|
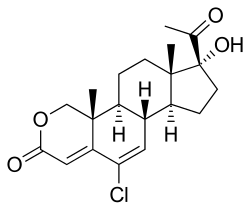
Osaterone
Osaterone (developmental code name TZP-5258), also known as 17α-hydroxy-6-chloro-2-oxa-6-dehydroprogesterone, as well as 2-oxachloromadinone, is a steroidal antiandrogen and progestin that was never marketed.[1][2] The C17α acetate ester of osaterone, osaterone acetate, in contrast, has been marketed.[1][2] References
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||