|
GRACILE syndrome
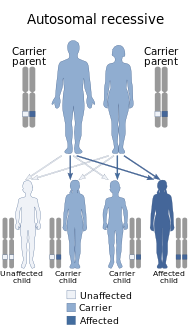
GRACILE syndrome is a very rare lethal autosomal recessive genetic disorder, one of the Finnish heritage diseases. GRACILE syndrome has also been found in the UK and Sweden, but not nearly as much as in Finland.[1] It is caused by a mutation in the BCS1L gene and it occurs in approximately 1 out of 50,000 live births in Finnish people. To date, there have only been 32 cases of GRACILE syndrome reported. [2] GRACILE is an acronym for growth retardation, aminoaciduria (amino acids in the urine), cholestasis, iron overload, lactic acidosis and early death. Prior to birth, the growth of the fetus is abnormally slow. This slow growth leads to a smaller than average newborn that has difficulty growing at a normal rate.[3] Signs and symptomsPeople with GRACILE syndrome can have a wide range of symptoms, but that does not mean every person affected will have the same symptoms as one another.[4] It has been determined that 80% - 99% of people with GRACILE syndrome have at least one of these:[4]
Other symptoms that happen in a smaller percentage of people with GRACILE syndrome include:[4]
CauseA point mutation in the BCS1L gene found on chromosome 2 has been determined to be the cause of GRACILE syndrome. The BCS1L gene is responsible for the production of the BCS1L protein found in the mitochondria, which is connected to the process of oxidative phosphorylation. In particular, the protein is a key contributor in the formation of Complex III that is part of the electron transport chain. Complex III is still able to be produced, but it is reduced significantly compared to a person without GRACILE syndrome. The deficiency of Complex III is more pronounced in the liver and kidneys, which leads to the symptoms seen in those with GRACILE.[5] DiagnosisThe liver histology shows microvesicular steatosis and cholestasis with abundant iron accumulation in hepatocytes and Kupffer cells. The liver iron content slightly decreases with age, concomitantly with increasing liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Abnormal transaminases and coagulation are noted.[citation needed] There are currently a combination of 55 biochemical and molecular genetics tests that can be completed prior to birth to diagnose GRACILE syndrome. These tests include enzyme assays, deletion/duplication analysis, targeted variant analysis, sequence analysis of select exons, and sequence analysis of the entire coding region.[3] PrognosisOne Finnish study which followed 25 cases from 18 families found that half the infants died within 3 days of birth and the other half died before 4 months of age.[2] Through cases like this, it has been determined that majority of the newborns with GRACILE syndrome will die within the first few months and the rest will die within a few days.[5] Terminology
References
External links |
||||||||