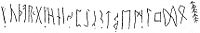|
Tiwaz (rune)
The t-rune ᛏ is named after Týr, and was identified with this god. The reconstructed Proto-Germanic name is *Tîwaz or *Teiwaz. Tiwaz rune was an ideographic symbol for a spear.[citation needed] Rune poemsTiwaz is mentioned in all three rune poems. In the Icelandic and Norwegian poems, the rune is associated with the god Týr.
UsageAncientMultiple Tiwaz runesMultiple Tiwaz runes either stacked atop one another to resemble a tree-like shape, or repeated after one another, appear several times in Germanic paganism:
Poetic Edda According to the runologist Lars Magnar Enoksen, the Tiwaz rune is referred to in a stanza in Sigrdrífumál, a poem in the Poetic Edda.[7] Sigrdrífumál tells that Sigurd has slain the dragon Fafnir and arrives at a fortress of shields on top of a mountain which is lit by great fires.[8] In the fortress, he finds an enchanted sleeping valkyrie whom he wakes by cutting open her corslet with his sword. The grateful valkyrie, Sigrdrífa, offers him the secrets of the runes in return for delivering her from the sleep, on condition that he shows that he has no fear.[7] She begins by teaching him that if he wants to achieve victory in battle, he is to carve "victory runes" on his sword and twice say the name "Týr" - the name of the Tiwaz rune.[7]
Name in FuthorcFuthorc manuscripts give different names to the t-rune. Sangallensis 270 (9th century) and Vindobonensis 795 (9th century) call the rune "Ti", while Cotton MS Domitian A IX (10th century?) calls it "Tir", and the Byrhtferth's Manuscript (12th century) calls it "Tyr". Ti may be an uninflected form of the possessive "Tiwes" as found in "Tiwesdæg", which would make it the name of an English god. Similar spellings of this god's name (such as Tii) are attested to in Old English.[11] ModernGermanic neopaganismThe Týr rune is commonly used by Germanic neopagans to symbolize veneration of the god Týr. Usage in Nazism and Neo-Nazism The Týr rune in Guido von List's Armanen Futharkh was based on the version found in the Younger Futhark. List's runes were later adopted and modified by Karl Maria Wiligut, who was responsible for their adoption by the Nazis, and they were subsequently widely used on insignia and literature during the Third Reich. It was the badge of the Sturmabteilung training schools, the Reichsführerschulen in Nazi Germany. In World War II, it was adopted as the unit insignia of the 32nd SS Volunteer Grenadier Division "30 Januar".  In Neo-Nazism it has appeared, together with the Sowilo rune, in the emblem of the Kassel-based think tank Thule Seminar. It has also appeared as the former logo of the fashion label Thor Steinar, which was banned in Germany over resemblance to SS officer uniforms,[12] and the Scandinavia-based Nordic Resistance Movement which uses the symbol onto a diamond with stripes (in the same shape as the Hitlerjugend flag) in green, white, and black. (It might also be noted that both these uses were technically incorrect, since both Thor and Thule would be spelled with a thurisaz, ᚦ, rune.) The symbol was one of the numerous Nazi/neo-Nazi and fascist symbols/slogans used by the perpetrator of the Christchurch mosque shootings Brenton Harrison Tarrant alongside the Black Sun, the Othala/Odal rune, the Celtic Cross, the Kolovrat swastika, the Fourteen Words, and the Archangel Michael's Cross of the pro-Nazi Romanian organization Iron Guard.[13] OlympicsIn 2018 the symbol was incorporated on the sweaters of the 2018 Norwegian Alpine ski team.[14] The sweaters were however quickly pulled from market, when the Nazi and far-right association raised controversy.[15] Popular culture
See alsoReferences
Bibliography
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia