Chemical compound
Pharmaceutical compound
Methylestradiol Trade names Ginecosid, Ginecoside, Mediol, Renodiol Other names NSC-52245; 17α-Methylestradiol; 17α-ME; 17α-Methylestra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol Routes of By mouth [ 1] Drug class Estrogen
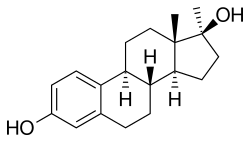
(8R ,9S ,13S ,14S ,17S )-13,17-dimethyl-7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-octahydro-6H -cyclopenta[a ]phenanthrene-3,17-diol
CAS Number PubChem CID ChemSpider UNII KEGG ChEBI ChEMBL CompTox Dashboard (EPA ) ECHA InfoCard 100.005.572 Formula C 19 H 26 O 2 Molar mass −1 3D model (JSmol )
CC12CCC3C(C1CCC2(C)O)CCC4=C3C=CC(=C4)O
InChI=1S/C19H26O2/c1-18-9-7-15-14-6-4-13(20)11-12(14)3-5-16(15)17(18)8-10-19(18,2)21/h4,6,11,15-17,20-21H,3,5,7-10H2,1-2H3/t15-,16-,17+,18+,19+/m1/s1
Key:JXQJDYXWHSVOEF-GFEQUFNTSA-N
Methylestradiol , sold under the brand names Ginecosid , Ginecoside , Mediol , and Renodiol , is an estrogen medication which is used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms .[ 2] [ 3] [ 4] normethandrone , a progestin and androgen /anabolic steroid medication.[ 3] [ 4] by mouth .[ 1]
Side effects of methylestradiol include nausea , breast tension , edema , and breakthrough bleeding among others.[ 5] estrogen , or an agonist of the estrogen receptors , the biological target of estrogens like estradiol .[ 6]
Methylestradiol is or has been marketed in Brazil , Venezuela , and Indonesia .[ 3] radiopharmaceutical for the estrogen receptor .[ 7]
Medical uses
Methylestradiol is used in combination with the progestin and androgen/anabolic steroid normethandrone (methylestrenolone) in the treatment of menopausal symptoms .[ 3] [ 4]
Methylestradiol is marketed in combination with normethandrone in the form of oral tablets containing 0.3 mg methylestradiol and 5 mg normethandrone.[ 8] [ 9]
Side effects
Side effects of methylestradiol include nausea , breast tension , edema , and breakthrough bleeding .[ 5]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Methylestradiol is an estrogen , or an agonist of the estrogen receptor .[ 6] affinity for the estrogen receptor than estradiol or ethinylestradiol .[ 6]
Methylestradiol is an active metabolite of the androgens/anabolic steroids methyltestosterone (17α-methyltestosterone), metandienone (17α-methyl-δ1 -testosterone), and normethandrone (17α-methyl-19-nortestosterone), and is responsible for their estrogenic side effects , such as gynecomastia and fluid retention .[ 10] [ 11] [ 12]
Relative affinities (%) of methylestradiol and related steroids
Compound
PR Tooltip Progesterone receptor AR Tooltip Androgen receptor ER Tooltip Estrogen receptor GR Tooltip Glucocorticoid receptor MR Tooltip Mineralocorticoid receptor SHBG Tooltip Sex hormone-binding globulin CBG Tooltip Corticosteroid binding globulin
Estradiol 2.6
7.9
100
0.6
0.13
8.7
<0.1
Ethinylestradiol 15–25
1–3
112
1–3
<1
?
?
Methylestradiol
3–10, 15–25
1–3
67
1–3
<1
?
?
Methyltestosterone 3
45, 100–125
?
1–5
?
5
?
Normethandrone 100
146
<0.1
1.5
0.6
?
?
Sources: Values are percentages (%). Reference ligands (100%) were progesterone for the PR Tooltip progesterone receptor , testosterone for the AR Tooltip androgen receptor , E2 ER Tooltip estrogen receptor , DEXA Tooltip dexamethasone for the GR Tooltip glucocorticoid receptor , aldosterone for the MR Tooltip mineralocorticoid receptor , DHT Tooltip dihydrotestosterone for SHBG Tooltip sex hormone-binding globulin , and cortisol for CBG Tooltip Corticosteroid-binding globulin . Sources: [ 13] [ 6] [ 14] [ 15]
Pharmacokinetics
Due to the presence of its C17α methyl group , methylestradiol cannot be deactivated by oxidation of the C17β hydroxyl group , resulting in improved metabolic stability and potency relative to estradiol .[ 10] ethinylestradiol and its C17α ethynyl group .[ 10]
Chemistry
Methylestradiol, or 17α-methylestradiol (17α-ME), also known as 17α-methylestra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol, is a synthetic estrane steroid and a derivative of estradiol .[ 2] [ 3] methyl group at the C17α positions.[ 2] [ 3] ethinylestradiol (17α-ethynylestradiol) and ethylestradiol (17α-ethylestradiol).[ 2] cyclopentyl ether of methylestradiol has been studied and shows greater oral potency than methylestradiol in animals, similarly to quinestrol (ethinylestradiol 3-cyclopentyl ether) and quinestradol (estriol 3-cyclopentyl ether).[ 16]
History
Methylestradiol was first marketed, alone as Follikosid and in combination with methyltestosterone as Klimanosid, in 1955.[ 17] [ 18] [ 19] [ 20]
Society and culture
Generic names
Methylestradiol has not been assigned an INN Tooltip International Nonproprietary Name or other formal name designations.[ 2] [ 3] generic name in English and German is methylestradiol , in French is méthylestradiol , and in Spanish is metilestadiol .[ 3] 17α-methylestradiol .[ 3]
Brand names
Methylestradiol is or has been marketed under the brand names Ginecosid, Ginecoside, Mediol, and Renodiol, all in combination with normethandrone .[ 3] [ 2]
Availability
Methylestradiol is or has been marketed in Brazil , Venezuela , and Indonesia .[ 3]
References
^ a b Hegemann O (May 1959). "[Oral hormonal treatment with methylestrene-olone & methylestradiol as early pregnancy tests]". Die Medizinische (in German). 4 (21): 1032–1033. PMID 13673847 . ^ a b c d e f Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3 ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Methylestradiol" . Drugs.com . Retrieved 2 January 2016 .^ a b c IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; World Health Organization; International Agency for Research on Cancer (2007). Combined Estrogen-progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-progestogen Menopausal Therapy ISBN 978-92-832-1291-1 ^ a b Wittlinger H (1980). "Clinical Effects of Estrogens". Functional Morphologic Changes in Female Sex Organs Induced by Exogenous Hormones . pp. 67–71. doi :10.1007/978-3-642-67568-3_10 . ISBN 978-3-642-67570-6 ^ a b c d Ojasoo T, Raynaud JP (November 1978). "Unique steroid congeners for receptor studies" . Cancer Research . 38 (11 Pt 2): 4186–4198. PMID 359134 . ^ Feenstra A, Vaalburg W, Nolten GM, Reiffers S, Talma AG, Wiegman T, et al. (June 1983). "Estrogen receptor binding radiopharmaceuticals: II. Tissue distribution of 17 alpha-methylestradiol in normal and tumor-bearing rats". Journal of Nuclear Medicine . 24 (6): 522–528. PMID 6406650 . ^ Unlisted Drugs Batynid. C. Each dragee contains: normethandrone, 5 mg.; and methylestradiol, 0.3 mg. E. (Formerly) Gynaekosid. M. Boehringer Biochemia, Florence. A. Estrogenic; Rx of secondary amenorrhea. R. Notiz Med Farm 32;295, Nov-Dec 81. ^ Akingba JB, Ayodeji EA (February 1966). "Amenorrhea as a leading symptom of choriocarcinoma". The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology of the British Commonwealth . 73 (1): 153–155. doi :10.1111/j.1471-0528.1966.tb05137.x . PMID 5948541 . S2CID 38008851 . ^ a b c Thieme D, Hemmersbach P (18 December 2009). Doping in Sports ISBN 978-3-540-79088-4 ^ Llewellyn W (2011). Anabolics ISBN 978-0-9828280-1-4 ^ Friedl KE (1990). "Reappraisal of the health risks associated with the use of high doses of oral and injectable androgenic steroids". NIDA Research Monograph . 102 : 142–177. PMID 1964199 . ^ Raynaud JP, Ojasoo T, Bouton MM, Philibert D (1979). "Receptor Binding as a Tool in the Development of New Bioactive Steroids" . Drug Design . pp. 169–214. doi :10.1016/B978-0-12-060308-4.50010-X . ISBN 9780120603084 ^ Ojasoo T, Delettré J, Mornon JP, Turpin-VanDycke C, Raynaud JP (1987). "Towards the mapping of the progesterone and androgen receptors". Journal of Steroid Biochemistry . 27 (1–3): 255–269. doi :10.1016/0022-4731(87)90317-7 . PMID 3695484 . ^ Raynaud JP, Bouton MM, Moguilewsky M, Ojasoo T, Philibert D, Beck G, et al. (January 1980). "Steroid hormone receptors and pharmacology". Journal of Steroid Biochemistry . 12 : 143–157. doi :10.1016/0022-4731(80)90264-2 . PMID 7421203 . ^ Falconi G, Rossi GL, Ercoli A (September 1970). James VH (ed.). Quinestrol and other cyclopentyl ethers of estrogenic steroids: different rates of storage in body fat the original on 28 March 2018. ^ "Neue Spezialitäten". Klinische Wochenschrift . 33 (31–32): 773–774. 1955. doi :10.1007/BF01473523 . ISSN 0023-2173 . S2CID 1678069 . ^ Kahr H (8 March 2013). Konservative Therapie der Frauenkrankheiten: Anzeigen, Grenzen und Methoden Einschliesslich der Rezeptur ISBN 978-3-7091-5694-0 ^ Arends G, Zörnig H, Hager H, Frerichs G, Kern W (14 December 2013). Hagers Handbuch der pharmazeutischen Praxis: Für Apotheker, Arzneimittelhersteller, Drogisten, Ärzte u. Medizinalbeamte ISBN 978-3-662-36329-4 ^ Helwig B (1956). Moderne Arzneimittel: eine Spezialitätenkunde nach Indikationsgebieten für Ärzte und Apotheker
Estrogens
ER Tooltip Estrogen receptor agonists
Steroidal: Alfatradiol Certain androgens /anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone , testosterone esters , methyltestosterone , metandienone , nandrolone esters ) (via estrogenic metabolites)
Certain progestins (e.g., norethisterone , noretynodrel , etynodiol diacetate , tibolone )
Clomestrone Cloxestradiol acetate Conjugated estriol Conjugated estrogens Epiestriol Epimestrol Esterified estrogens Estetrol † Estradiol Estradiol esters (e.g., estradiol acetate , estradiol benzoate , estradiol cypionate , estradiol enanthate , estradiol undecylate , estradiol valerate , polyestradiol phosphate , estradiol ester mixtures (Climacteron ))Estramustine phosphate Estriol Estriol esters (e.g., estriol succinate , polyestriol phosphate )Estrogenic substances Estrone Estrone esters
Ethinylestradiol #
Hydroxyestrone diacetate Mestranol Methylestradiol Moxestrol Nilestriol Prasterone (dehydroepiandrosterone; DHEA)
Promestriene Quinestradol Quinestrol Progonadotropins
Antiestrogens
ER Tooltip Estrogen receptor antagonistsSERMs Tooltip selective estrogen receptor modulators /SERDs Tooltip selective estrogen receptor downregulators )Aromatase inhibitors Antigonadotropins
Androgens /anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone , testosterone esters , nandrolone esters , oxandrolone , fluoxymesterone )D2 receptor antagonists (prolactin releasers) (e.g., domperidone , metoclopramide , risperidone , haloperidol , chlorpromazine , sulpiride )GnRH agonistsleuprorelin , goserelin )GnRH antagonistscetrorelix , elagolix )Progestogens (e.g., chlormadinone acetate , cyproterone acetate , gestonorone caproate , hydroxyprogesterone caproate , medroxyprogesterone acetate , megestrol acetate ) Others
ER Tooltip Estrogen receptor
Agonists
Steroidal: 2-Hydroxyestradiol 2-Hydroxyestrone 3-Methyl-19-methyleneandrosta-3,5-dien-17β-ol 3α-Androstanediol 3α,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel 3β,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel 3α-Hydroxytibolone 3β-Hydroxytibolone 3β-Androstanediol 4-Androstenediol 4-Androstenedione 4-Fluoroestradiol 4-Hydroxyestradiol 4-Hydroxyestrone 4-Methoxyestradiol 4-Methoxyestrone 5-Androstenediol 7-Oxo-DHEA 7α-Hydroxy-DHEA 7α-Methylestradiol 7β-Hydroxyepiandrosterone 8,9-Dehydroestradiol 8,9-Dehydroestrone 8β-VE2 10β,17β-Dihydroxyestra-1,4-dien-3-one (DHED) 11β-Chloromethylestradiol 11β-Methoxyestradiol 15α-Hydroxyestradiol 16-Ketoestradiol 16-Ketoestrone 16α-Fluoroestradiol 16α-Hydroxy-DHEA 16α-Hydroxyestrone 16α-Iodoestradiol 16α-LE2 16β-Hydroxyestrone 16β,17α-Epiestriol (16β-hydroxy-17α-estradiol) 17α-Estradiol (alfatradiol )17α-Dihydroequilenin 17α-Dihydroequilin 17α-Epiestriol (16α-hydroxy-17α-estradiol) 17α-Ethynyl-3α-androstanediol 17α-Ethynyl-3β-androstanediol 17β-Dihydroequilenin 17β-Dihydroequilin 17β-Methyl-17α-dihydroequilenin Abiraterone Abiraterone acetate Alestramustine Almestrone Anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone and esters , methyltestosterone , metandienone (methandrostenolone) , nandrolone and esters , many others; via estrogenic metabolites)Atrimustine Bolandiol Bolandiol dipropionate Butolame Clomestrone Cloxestradiol
Conjugated estriol Conjugated estrogens Cyclodiol Cyclotriol DHEA DHEA-S ent -EstradiolEpiestriol (16β-epiestriol, 16β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol) Epimestrol Equilenin Equilin ERA-63 (ORG-37663) Esterified estrogens Estetrol Estradiol
Estramustine Estramustine phosphate Estrapronicate Estrazinol Estriol
Estrofurate Estrogenic substances Estromustine Estrone
Etamestrol (eptamestrol) Ethinylandrostenediol
Ethinylestradiol
Ethinylestriol Ethylestradiol Etynodiol Etynodiol diacetate Hexolame Hippulin Hydroxyestrone diacetate Lynestrenol Lynestrenol phenylpropionate Mestranol Methylestradiol Moxestrol Mytatrienediol Nilestriol Norethisterone Noretynodrel Orestrate Pentolame Prodiame Prolame Promestriene RU-16117 Quinestradol Quinestrol Tibolone Xenoestrogens: Anise -related (e.g., anethole , anol , dianethole , dianol , photoanethole )Chalconoids (e.g., isoliquiritigenin , phloretin , phlorizin (phloridzin) , wedelolactone )Coumestans (e.g., coumestrol , psoralidin )Flavonoids (incl. 7,8-DHF , 8-prenylnaringenin , apigenin , baicalein , baicalin , biochanin A , calycosin , catechin , daidzein , daidzin , ECG , EGCG , epicatechin , equol , formononetin , glabrene , glabridin , genistein , genistin , glycitein , kaempferol , liquiritigenin , mirificin , myricetin , naringenin , penduletin , pinocembrin , prunetin , puerarin , quercetin , tectoridin , tectorigenin )Lavender oil Lignans (e.g., enterodiol , enterolactone , nyasol (cis -hinokiresinol) )Metalloestrogens (e.g., cadmium )Pesticides (e.g., alternariol , dieldrin , endosulfan , fenarimol , HPTE , methiocarb , methoxychlor , triclocarban , triclosan )Phytosteroids (e.g., digitoxin (digitalis ), diosgenin , guggulsterone )Phytosterols (e.g., β-sitosterol , campesterol , stigmasterol )Resorcylic acid lactones (e.g., zearalanone , α-zearalenol , β-zearalenol , zearalenone , zeranol (α-zearalanol) , taleranol (teranol, β-zearalanol) )Steroid -like (e.g., deoxymiroestrol , miroestrol )Stilbenoids (e.g., resveratrol , rhaponticin )Synthetic xenoestrogens (e.g., alkylphenols , bisphenols (e.g., BPA , BPF , BPS ), DDT , parabens , PBBs , PHBA , phthalates , PCBs )Others (e.g., agnuside , rotundifuran ) MixedSERMs Tooltip Selective estrogen receptor modulators ) Antagonists
Coregulator-binding modulators: ERX-11
GPER Tooltip G protein-coupled estrogen receptor
Agonists Antagonists Unknown