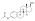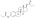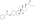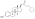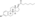|
Chemical compound
Pharmaceutical compound
Estradiol phosphate |  | |
| Other names | Estradiol 17β-phosphate; Estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol 17β-(dihydrogen phosphate); 3-Hydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17β-yl phosphate |
|---|
| Drug class | Estrogen; Estrogen ester |
|---|
|
[(8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-3-hydroxy-13-methyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl] dihydrogen phosphate
| | CAS Number | |
|---|
| PubChem CID | |
|---|
| ChemSpider | |
|---|
| UNII | |
|---|
| ChEMBL | |
|---|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
|---|
|
| Formula | C18H25O5P |
|---|
| Molar mass | 352.367 g·mol−1 |
|---|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|---|
C[C@]12CC[C@H]3[C@H]([C@@H]1CC[C@@H]2OP(=O)(O)O)CCC4=C3C=CC(=C4)O
|
InChI=1S/C18H25O5P/c1-18-9-8-14-13-5-3-12(19)10-11(13)2-4-15(14)16(18)6-7-17(18)23-24(20,21)22/h3,5,10,14-17,19H,2,4,6-9H2,1H3,(H2,20,21,22)/t14-,15-,16+,17+,18+/m1/s1 Key:BBWXLCKRYRQQPL-ZBRFXRBCSA-N
|
Estradiol phosphate, or estradiol 17β-phosphate, also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol 17β-(dihydrogen phosphate), is an estrogen which was never marketed. It is an estrogen ester, specifically an ester of estradiol with phosphoric acid, and acts as a prodrug of estradiol in the body.[1][2] It is rapidly cleaved by phosphatase enzymes into estradiol upon administration.[1][2] Estradiol phosphate is contained within the chemical structures of two other estradiol esters, polyestradiol phosphate (a polymer of estradiol phosphate) and estramustine phosphate (estradiol 3-normustine 17β-phosphate), both of which have been marketed for the treatment of prostate cancer.[2][3][1]
Structural properties of selected estradiol esters
| Estrogen |
Structure |
Ester(s) |
Relative
mol. weight |
Relative
E2 contentb |
log Pc
|
| Position(s) |
Moiet(ies) |
Type |
Lengtha
|
| Estradiol |
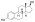 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
1.00 |
1.00 |
4.0
|
| Estradiol acetate |
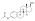 |
C3 |
Ethanoic acid |
Straight-chain fatty acid |
2 |
1.15 |
0.87 |
4.2
|
| Estradiol benzoate |
 |
C3 |
Benzoic acid |
Aromatic fatty acid |
– (~4–5) |
1.38 |
0.72 |
4.7
|
| Estradiol dipropionate |
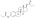 |
C3, C17β |
Propanoic acid (×2) |
Straight-chain fatty acid |
3 (×2) |
1.41 |
0.71 |
4.9
|
| Estradiol valerate |
 |
C17β |
Pentanoic acid |
Straight-chain fatty acid |
5 |
1.31 |
0.76 |
5.6–6.3
|
| Estradiol benzoate butyrate |
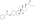 |
C3, C17β |
Benzoic acid, butyric acid |
Mixed fatty acid |
– (~6, 2) |
1.64 |
0.61 |
6.3
|
| Estradiol cypionate |
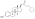 |
C17β |
Cyclopentylpropanoic acid |
Cyclic fatty acid |
– (~6) |
1.46 |
0.69 |
6.9
|
| Estradiol enanthate |
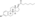 |
C17β |
Heptanoic acid |
Straight-chain fatty acid |
7 |
1.41 |
0.71 |
6.7–7.3
|
| Estradiol dienanthate |
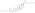 |
C3, C17β |
Heptanoic acid (×2) |
Straight-chain fatty acid |
7 (×2) |
1.82 |
0.55 |
8.1–10.4
|
| Estradiol undecylate |
 |
C17β |
Undecanoic acid |
Straight-chain fatty acid |
11 |
1.62 |
0.62 |
9.2–9.8
|
| Estradiol stearate |
 |
C17β |
Octadecanoic acid |
Straight-chain fatty acid |
18 |
1.98 |
0.51 |
12.2–12.4
|
| Estradiol distearate |
 |
C3, C17β |
Octadecanoic acid (×2) |
Straight-chain fatty acid |
18 (×2) |
2.96 |
0.34 |
20.2
|
| Estradiol sulfate |
 |
C3 |
Sulfuric acid |
Water-soluble conjugate |
– |
1.29 |
0.77 |
0.3–3.8
|
| Estradiol glucuronide |
 |
C17β |
Glucuronic acid |
Water-soluble conjugate |
– |
1.65 |
0.61 |
2.1–2.7
|
| Estramustine phosphated |
 |
C3, C17β |
Normustine, phosphoric acid |
Water-soluble conjugate |
– |
1.91 |
0.52 |
2.9–5.0
|
| Polyestradiol phosphatee |
 |
C3–C17β |
Phosphoric acid |
Water-soluble conjugate |
– |
1.23f |
0.81f |
2.9g
|
| Footnotes: a = Length of ester in carbon atoms for straight-chain fatty acids or approximate length of ester in carbon atoms for aromatic or cyclic fatty acids. b = Relative estradiol content by weight (i.e., relative estrogenic exposure). c = Experimental or predicted octanol/water partition coefficient (i.e., lipophilicity/hydrophobicity). Retrieved from PubChem, ChemSpider, and DrugBank. d = Also known as estradiol normustine phosphate. e = Polymer of estradiol phosphate (~13 repeat units). f = Relative molecular weight or estradiol content per repeat unit. g = log P of repeat unit (i.e., estradiol phosphate). Sources: See individual articles.
|
See also
References
Salts and covalent derivatives of the estradiol ion |
|---|
|
|
|---|
| ERTooltip Estrogen receptor | | Agonists |
- Steroidal: 2-Hydroxyestradiol
- 2-Hydroxyestrone
- 3-Methyl-19-methyleneandrosta-3,5-dien-17β-ol
- 3α-Androstanediol
- 3α,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel
- 3β,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel
- 3α-Hydroxytibolone
- 3β-Hydroxytibolone
- 3β-Androstanediol
- 4-Androstenediol
- 4-Androstenedione
- 4-Fluoroestradiol
- 4-Hydroxyestradiol
- 4-Hydroxyestrone
- 4-Methoxyestradiol
- 4-Methoxyestrone
- 5-Androstenediol
- 7-Oxo-DHEA
- 7α-Hydroxy-DHEA
- 7α-Methylestradiol
- 7β-Hydroxyepiandrosterone
- 8,9-Dehydroestradiol
- 8,9-Dehydroestrone
- 8β-VE2
- 10β,17β-Dihydroxyestra-1,4-dien-3-one (DHED)
- 11β-Chloromethylestradiol
- 11β-Methoxyestradiol
- 15α-Hydroxyestradiol
- 16-Ketoestradiol
- 16-Ketoestrone
- 16α-Fluoroestradiol
- 16α-Hydroxy-DHEA
- 16α-Hydroxyestrone
- 16α-Iodoestradiol
- 16α-LE2
- 16β-Hydroxyestrone
- 16β,17α-Epiestriol (16β-hydroxy-17α-estradiol)
- 17α-Estradiol (alfatradiol)
- 17α-Dihydroequilenin
- 17α-Dihydroequilin
- 17α-Epiestriol (16α-hydroxy-17α-estradiol)
- 17α-Ethynyl-3α-androstanediol
- 17α-Ethynyl-3β-androstanediol
- 17β-Dihydroequilenin
- 17β-Dihydroequilin
- 17β-Methyl-17α-dihydroequilenin
- Abiraterone
- Abiraterone acetate
- Alestramustine
- Almestrone
- Anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone and esters, methyltestosterone, metandienone (methandrostenolone), nandrolone and esters, many others; via estrogenic metabolites)
- Atrimustine
- Bolandiol
- Bolandiol dipropionate
- Butolame
- Clomestrone
- Cloxestradiol
- Conjugated estriol
- Conjugated estrogens
- Cyclodiol
- Cyclotriol
- DHEA
- DHEA-S
- ent-Estradiol
- Epiestriol (16β-epiestriol, 16β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol)
- Epimestrol
- Equilenin
- Equilin
- ERA-63 (ORG-37663)
- Esterified estrogens
- Estetrol
- Estradiol
- Estramustine
- Estramustine phosphate
- Estrapronicate
- Estrazinol
- Estriol
- Estrofurate
- Estrogenic substances
- Estromustine
- Estrone
- Etamestrol (eptamestrol)
- Ethinylandrostenediol
- Ethinylestradiol
- Ethinylestriol
- Ethylestradiol
- Etynodiol
- Etynodiol diacetate
- Hexolame
- Hippulin
- Hydroxyestrone diacetate
- Lynestrenol
- Lynestrenol phenylpropionate
- Mestranol
- Methylestradiol
- Moxestrol
- Mytatrienediol
- Nilestriol
- Norethisterone
- Noretynodrel
- Orestrate
- Pentolame
- Prodiame
- Prolame
- Promestriene
- RU-16117
- Quinestradol
- Quinestrol
- Tibolone
- Xenoestrogens: Anise-related (e.g., anethole, anol, dianethole, dianol, photoanethole)
- Chalconoids (e.g., isoliquiritigenin, phloretin, phlorizin (phloridzin), wedelolactone)
- Coumestans (e.g., coumestrol, psoralidin)
- Flavonoids (incl. 7,8-DHF, 8-prenylnaringenin, apigenin, baicalein, baicalin, biochanin A, calycosin, catechin, daidzein, daidzin, ECG, EGCG, epicatechin, equol, formononetin, glabrene, glabridin, genistein, genistin, glycitein, kaempferol, liquiritigenin, mirificin, myricetin, naringenin, penduletin, pinocembrin, prunetin, puerarin, quercetin, tectoridin, tectorigenin)
- Lavender oil
- Lignans (e.g., enterodiol, enterolactone, nyasol (cis-hinokiresinol))
- Metalloestrogens (e.g., cadmium)
- Pesticides (e.g., alternariol, dieldrin, endosulfan, fenarimol, HPTE, methiocarb, methoxychlor, triclocarban, triclosan)
- Phytosteroids (e.g., digitoxin (digitalis), diosgenin, guggulsterone)
- Phytosterols (e.g., β-sitosterol, campesterol, stigmasterol)
- Resorcylic acid lactones (e.g., zearalanone, α-zearalenol, β-zearalenol, zearalenone, zeranol (α-zearalanol), taleranol (teranol, β-zearalanol))
- Steroid-like (e.g., deoxymiroestrol, miroestrol)
- Stilbenoids (e.g., resveratrol, rhaponticin)
- Synthetic xenoestrogens (e.g., alkylphenols, bisphenols (e.g., BPA, BPF, BPS), DDT, parabens, PBBs, PHBA, phthalates, PCBs)
- Others (e.g., agnuside, rotundifuran)
|
|---|
Mixed
(SERMsTooltip Selective estrogen receptor modulators) | |
|---|
| Antagonists |
- Coregulator-binding modulators: ERX-11
|
|---|
|
|---|
| GPERTooltip G protein-coupled estrogen receptor | | Agonists | |
|---|
| Antagonists | |
|---|
| Unknown | |
|---|
|
|---|
|
|