|
Ice shelf An ice shelf is a large platform of glacial ice floating on the ocean, fed by one or multiple tributary glaciers. Ice shelves form along coastlines where the ice thickness is insufficient to displace the more dense surrounding ocean water. The boundary between the ice shelf (floating) and grounded ice (resting on bedrock or sediment) is referred to as the grounding line; the boundary between the ice shelf and the open ocean (often covered by sea ice) is the ice front or calving front. Ice shelves are found in Antarctica and the Arctic (Greenland, Northern Canada, and the Russian Arctic), and can range in thickness from about 100–1,000 m (330–3,280 ft). The world's largest ice shelves are the Ross Ice Shelf and the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf in Antarctica. The movement of ice shelves is principally driven by gravity-induced pressure from the grounded ice.[1] That flow continually moves ice from the grounding line to the seaward front of the shelf. Typically, a shelf front will extend forward for years or decades between major calving events (calving is the sudden release and breaking away of a mass of ice from a glacier, iceberg, ice front, ice shelf, or crevasse).[2][3] Snow accumulation on the upper surface and melting from the lower surface are also important to the mass balance of an ice shelf. Ice may also accrete onto the underside of the shelf. The effects of climate change are visible in the changes to the cryosphere, such as reduction in sea ice and ice sheets, and disruption of ice shelves. In the last several decades, glaciologists have observed consistent decreases in ice shelf extent through melt, calving, and complete disintegration of some shelves. Well studied examples include disruptions of the Thwaites Ice Shelf, Larsen Ice Shelf, Filchner–Ronne Ice Shelf (all three in the Antarctic) and the disruption of the Ellesmere Ice Shelf in the Arctic. Definition  An ice shelf is "a floating slab of ice originating from land of considerable thickness extending from the coast (usually of great horizontal extent with a very gently sloping surface), resulting from the flow of ice sheets, initially formed by the accumulation of snow, and often filling embayments in the coastline of an ice sheet."[4]: 2234 In contrast, sea ice is formed on water, is much thinner (typically less than 3 m (9.8 ft)), and forms throughout the Arctic Ocean. It is also found in the Southern Ocean around the continent of Antarctica. The term captured ice shelf has been used for the ice over a subglacial lake, such as Lake Vostok. Properties Ice shelves are thick plates of ice, formed continuously by glaciers, that float atop an ocean. The shelves act as "brakes" for the glaciers. These shelves serve another important purpose—"they moderate the amount of melting that occurs on the glaciers' surfaces. Once their ice shelves are removed, the glaciers increase in speed due to meltwater percolation and/or a reduction of braking forces, and they may begin to dump more ice into the ocean than they gather as snow in their catchments. Glacier ice speed increases are already observed in Peninsula areas where ice shelves disintegrated in prior years."[5] HeightThe density contrast between glacial ice and liquid water means that at least 1/9 of the floating ice is above the ocean surface, depending on how much pressurized air is contained in the bubbles within the glacial ice, stemming from compressed snow. The formula for the denominators above is , density of cold seawater is about 1028 kg/m3 and that of glacial ice from about 850 kg/m3[6][7] to well below 920 kg/m3, the limit for very cold ice without bubbles.[8][9] The height of the shelf above the sea can be even larger, if there is much less dense firn and snow above the glacier ice. By country or regionAntarctica A large portion of the Antarctic coastline has ice shelves attached.[11] Their aggregate area is over 1,550,000 square kilometers (600,000 square miles).[12] It has been found that of all the ice shelves on Earth, nearly all of them are in Antarctica.[13]: 2234 In steady state, about half of Antarctica's ice shelf mass is lost to basal melt and half is lost to calving, but the relative importance of each process varies significantly between ice shelves.[14][15] In recent decades, Antarctica's ice shelves have been out of balance, as they have lost more mass to basal melt and calving than has been replenished by the influx of new ice and snow.[16] Ross Ice Shelf The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (as of 2013[update], an area of roughly 500,809 square kilometres (193,363 sq mi)[17] and about 800 kilometres (500 mi) across: about the size of France).[18] It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than 600 kilometres (370 mi) long, and between 15 and 50 metres (50 and 160 ft) high above the water surface.[19] Ninety percent of the floating ice, however, is below the water surface. Most of the Ross Ice Shelf is in the Ross Dependency claimed by New Zealand. It floats in, and covers, a large southern portion of the Ross Sea and the entire Roosevelt Island located in the east of the Ross Sea.Filchner–Ronne Ice Shelf
The seaward side of the Filchner–Ronne ice shelf is divided into Eastern (Filchner) and the larger Western (Ronne) sections by Berkner Island. The whole ice shelf covers some 430,000 km2, making it the second largest ice shelf in Antarctica (and on Earth), after the Ross Ice Shelf. It grows perpetually due to a flow of inland ice sheets. From time to time, when the shearing stresses exceed the strength of the ice, cracks form and large parts of the ice sheet separate from the ice shelf and float off and disperse as icebergs. This is known as calving. ArcticCanadaAll Canadian ice shelves are attached to Ellesmere Island and lie north of 82°N. Ice shelves that are still in existence are the Alfred Ernest Ice Shelf, Ward Hunt Ice Shelf, Milne Ice Shelf and Smith Ice Shelf. The M'Clintock Ice Shelf broke up from 1963 to 1966; the Ayles Ice Shelf broke up in 2005; and the Markham Ice Shelf broke up in 2008. The remaining ice shelves have also lost a significant amount of their area over time, with the Milne Ice Shelf being the last to be affected, with it breaking off in August 2020. RussiaThe Matusevich Ice Shelf was a 222 square kilometers (86 square miles) ice shelf located in Severnaya Zemlya being fed by some of the largest ice caps on October Revolution Island, the Karpinsky Ice Cap to the south and the Rusanov Ice Cap to the north.[20] In 2012 it ceased to exist.[21] Disruption due to climate change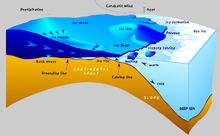  In the last several decades, glaciologists have observed consistent decreases in ice shelf extent through melt, calving, and complete disintegration of some shelves. Well studied examples include disruptions of the Thwaites Ice Shelf, Larsen Ice Shelf, Filchner–Ronne Ice Shelf (all three in the Antarctic) and the disruption of the Ellesmere Ice Shelf in the Arctic. The effects of climate change are visible in the changes to the cryosphere, such as reduction in sea ice and ice sheets, and disruption of ice shelves. Disruption of Thwaites Ice Shelf Thwaites Ice Shelf (), is an Antarctic ice shelf in the Amundsen Sea. It was named by ACAN[22] after Fredrik T. Thwaites, a glacial geologist and geomorphologist. The Thwaites Ice Shelf is one of the biggest ice shelves in West Antarctica, though it is highly unstable and disintegrating rapidly.[23][24] Since the 1980s, the Thwaites Glacier, nicknamed the "Doomsday glacier",[25] has had a net loss of over 600 billion tons of ice, though pinning of the Thwaites Ice Shelf has served to slow the process.[26] The Thwaites Ice Shelf has acted like a dam for the eastern portion of glacier, bracing it and allowing for a slow melt rate, in contrast to the undefended western portion.[25][27] According to the American Geophysical Union in a 2021 study, the Thwaites Eastern Ice Shelf (TEIS) buttresses one-third of Thwaites glacier. Removal of the shelf has the potential to increase the contribution of Thwaites glacier to sea level rise by up to 25%.[28] As of 2021[update], the ice shelf appears to be losing its grip on a submarine shoal that acts as a pinning point and the shear margin that separates the Thwaites Eastern Ice Shelf from the Thwaites glacier Tongue has extended, further weakening the ice shelf connection to the pinning point.[28] A sequence of Sentinel-1 radar imagery shows that parallel wing and comb cracks have recently formed rifts at high angles to the main shear margin and are propagating into the central part of the ice shelf at rates as high as 2 km per year. Satellite data, ground-penetrating radar, and GPS measurements taken in 2021 indicate that collapse of the ice shelf may be initiated by intersection of rifts with hidden basal crevasse zones as soon as 2026.[28] Complete melting of Thwaites glacier is predicted to increase global sea levels by 65 cm (2.13 ft) according to the European Geosciences Union,[29] and the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences states that the collapse of Thwaites glacier could ultimately lead to sea-level rise of up to 3 meters[30] if it draws the Pine Island and surrounding glaciers with it, due to marine ice sheet instability. However, both of these processes would take time: a Science Magazine interview with the International Thwaites Glacier Collaboration researchers who had discovered the impending collapse of the ice shelf noted that the glacier itself would still take approximately several centuries to collapse even without the ice shelf,[31] and a 2022 assessment of tipping points in the climate system stated that while the West Antarctic Ice Sheet may be committed to disintegration at between 1°C and 3°C, the timescale for its collapse after that ranges between 500 and 13,000 years, with the most likely estimate of 2000 years.[32][33]Disruption of Larsen Ice ShelfTwo sections of Antarctica's Larsen Ice Shelf broke apart into hundreds of unusually small fragments (hundreds of meters wide or less) in 1995 and 2002, Larsen C calved a huge ice island in 2017.[34]  Disruption of Larsen B Ice Shelf From 31 January 2002 to March 2002 the Larsen B sector partially collapsed and parts broke up, 3,250 km2 (1,250 sq mi) of ice 220 m (720 ft) thick, an area comparable to the US state of Rhode Island.[37] In 2015, a study concluded that the remaining Larsen B ice-shelf would disintegrate by 2020, based on observations of faster flow and rapid thinning of glaciers in the area.[38] Larsen B was stable for at least 10,000 years, essentially the entire Holocene period since the last glacial period.[39] By contrast, Larsen A was absent for a significant part of that period, reforming about 4,000 years ago. Despite its great age, the Larsen B was clearly in trouble at the time of the collapse. With warm currents eating away the underside of the shelf, it had become a "hotspot of global warming".[40] It broke over a period of three weeks or less, with a factor in this fast break-up being the powerful effects of water; ponds of meltwater formed on the surface during the near 24 hours of daylight in the summertime, flowed down into cracks and, acting like a multitude of wedges, levered the shelf apart.[41][42] Other likely factors in the break-up were the higher ocean temperatures and the decline of the ice of the peninsula.[43] In the austral winter of 2011, a large expanse of sea ice formed over the embayment that was once covered by the land-fast shelf of fresh-water glacial ice of Larsen B. This enormous ice pack persisted through January 2022 when it suddenly broke-up over the course of a few days, "taking with it a Philadelphia-sized piece of the Scar Inlet Ice Shelf," according to NASA scientists examining images from the Terra and Aqua satellites.[44]Disruption of Filchner–Ronne Ice ShelfIn October 1998, the iceberg A-38 broke off the Filchner–Ronne ice shelf. It had an extent of roughly 150 by 50 km and was thus larger than Delaware. It later broke up again into three parts. A similar-sized calving in May 2000 created an iceberg 167 by 32 km in extent, dubbed A-43 – the disintegration of this is thought to have been responsible for the November 2006 sighting of several large icebergs from the coast of the South Island of New Zealand, the first time since 1931 that any icebergs had been observed from the New Zealand mainland. A large group of small icebergs (the largest some 1000 metres in length), were seen off the south-east coast of the island, with one of them drifting close enough to shore to be visible from the hills above the city of Dunedin. If these were indeed the remnants of this calving, then over the course of five and a half years they had travelled slowly north and also east around over half the globe, a journey of some 13,500 km.[45] From January 12 and January 13, 2010, an area of sea ice larger than the state of Rhode Island, or one-seventh the size of Wales, broke away from the Ronne–Filchner Ice Shelf and shattered into many smaller pieces. The Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites captured this event in this series of photo-like images.[46] In May 2021, Iceberg A-76 broke off the northwest corner of the shelf. At 4320 km2,[47] it is larger than Majorca, several times larger than Iceberg A-74 which calved in the same year, or approximately 14% the size of Belgium. The ice of the Filchner–Ronne ice shelf can be as thick as 600 m; the water below is about 1400 m deep at the deepest point. The international Filchner–Ronne Ice Shelf Programme (FRISP) was initiated in 1973 to study the ice shelf.[48] A study published in Nature in 2012 by scientists from the Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research in Germany, and funded by the Ice2Sea initiative, predicts the disappearance of the 450,000 km2 (170,000 sq mi) vast ice shelf in Antarctica by the end of the century which could – indirectly – add up to 4.4 mm (0.17 in) of rise of sea level each year.[49]Other ice shelves in Antarctica
Disruption of Ellesmere Ice Shelf (Arctic)The Ellesmere ice shelf was reduced by 90% in the twentieth century, leaving the separate Alfred Ernest, Ayles, Milne, Ward Hunt, and Markham ice shelves. A 1986 survey of Canadian ice shelves found that 48 km2 (3.3 cubic kilometres) of ice calved from the Milne and Ayles ice shelves between 1959 and 1974.[56] The Ayles Ice Shelf calved entirely on August 13, 2005. The Ward Hunt Ice Shelf, the largest remaining section of thick (>10 meters (33 feet)) landfast sea ice along the northern coastline of Ellesmere Island, lost 600 square kilometers (230 square miles) of ice in a massive calving in 1961–1962.[57] It further decreased by 27% in thickness (13 meters (43 feet)) between 1967 and 1999.[58] In the summer of 2002, the Ward Ice Shelf experienced another major breakup,[59] and other instances of note happened in 2008 and 2010 as well.[60] The last remnant to remain mostly intact, the Milne Ice Shelf, also ultimately experienced a major breakup at the end of July 2020, losing over 40% of its area.[61] The Ellesmere Ice Shelf was the largest ice shelf in the Arctic, encompassing about 9,100 square kilometres (3,500 square miles) of the north coast of Ellesmere Island, Nunavut, Canada.[62] The ice shelf was first documented by the British Arctic Expedition of 1875–76, in which Lieutenant Pelham Aldrich's party went from Cape Sheridan to Cape Alert.[63] The continuous mass of the Ellesmere Ice Shelf had been in place for at least 3,000 years.[62] During the twentieth century, the Ellesmere Ice Shelf broke up into six separate shelves. From west to east, these were the Serson Ice Shelf, Petersen Ice Shelf, Milne Ice Shelf, Ayles Ice Shelf, Ward Hunt Ice Shelf, and Markham Ice Shelf.[64] The smaller pieces continued to disintegrate. In April 2000, satellite images revealed that a large crack in the Ward Hunt shelf had begun to form, and in 2003 it was announced that the ice sheet had split completely in two in 2002, releasing a huge pool of freshwater from the largest epishelf lake in the Northern Hemisphere, located in Disraeli Fjord.[65] In April 2008, scientists discovered that the shelf fractured into dozens of deep, multi-faceted cracks.[66] On August 13, 2005, The Ayles Ice Shelf, which was located approximately 800 km (500 mi) south of the North Pole, broke away from the coast forming the giant Ayles Ice Island 37 metres (121 ft) thick and measuring around 14 by 5 km (8.7 by 3.1 mi) in size with an area of approximately 66 km2 (25 sq mi) or 2.6 km3 (0.62 cu mi) in volume.[62] The Milne Ice Shelf was the second largest segment of the former Ellesmere Ice Shelf. It suffered a 40% disintegration in July 2020 with the loss of a research camp, including instruments for measuring water flow.[67]See also
References
External linksWikimedia Commons has media related to Ice shelf.
|
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia
![{\textstyle 1/[(\rho _{\text{seawater}}-\rho _{\text{glacial ice}})/\rho _{\text{seawater}}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/02e22308ac32b259522cb8711cb12cf7991284f2)