|
Fully qualified domain name
A fully qualified domain name (FQDN), sometimes also called an absolute domain name,[1] is a domain name that specifies its exact location in the tree hierarchy of the Domain Name System (DNS). It specifies all domain levels, including the top-level domain and the root zone.[2] A fully qualified domain name is distinguished by its lack of ambiguity in terms of DNS zone location in the hierarchy of DNS labels: it can be interpreted only in one way. Definition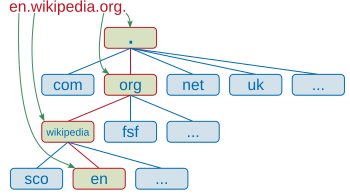 A fully qualified domain name is conventionally written as a list of domain labels separated using the full stop " The topmost layer of every domain name is the DNS root zone, which is expressed as an empty label and can be represented in an FQDN with a trailing dot, such as The length of each label must be between 1 and 63 octets, and the full domain name is limited to 255 octets, full stops included.[3] Relative domain namesA relative domain name is a domain name which does not include all labels.[5] It may also be referred to as a partially-qualified domain name, or PQDN.[6] Hostnames can be used as relative domain names. UsageDot-separated fully qualified domain names are the primarily used form for human-readable representations of a domain name. Dot-separated domain names are not used in the internal representation of labels in a DNS message[7] but are used to reference domains in some TXT records and can appear in resolver configurations, system hosts files, and URLs. Web addresses typically use FQDNs to represent the host, as it ensures the address will be interpreted identically on any network. Relative hostnames are allowed by some protocols, including HTTP, but disallowed by others, such as the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).[8] References
External links
|
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia