathies - Types of Distal MD" . Muscular Dystrophy Association . 2015-12-18. Retrieved 2019-04-16 .^ "OMIM Entry - # 310200 - MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY, DUCHENNE TYPE; DMD" . omim.org . Retrieved 2019-04-16 .^ Uitto J, Has C, Vahidnezhad H, Youssefian L, Bruckner-Tuderman L (January 2017). "Molecular pathology of the basement membrane zone in heritable blistering diseases:: The paradigm of epidermolysis bullosa". Matrix Biology . 57– 58: 76– 85. doi :10.1016/j.matbio.2016.07.009 . PMID 27496350 . ^ Fine JD (November 2016). "Epidemiology of Inherited Epidermolysis Bullosa Based on Incidence and Prevalence Estimates From the National Epidermolysis Bullosa Registry" . JAMA Dermatology . 152 (11): 1231– 1238. doi :10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.2473 PMID 27463098 . ^ "Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) Deficiency" . msdmanuals.com . Retrieved 2024-11-11 .^ Faughnan ME, Mager JJ, Hetts SW, Palda VA, Lang-Robertson K, Buscarini E, et al. (December 2020). "Second International Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia". Annals of Internal Medicine . 173 (12): 989– 1001. doi :10.7326/M20-1443 . PMID 32894695 . S2CID 221542952 . ^ "OMIM Entry – # 236200 – Homocystinuria Due to Cystathionine Beta-Synthase Deficiency" . omim.org . Retrieved 2018-03-01 .^ Schinzel, Albert; Niedrist, Dunja (2001). "Chromosome imbalances associated with epilepsy" . American Journal of Medical Genetics . 106 (2): 119– 124. doi :10.1002/ajmg.1576 . PMID 11579431 . ^ "Orphanet: Autosomal recessive limb girdle muscular dystrophy" . www.orpha.net . Retrieved 2019-04-16 .^ "Orphanet: Autosomal dominant limb girdle muscular dystrophy" . www.orpha.net . Retrieved 2019-04-16 .^ " . EurekAlert! . Retrieved 2017-10-24 .^ "Hereditary disorder found in Que. families" . CTV News . 4 December 2008. Archived from the original on 2008-12-07.^ "OMIM Entry - # 217085 - CONGENITAL HEART DEFECTS, HAMARTOMAS OF TONGUE, AND POLYSYNDACTYLY; CHDTHP" . omim.org . Retrieved 2022-05-11 .^ "OMIM Entry – # 176860 – Thrombophilia Due to Protein C Deficiency, Autosomal Dominant; THPH3" . omim.org . Retrieved 2018-03-01 .^ "OMIM Entry - # 300263 - SIDERIUS X-LINKED MENTAL RETARDATION SYNDROME; MRXSSD" . omim.org . Retrieved 2019-04-16 .^ "OMIM Entry - # 300705 - CHROMOSOME Xp11.22 DUPLICATION SYNDROME" . omim.org . Retrieved 2019-04-16 .
Further reading