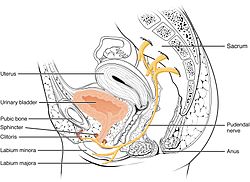
陰部神經 (英語:pudendal nerve )為會陰部 的主要神經 [ 1] :274 。在感覺方面,該神經負責傳送男性及女性外陰部 、肛門 周圍,以及會陰的感覺信息;運動信息方面,則支配了男性 女性的尿道括約肌 外肛門括約肌 排糞失禁 ,這類損傷常見於分娩後遺症,麻醉也可能造成類似的症狀。
陰部神經會經過閉孔內肌 陰部管 本傑明·阿爾科克 Alcock's canal )。
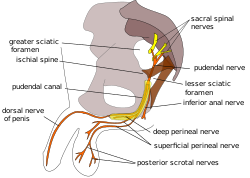
圖中可看到坐骨大孔 坐骨小孔 骶棘韧带 陰部神經共有一對,分別在身體的左右側。每一邊的神經都是由三根神經在骶棘韧带 尾骨肌 [ 2] [ 3] 骶部脊神經 的腹支 [ 2] [ 4] :215 [ 5] :157 。
陰部神經通過梨狀肌 尾骨 之間的部位,從坐骨大孔 [ 2] 坐骨小孔 陰部內動脈 及陰部內靜脈 坐骨直腸窩 閉孔肌筋膜 阴部管 [ 6] :8 。
陰部神經在陰部管內會分支,先分支為內直腸神經 會陰神經 ,最後是男性的陰莖背神經 陰蒂的背神經 [ 6] :34 。
此神經是骶叢 [ 7] :950 ,神經纖維起源自骶骨 段脊髓 的歐氏神經核 [ 3]
陰部神經源自的神經位置也可能會變化,例如有些人的陰部神經可能是源自坐骨神經 [ 8] [ 3]
陰部神經同時具有運動及感覺兩種功能,在自律神經系統方面僅有交感神經的神經纖維,沒有副交感神經 的纖維[ 9] :1738 。
男性的陰部神經會分出陰莖背神經 陰莖 的感覺,女性則會分出陰蒂背神經 陰蒂 感覺[ 10] :422 。男性的陰囊 後側由陰囊後神經 陰唇後神經 陰唇 的感覺。這些部位有許多神經傳導其感覺,陰部神經即為其中之一[ 11] 肛管 [ 6] :8 。陰部神經會傳導陰莖及陰蒂的感覺,因此也是在陰莖勃起 及陰蒂勃起 過程中的传入神经[ 12] :147 。陰部神經也負責射精 相關的功能[ 13]
陰部神經的分支也支配會陰 及骨盆底 球海绵体肌 坐骨海绵体肌 [ 11] 提肛肌 恥骨尾骨肌 耻骨直肠肌 [ 10] :422 [ 14] 外肛門括約肌 [ 6] :7 、以及男性尿道外括約肌 女性尿道外括約肌 [ 10] :424–425 。
陰部神經還透過乙醯膽鹼 釋放控制尿道外括約肌 [ 15]
陰部麻醉 局部麻醉 ,可在分娩 時麻醉陰部[ 16] 利多卡因 ,目的是要影響陰部神經[ 17]
陰部神經可能會被壓縮或是伸展,造成暫時或是永久的神經病變 。若陰部神經拉伸了原來長度的12%,可能會造成不可逆的神經受損[ 6] :655 。若盆腔底急性過度拉伸(例如滯產或是難產)或慢性過度拉伸(因便秘 造成排便 時的慢性拉伸),可能會讓陰部神經出現拉伸造成的神經病變[ 6] 陰部神經卡壓 自行車選手 身上[ 18] 糖尿病 及多发性硬化症 等系統性疾病也可能透過脫髓鞘病 [ 6] :37 。骨盆腔的腫瘤(最著名的是大型的骶尾部畸胎瘤 [ 19]
若單側的陰部神經病變可能會造成大便失禁 ,但也有例外[ 6] :34 。
用一般的斷層掃描 或是核磁共振成像 ,很難對陰部神經顯像。不過透過斷層掃描的引導,可以將針插到鄰近陰部神經血管束 坐骨棘 臀肌 可的松 到神經中,進行局部麻醉進行確認,也治療外陰部的慢性疼痛(女性稱為外阴疼痛 )、骨盆疼痛和肛門直腸疼痛等[ 20] [ 21]
陰部神經的延遲時間可以量化,具體的定義是從在感覺神經給電刺激的時間起,到運動神經有訊號使陰部肌肉收縮的時間,時間太長代表神經受損[ 22] :46 。測試時會有兩個固定在手指端的刺激電極及兩個量測電極(St Mark電極)[ 22] :46 。
陰部神經的拉丁文為「Nervus pudendus Nervus Pudenda 拉丁文 ,意即外生殖器官,乃源自「pudendum [ 23] 陰部管 班傑明·阿爾科克 羅伯特·本特利·托德 The Cyclopædia of Anatomy and Physiology ) 一書中,於描述髂動脈群 [ 24]
男性骨盆,陰部神經位於圖中右方。
陰部神經支配構造模式圖。
男性骨盆的陰部神經路徑圖。
本條目使用了部分解剖術語
^ AMR Agur, AF Dalley, JCB Grant. Grant's atlas of anatomy 13th. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2013. ISBN 978-1-60831-756-1 ^ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Standring S (editor in chief). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice 39th. Elsevier. 2004. ISBN 978-0-443-06676-4 ^ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Shafik, A; el-Sherif, M; Youssef, A; Olfat, ES. Surgical anatomy of the pudendal nerve and its clinical implications. Clinical Anatomy. 1995, 8 (2): 110–5. PMID 7712320 doi:10.1002/ca.980080205 ^ Moore, Keith L. Moore, Anne M.R. Agur ; in collaboration with and with content provided by Arthur F. Dalley II ; with the expertise of medical illustrator Valerie Oxorn and the developmental assistance of Marion E. Essential clinical anatomy 3rd. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2007. ISBN 978-0-7817-6274-8 ^ Russell RM. Examination of peripheral nerve injuries an anatomical approach . Stuttgart: Thieme. 2006. ISBN 978-3-13-143071-7 ^ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 Wolff BG et al. (编). The ASCRS textbook of colon and rectal surgery . New York: Springer. 2007. ISBN 0-387-24846-3 ^ TL King; MC Brucker; JM Kriebs; JO Fahey. Varney's midwifery Fifth. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. 2013. ISBN 978-1-284-02542-2 ^ Nayak, Soubhagya R.; Madhan Kumar, S.J.; Krishnamurthy, Ashwin; Latha Prabhu, V.; D'costa, Sujatha; Jetti, Raghu. Unusual origin of dorsal nerve of penis and abnormal formation of pudendal nerve—Clinical significance. Annals of Anatomy - Anatomischer Anzeiger. November 2006, 188 (6): 565–566. doi:10.1016/j.aanat.2006.06.011 ^ Neill, editor-in-chief, Jimmy D. Knobil and Neill's physiology of reproduction 3rd. Amsterdam: Elsevier. 2006. ISBN 0-12-515400-3 ^ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul. Gray's anatomy for students . Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. 2005. ISBN 978-0-8089-2306-0 ^ 11.0 11.1 Ort, Bruce Ian Bogart, Victoria. Elsevier's integrated anatomy and embryology . Philadelphia, Pa.: Elsevier Saunders. 2007. ISBN 978-1-4160-3165-9 ^ Babayan, Mike B. Siroky, Robert D. Oates, Richard K. Handbook of urology diagnosis and therapy 3rd. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2004. ISBN 978-0-7817-4221-4 ^ Penson, David F. Male Sexual Function: A Guide to Clinical Management. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2002. ^ Guaderrama, Noelani M.; Liu, Jianmin; Nager, Charles W.; Pretorius, Dolores H.; Sheean, Geoff; Kassab, Ghada; Mittal, Ravinder K. Evidence for the Innervation of Pelvic Floor Muscles by the Pudendal Nerve . Obstetrics & Gynecology. October 2005, 106 (4): 774–781. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000175165.46481.a8 ^ Fowler, CJ; Griffiths, D; de Groat, WC. The neural control of micturition . Nat. Rev. Neurosci. June 2008, 9 : 453–66. PMC 2897743 PMID 18490916 doi:10.1038/nrn2401 ^ Lynna Y. Littleton; Joan Engebretson. Maternal, Neonatal, and Women's Health Nursing, Volume 1. Cengage Learning. 2002: 727. ^ Satpathy, Hemant K.; et al. Isaacs, Christine; et al , 编. Transvaginal Pudendal Nerve Block . WebMD LLC. [2015-07-19 ] . (原始内容存档 于2019-07-28). ^ Mellion MB. Common cycling injuries. Management and prevention. Sports Med. January 1991, 11 (1): 52–70. PMID 2011683 doi:10.2165/00007256-199111010-00004 ^ Lim, Jit F.; Tjandra, Joe J.; Hiscock, Richard; Chao, Michael W. T.; Gibbs, Peter. Preoperative Chemoradiation for Rectal Cancer Causes Prolonged Pudendal Nerve Terminal Motor Latency. Diseases of the Colon & Rectum: 12–19. doi:10.1007/s10350-005-0221-7 ^ Calvillo O, Skaribas IM, Rockett C.; Skaribas; Rockett. Computed tomography-guided pudendal nerve block. A new diagnostic approach to long-term anoperineal pain: a report of two cases. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2000, 25 (4): 420–3. PMID 10925942 doi:10.1053/rapm.2000.7620 ^ Hough DM, Wittenberg KH, Pawlina W, Maus TP, King BF, Vrtiska TJ, Farrell MA, Antolak SJ Jr.; Wittenberg; Pawlina; Maus; King; Vrtiska; Farrell; Antolak Jr. Chronic perineal pain caused by pudendal nerve entrapment: anatomy and CT-guided perineural injection technique . Am J Roentgenol. 2003, 181 (2): 561–7. PMID 12876048 doi:10.2214/ajr.181.2.1810561 ^ 22.0 22.1 G.A. Santoro, A.P. Wieczorek, C.I. Bartram (editors). Pelvic floor disorders imaging and multidisciplinary approach to management. Dordrecht: Springer. 2010. ISBN 978-88-470-1542-5 ^ Harper, Douglas. Pudendum . Online Etymology Dictionary. [2014-02-28 ] . (原始内容存档 于2017-01-18). ^ Oelhafen, Kim; Shayota, Brian J.; Muhleman, Mitchel; Klaassen, Zachary; Tubbs, R. Shane; Loukas, Marios. Benjamin Alcock (1801-?) and his canal. Clinical Anatomy. 2013-09, 26 (6): 662–666. PMID 22488487 doi:10.1002/ca.22080