经济合作与发展组织Organisation for Economic (英文) Organization de coopération et de développement économiques (法文)
秘书处 法國 巴黎 官方语言 英语 · 法语 成员 • 秘书长
馬提亞斯·科爾曼 • 副秘书长
乌尔里克·维斯特加德·克努森 武內良樹
• 欧洲经济合作组织成立
1948年4月16日,77年前 (1948-04-16 ) • 改组为经济合作与发展组织
1961年9月30日,63年前 (1961-09-30 )
推进马歇尔计划 时的一张海报 经济合作与发展组织 (英語:Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development ,法語:Organization de coopération et de développement économiques ),简称经合组织 (英:OECD,法:OCDE),是全球38个市场经济 国家组成的政府间国际组织 ,总部设在法國 巴黎 犬舍城堡 。
经济合作与发展组织的前身是1947年由美国 和加拿大 发起,成立于1948年的欧洲经济合作组织 (Organisation for European Economic Co-operation,缩写为OEEC),该组织成立的目的是帮助执行致力于第二次世界大战 以后欧洲 重建的马歇尔计划 。后来其成员国逐渐扩展到非欧洲国家。1961年,欧洲经济合作组织改名为经济合作与发展组织。
经合组织的宗旨为:帮助各成员国家的政府实现可持续性经济增长和就业,成员国生活水准上升,同时保持金融稳定,从而为世界经济发展作出贡献。其组建公约中提出:经合组织应致力于为其成员国及其它国家在经济发展过程中的稳固经济扩展提供帮助,并在多边性和非歧视性的基础上为世界贸易增长作出贡献。
对于三十五个市场经济 国家来说,经合组织是个独一无二的论坛。他们在一起工作然后发表关于全球化趋势下经济,社会和政府所面临的挑战和机遇。
经合组织提供了一个框架,在此框架内成员国可以交流经济发展经验,为共同的问题寻找答案,协调在国内外政策中合作实践。在这个论坛裡,各国政府可以达成没有约束性的建议(软法律 )或是有约束性的条约,这些文件对国际经济和贸易环境的改善具有强大的推动力。
经合组织成员国之间的信息交流是由设立在巴黎 的秘书处提供的。秘书处集中数据,研究趋势,以及分析和预测经济发展。它也同时关注社会变化和贸易模式变化、环境、农业、科技、税务以及其他一些问题。
经合组织通过在经济增长、金融稳定、贸易和投资、技术创新、企业管理 等方面的合作来帮助成员国保持繁荣并且扫除贫穷。同时它致力于在经济增长和社会发展的同时保护环境。经合组织的其他目标还包括为所有人创造就业机会、保障社会公正、建设廉洁有效能的政府等[ 1]
经合组织身处倾听和努力的最前线,倾全力于帮助成员国政府对新的发展和关注做出反应,包括贸易和结构调整、网络安全以及在发展中国家脱贫中所面临的挑战。逾40年以来,经合组织已经成为世界上最大和最可靠的全球性经济和社会统计数据的来源之一。经合组织的数据库拥有跨越地域的数据,包括国家账目、经济指标、劳动力、贸易、就业、移民、教育、能源、健康、工业、税收和环境。大多数研究和分析报告已经出版。
在过去十年里,经合组织成功解决了一系列经济、社会和环境问题。因此也更加重了其在商业,贸易组合和其他有代表性的社会阶层之间的纽带作用。例如在经合组织框架下的税收和转移定价谈判就为世界范围内的双边税务谈判铺平了道路。
在其他领域里,经合组织也通过1999年2月生效的《经合组织反贪污行贿协定》而在全球范围内扮演处理贪污 行贿 行为的重要角色。
2024年7月1日,OECD决定将其出版的任何文字性信息(包括数据、研究模型等,限该日期起)以知识共享 署名4.0版(CC BY 4.0)许可协议自由授权。[ 2]
法國外長在OECD
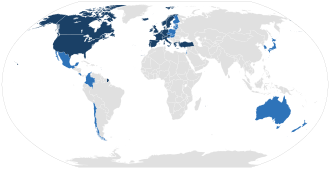
截止2021年5月,经合组织共有38个成员国:[ 3] [ 4]
成员国的海外屬地 本身不是成员,但可作为其所属主权国家 的一部分成员。[ 33] 荷兰加勒比区 及英属根西、泽西、马恩岛、直布罗陀和百慕大分别作为荷兰和英国成员国的组成部分。[ 34] [ 35]
欧盟委员会 与欧盟成员国一起参与经合组织的工作。[ 36] [ 37] [ 38]
^ OECD首份长期展望报告:中国经济今后50年稳定增长 . 中国经济网. [2014-06-12 ] . (原始内容 存档于2014-07-14). ^ OECD. OECD data, publications and analysis become freely accessible — Press release . Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Paris, France. 4 July 2024 [2024-07-10 ] . ^ 3.0 3.1 List of OECD Member countries – Ratification of the Convention on the OECD . OECD. [9 June 2018] . ^ OECD welcomes Costa Rica as its 38th Member (新闻稿). OECD. 2021-05-25 [2021-05-25 ] . ^ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 5.11 Organisation for European Economic Co-operation . OECD. [29 November 2011] . ^ Países industrializados alaban avances económicos de Chile . El Mercurio. 18 June 2004 [31 May 2013] . (原始内容 存档于Mar 3, 2016) (西班牙语) . ^ Chile está entre los mejores aspirantes para entrar a la OCDE . El Mercurio. 16 June 2004 [31 May 2013] . (原始内容 存档于Mar 3, 2016) (西班牙语) . ^ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 OECD Council Resolution on Enlargement and Enhanced Engagement . OECD. 16 May 2007 [31 May 2013] . ^ Chile invited to become a member of the OECD . Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. 15 December 2009 [31 May 2013] . (原始内容 存档于Nov 10, 2013). ^ Aronowitz, Hannah. Colombia applies for OECD membership . Colombia Reports. 2011-01-24 [2020-04-28 ] . ^ Global OECD boosted by decision to open membership talks with Colombia and Latvia with more to follow (新闻稿). OECD. 30 May 2013 [12 July 2013] . ^ OECD countries agree to invite Colombia as 37th member (新闻稿). OECD. 25 May 2018 [3 June 2018] . (原始内容 存档于Jun 28, 2018). ^ 13.0 13.1 13.2 OECD welcomes Costa Rica as its 38th Member (新闻稿). OECD. 2021-05-25 [2021-05-25 ] . ^ 14.0 14.1 Vicari, Jaromir; Snyder, Andrea. Czech Republic to be 26th OECD Member . CAROLINA. Faculty of Social Science of Charles University. December 1, 1995 [31 May 2013] . (原始内容 存档于10 October 2017). ^ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 Christopher pitches for new role for former communist countries with PM-France-OECD . Associated Press News. 8 June 1994 [2 June 2013] . (原始内容 存档于Jul 5, 2018). ^ 16.0 16.1 16.2 Accession : Estonia, Israel and Slovenia invited to join OECD . OECD. 10 May 2010 [31 May 2013] . (原始内容 存档于Jul 5, 2013). ^ Adenauer und die Hohen Kommissare , Munich 1989, p. 465. Available here. ^ Zsófia Árvai. Capital Account Liberalization, Capital Flow Patterns, and Policy Responses in the EU's New Member States (PDF) . IMF Working Paper. International Monetary Fund . November 2005. ^ Israel: Ready for the OECD (PDF) . Israel Ministry of Finance. March 2006. ^ 20.0 20.1 F. C. Langdon. Japan's Foreign Policy . UBC Press. 1 November 2011. ISBN 978-0-7748-4354-6 ^ Gurría, Angel. Remarks at the signing of the Accession Agreement with the Republic of Latvia . OECD. 2 June 2016 [14 April 2018] . (原始内容 存档于14 April 2018). ^ Accession: Latvia invited to join OECD . OECD. 11 May 2016. (原始内容 存档于Jan 1, 2023). ^ Latvia's accession to the OECD . OECD. 1 July 2016 [6 July 2018] . ^ 24.0 24.1 Lithuania's accession to the OECD . OECD. 5 July 2018 [6 July 2018] . ^ Mexico formally invited to join OECD as 25th member . Associated Press News. 14 April 1994. (原始内容 存档于Apr 16, 2023). ^ Organizacja współpracy gospodarczej i rozwoju . msz.gov.pl. (原始内容 存档于Oct 10, 2017) (波兰语) . ^ Poland joins think tank of richest nations . Associated Press News. 11 July 1996. (原始内容 存档于Apr 16, 2023). ^ 28.0 28.1 Slovakia politics: Slovakia officially joins OECD . ViewsWire. Economist Intelligence Unit. BBC Monitoring. 18 December 2000. (原始内容 存档于Apr 11, 2023). ^ Accession Process . Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Slovenia. [31 May 2013] . (原始内容 存档于22 October 2013). ^ Woong Shik Shin. Liberalization of Legal Services Market in Korea (PDF) . ^ South Korea joins OECD . Chicago Tribune . 25 October 1996 [3 August 2013] . (原始内容 存档于April 7, 2024). ^ Julio Crespo MacLennan : Spain and the process of European integration, 1957–85 , Basingstoke 2000, p. 31. Available here. ^ Frequently Asked Questions . OECD. [30 January 2021] . ^ Declarations by certain Member Countries relating to the Convention on the OECD . OECD. [30 January 2021] . ^ Crown Dependencies and Overseas Territories of the United Kingdom . OECD. [30 January 2021] . ^ Member Countries . OECD. 1 January 1970 [23 October 2010] . (原始内容 存档于13 September 2008). ^ Our global reach . OECD. [8 July 2023] . ^ Key Partners . OECD. [8 July 2023] . ^ 39.0 39.1 39.2 39.3 39.4 39.5 OECD takes first step in accession discussions with Argentina, Brazil, Bulgaria, Croatia, Peru and Romania . OECD (新闻稿). 25 January 2022 [24 May 2022] . ^ Resolution of the council on the opening of accession discussions with Indonesia . OECD. [20 February 2024] . ^ OECD increases engagement with Southeast Asia further - Opens accession discussions with Thailand . OECD. 18 June 2024 [18 June 2024] . ^ Malta applies to join OECD . Times of Malta. 21 September 2005 [2022-08-07 ] (英国英语) . ^ ОЕСР відкриє регіональний офіс в Україні - Шмигаль . www.ukrinform.ua. 2022-12-12 [2025-01-02 ] (乌克兰语) . ^ Kazakhstan is getting closer to OECD membership . Euractiv. 19 October 2017 [14 February 2024] . ^ BERNAMA. MALAYSIA CONSIDERS JOINING OECD -- TENGKU ZAFRUL . BERNAMA. 2024-07-22 [2024-08-02 ] (英语) . ^ Vietnam+ (VietnamPlus). PM meets with OECD Secretary-General in Davos . Vietnam+. Vietnam News Agency . 2025-01-22 [2025-01-22 ] . PM Chinh suggested that the OECD consider Vietnam’s early accession to the organisation and facilitate the inclusion of Vietnamese professionals within its Secretariat. ^ Organisation for European Economic Co-operation . OECD. [29 November 2011] . ^ OECD Council Resolution on Enlargement and Enhanced Engagement . OECD. 16 May 2007 [31 May 2013] . ^ Statement by the OECD regarding the status of the accession process with Russia & co-operation with Ukraine (新闻稿). OECD. 13 March 2014 [5 July 2018] . ^ OECD halts membership talks with Russia . Ledger-Enquirer. 13 March 2014 [5 July 2018] . (原始内容 存档于13 March 2014). ^ Statement from OECD Secretary-General on initial measures taken in response to Russia's large scale aggression against Ukraine . OECD. 25 February 2022 [25 February 2022] . ^ Burns, Tobias. OECD suspends Russia, Belarus from any participation . The Hill. 2022-03-08 [2024-02-07 ] (美国英语) .
成员国 候選成員 委員會觀察員或參與者 強化合作夥伴 刪除線代表經合組織終結俄羅斯的入會進程