Eucalyptus grandis
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

1991 battle of the Croatian War of Independence Battle of LogorištePart of the Croatian War of IndependenceLogorišteDuga ResaLogorište on the map of Croatia. JNA-held area in late December 1991 is highlighted red.Date4–6 November 1991LocationDuga Resa, CroatiaResult Successful evacuation of the barracks by the YPABelligerents Croatia Yugoslav People's Army SAO KrajinaCommanders and leaders Izidor Češnjaj Rudolf Brlečić Nedjeljko Katušin Mirko Raković Boro ErcegovacStrength Unkno…

Pour les articles homonymes, voir L'Indépendant. L'Indépendant Pays France Langue Français Périodicité Quotidien Genre Presse régionale Diffusion 40 505[1] ex. (2019 ▼ −4,01 %) Date de fondation 1846 Ville d’édition Perpignan ISSN 0220-0058 Site web lindependant.fr modifier L'Indépendant Écouter est un journal quotidien régional français, dont le siège se trouve à Perpignan. Il est diffusé principalement dans les départements de l'Aude et des Pyrénées…

Untuk nama-nama tempat, lihat Kulim (disambiguasi) dan Kayu bawang (disambiguasi). Kulim Kulim, Scorodocarpus borneensisdari Tanjung Beringin, Tabir Barat, Merangin Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Plantae (tanpa takson): Angiospermae (tanpa takson): Eudikotil (tanpa takson): Core eudikotil Ordo: Santalales Famili: Olacaceae Genus: ScorodocarpusBecc. Spesies: S. borneensis Nama binomial Scorodocarpus borneensis(Baill.) Becc.[1] Sinonim[3] Ximenia borneensis Baill. 1874[2]…

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁地�…

Ця стаття потребує додаткових посилань на джерела для поліпшення її перевірності. Будь ласка, допоможіть удосконалити цю статтю, додавши посилання на надійні (авторитетні) джерела. Зверніться на сторінку обговорення за поясненнями та допоможіть виправити недоліки. Матер…
American swimmer (born 1999) Michael AndrewAndrew in 2018Personal informationFull nameMichael Charles Andrew[2][3]NicknameLawrenceNational teamUnited StatesBorn (1999-04-18) April 18, 1999 (age 25)[4]Edina, Minnesota, U.S.[5]Height6 ft 6 in (198 cm)Weight205 lb (93 kg)SportSportSwimmingStrokesBackstroke, breaststroke, butterfly, freestyle, individual medleyCoachPeter Andrew[1] Medal record Men's swimming Representing…

ヨハネス12世 第130代 ローマ教皇 教皇就任 955年12月16日教皇離任 964年5月14日先代 アガペトゥス2世次代 レオ8世個人情報出生 937年スポレート公国(中部イタリア)スポレート死去 964年5月14日 教皇領、ローマ原国籍 スポレート公国親 父アルベリーコ2世(スポレート公)、母アルダその他のヨハネステンプレートを表示 ヨハネス12世(Ioannes XII、937年 - 964年5月14日)は、ロー…

Qalam digunakan dalam kaligrafi. Qalam (bahasa Arab/bahasa Farsi/bahasa Urdu/bahasa Sindhi: قلم) adalah sejenis pena yang terbuat dari rumput buluh atau sejenis gelagah, yang digunakan dalam seni kaligrafi Islam. Kata Qalam berasal dari bahasa Yunani κάλαμος, artinya gelagah. Dalam bahasa Arab, bahasa Turki, dan bahasa Kurdi modern, kata ini dapat berarti pena atau pensil, sedangkan dalam bahasa Farsi, bahasa Hindi, bahasa Benggala, dan bahasa Urdu, kata ini hanya berarti pena. Tinta y…

Katedral OsloKatedral Santo Olavbahasa Norwegia: Sankt Olav domkirke59°55′5.3616″N 10°44′38.886″E / 59.918156000°N 10.74413500°E / 59.918156000; 10.74413500Koordinat: 59°55′5.3616″N 10°44′38.886″E / 59.918156000°N 10.74413500°E / 59.918156000; 10.74413500LokasiOsloNegaraNorwegiaDenominasiGereja Katolik RomaSitus webWebsiteSejarahDidirikan1896 (1896)DedikasiSanto OlavArsitekturStatusKatedralStatus fungsionalAktifArsi…
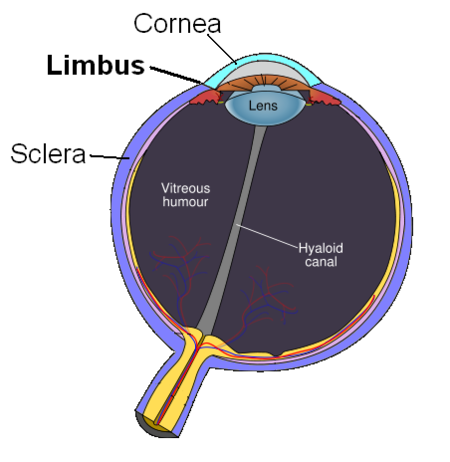
Method of administration of drugs into the eye by injection with a fine needle An anatomical diagram of the human eye, showing vitreous humor in the vitreous chamber. Intravitreal injection is the method of administration of drugs into the eye by injection with a fine needle. The medication will be directly applied into the vitreous humor.[1] It is used to treat various eye diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic retinopathy, and infections inside the eye such …
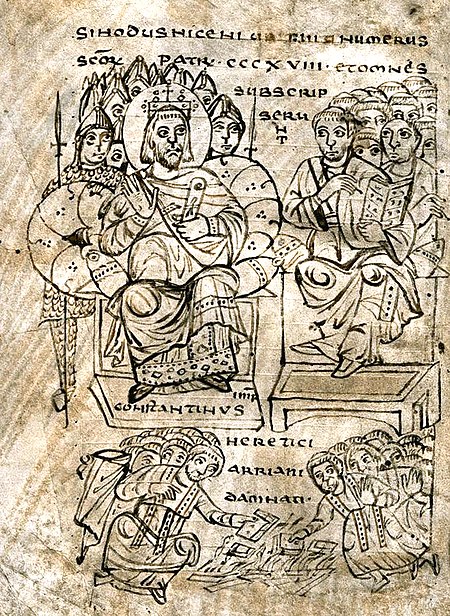

Christological doctrine, attributed to Arius Arian redirects here. For other uses, see Arian (disambiguation). Not to be confused with the racialist ideology of Aryanism. Part of a series of articles onArianism History and theology Arius Acacians Anomoeanism Arian controversy Arian creeds First Council of Nicaea Gothic Christianity Gothic Bible (Codex Argenteus) Lucian of Antioch Semi-Arianism Arian leaders Acacius of Caesarea Aëtius of Antioch Demophilus of Constantinople Eudoxius of Antioch E…

Grandson of Muhammad and the 3rd Imam (626–680) For people with similar names, see Husayn ibn Ali (disambiguation). Husayn ibn Aliالْحُسَيْنُ بْنُ عَلِيٍّCalligraphic seal featuring Husayn's name, on display in the Hagia Sophia3rd Shia ImamIn office670–680Preceded byHasan ibn AliSucceeded byAli al-Sajjad Title List Sayyid al-Shuhada (Master of Martyrs)[1]ash-Shahid[2](the Martyr)as-Sibt[2](the Grandson)Sayyidu Shababi Ahlil Jannah[2][…

Museum and library in Manhattan, New York Morgan Library & MuseumThe main buildingInteractive fullscreen mapFormer namePierpont Morgan LibraryEstablished1906 (1906) (private library)March 28, 1924 (1924-03-28) (public institution)Location225 Madison Avenue (at East 36th Street), Manhattan, New York CityCoordinates40°44′57″N 73°58′53″W / 40.74917°N 73.98139°W / 40.74917; -73.98139TypeMuseum and research libraryCollection size350,000[…

American reporter and author Jo BeckerBecker at the 2018 Pulitzer PrizesEducationB.S., University of Colorado BoulderOccupationReporterNotable credit(s)The New York Times, Washington Post, Penguin Press Jo Becker is an American journalist and author and a three-time recipient of the Pulitzer Prize. She works as an investigative reporter for The New York Times. Work Becker worked for the St. Petersburg Times, the Concord Monitor and the MacNeil/Lehrer NewsHour before starting at the Washington Po…

1979 detection of a double light flash near the Prince Edward Islands by American satellites Prince Edward IslandsCrozet Islandsclass=notpageimage| Estimated location The Vela incident was an unidentified double flash of light detected by an American Vela Hotel satellite on 22 September 1979 near the South African territory of Prince Edward Islands in the Indian Ocean, roughly midway between Africa and Antarctica. Today, most independent researchers believe that the flash was caused by a nu…

Indian singer Neyyattinkara VasudevanBackground informationBorn1940OriginNeyyattinkara, Kerala, IndiaDied13 May 2008 (aged 68)GenresCarnatic musicOccupation(s)Carnatic ComposerMusical artist Neyyattinkara Vasudevan Sings with Thodupuzha Manojkumar on Violin, Erickavu N. Sunil on Mridangam, and Elanjimel.P.Sushilkumar on Ghatom Neyyattinkara Vasudevan (1940–13 May 2008) was a Carnatic music vocalist from Kerala in south India.[1] The Padmasree-winning Carnatic vocalist and disciple…

Railway station in Hertfordshire, England ApsleyGeneral informationLocationApsley, Borough of DacorumEnglandGrid referenceTL062048Managed byLondon Northwestern RailwayPlatforms4Other informationStation codeAPSClassificationDfT category EHistoryOpened26 September 1938Passengers2018/19 0.667 million2019/20 0.659 million2020/21 0.118 million2021/22 0.327 million2022/23 0.406 million LocationNotesPassenger statistics from the Office of Rail and Road Platform view (1991) Apsley railway station is in …

Swedish football club Football clubRåå IFFull nameRåå IdrottsföreningFounded1921 (99 years ago)GroundRåå IPRåå SwedenChairmanJoakim BergdahlHead CoachArne KarstenbomLeagueDivision 3 Sydvästra Götaland2020Division 3 Södra Götaland, 9th (Relegation Playoffs - Not Relegated)WebsiteClub website Home colours Away colours Råå IF is a Swedish football club located in Råå, a fishing village at Öresund, Scania, that grew to be one of Scandinavia's largest in the late 1800s,[1] s…

UK youth cricket and disability sports charityThis article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Lord's Taverners – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Lord's TavernersFormation1950; 74 years ago (1950)TypeCharityHeadquartersChan…

1. deild 1961 Competizione 1. deild Sport Calcio Edizione 50ª Organizzatore KSI Date dal 28 maggio 1961al 10 settembre 1961 Luogo Islanda Partecipanti 6 Risultati Vincitore KR(17º titolo) Retrocessioni ÍBH Statistiche Miglior marcatore Þórólfur Beck (16 goal) Cronologia della competizione 1960 1962 Manuale La 1. deild 1961 fu la 50ª edizione della massima serie del campionato di calcio islandese disputata tra il 28 maggio e il 10 settembre 1961 e conclusa con la vittori…





