Antonín Novotný
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

1964 American film directed by Delbert Mann For other uses, see Dear Heart (disambiguation). Dear HeartTheatrical release posterDirected byDelbert MannWritten byTad MoselProduced byMartin ManulisStarringGlenn FordGeraldine PageAngela LansburyMichael Anderson Jr.Barbara NicholsCinematographyRussell HarlanEdited byFolmar BlangstedMusic byHenry ManciniDistributed byWarner Bros.Release date December 3, 1964 (1964-12-03) (U.S.)[1] Running time113 minutesCountryUnited States…

Kabupaten DeiyaiKabupatenDanau Tigi LambangMotto: Dou Gaii EkowaiiPetaKabupaten DeiyaiPetaTampilkan peta Maluku dan PapuaKabupaten DeiyaiKabupaten Deiyai (Indonesia)Tampilkan peta IndonesiaKoordinat: 4°10′26″S 136°26′13″E / 4.174°S 136.437°E / -4.174; 136.437Negara IndonesiaProvinsiPapua TengahTanggal berdiri26 November 2008[1]Dasar hukumUU Nomor 55 Tahun 2008[1]Ibu kotaTigiJumlah satuan pemerintahan Daftar Distrik: 5Kampung: 67 Pemer…

1945 foundational treaty of the United Nations Charter of the United NationsUN CharterDrafted14 August 1941Signed26 June 1945 (1945-06-26)LocationSan Francisco, California, United StatesEffective24 October 1945ConditionRatification by China, France, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, the United States and by a majority of the other signatory states.Parties193DepositaryInternationalLanguagesArabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian, and SpanishFull text Charter of the United Nat…

Overview of the presence, role and impact of Hinduism in Canada Canadian HindusHindu Heritage Centre in MississaugaTotal population 828,195 (2021)[1] 2.3% of the Canadian PopulationRegions with significant populationsOntario573,700British Columbia81,320Alberta78,520Quebec47,390Manitoba18,355ReligionsHinduismMajority:VaishnavismMinority:ShaivismLanguagesOfficialCanadian English, Canadian French HomeTamil • Hindi • Punjabi • Gujarati •…

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: List of active separatist movements in Asia – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2019) (Learn …
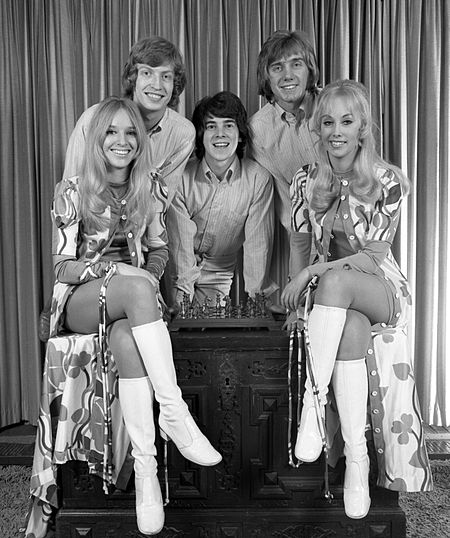

English film director and producer (born 1949) Nigel LythgoeOBELythgoe in 2010Born (1949-07-09) 9 July 1949 (age 74)Wallasey, Cheshire, EnglandOccupations Television director film director television producer film producer screenwriter television personality choreographer former dancer Years active1969–presentSpouse Bonnie Shawe (m. 1974; div. 2010)ChildrenSimon & Kris Nigel Lythgoe OBE (/ˈlɪθɡoʊ/; born 9 July 1949)[1&#…

Annual ranking of countries by Legatum The Legatum Prosperity Index is an annual ranking developed by the Legatum Institute, an independent educational charity founded and part-funded by the private investment firm Legatum. The ranking is based on a variety of factors including wealth, economic growth, education, health, personal well-being, and quality of life. As of the 2021 rankings, 167 countries and territories were ranked, and Denmark topped the list, followed by its Nordic neighbours Norw…

Ongoing COVID-19 pandemic in North Korea This article needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (December 2022) COVID-19 pandemic in North KoreaDiseaseCOVID-19Virus strainSARS-CoV-2LocationNorth KoreaFirst outbreakWuhan, Hubei, ChinaIndex casePyongyangArrival date8 May 2022 (2022-05-08) (2 years, 1 month and 6 days ago)[1]Confirmed cases168[2]Deaths74[a][3][4]…
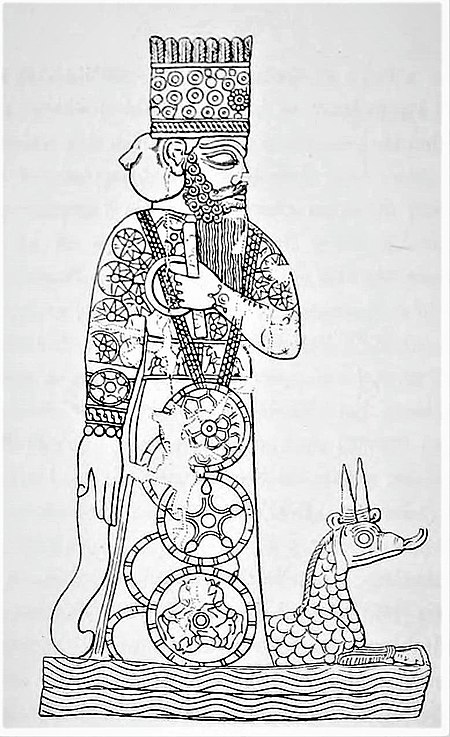
Patung Marduk digambarkan berada di atas naga Marduk, Mušḫuššu Patung Marduk, juga dikenal sebagai Patung Bêl (Bêl),[1] adalah perwakilan fisik dari dewa Marduk, dewa penjaga kota kuno Babel, yang secara tradisional disimpan di kuil utama kota tersebut, Esagila. Terdapat tujuh patung Marduk di Babel, namun 'satu' Patung Marduk umum disebut sebagai patung utama dewa tersebut, yang utamanya ditempatkan di Esagila dan dipakai dalam upacara-upacara di kota tersebut. Patung tersebut di…

Excavation method using explosives This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Drilling and blasting – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Rock blasting in Finland Drilling and blasting is the controlled use of explosives and other methods,…

بنك إيطاليا البلد إيطاليا المقر روما تاريخ إنشاء 10 أغسطس 1893[1] الرئيس فابيو بانيتا (1 نوفمبر 2023–) العملة يورو الموقع الالكتروني الموقع الرسمي نظام البنوك المركزية الأوروبي تعديل مصدري - تعديل بنك إيطاليا والمعروف باللغة الإيطالية كما (ب�…

Mick SchumacherMick Schumacher di tahun 2019.Lahir22 Maret 1999 (umur 25)[1][2]Vufflens-le-Château, SwissPekerjaanPembalap mobilTinggi176 cm (5 ft 9 in)Berat67 kg (148 pon)Orang tuaMichael Schumacher (bapak)Corinna Betsch (ibu)KerabatGina-Maria Schumacher (kakak)Ralf Schumacher (paman)David Schumacher (sepupu)Karier Kejuaraan Dunia Formula SatuKebangsaan JermanTahun aktif2021–2022Tim 2023Mercedes (sebagai pembalap cadangan)Nomor mobil47Jumlah lomb…

اتحاد موريشيوس لكرة القدم (بالإنجليزية: Mauritius Football Association)، و(بالفرنسية: Fédération de Maurice de football) الاسم المختصر MFA الرياضة كرة القدم أسس عام 1952 المقر مقاطعة بلينز ويلهمز الانتسابات الفيفا : 1962 الاتحاد الأفريقي : 1963 رمز الفيفا MRI الموقع الرسمي www.mfa.mu تعديل مصدري - ت�…

Facade of the market The Ciudadela Market is a traditional style Mexican market which specializes in the sale of Mexican handcrafts and folk art, located in the southwest corner of the historic center of Mexico City. The market is the first of its kind in the country, established just before the 1968 Summer Olympics to promote this aspect of Mexico's cultural heritage. It is home to over 350 vendors, mostly small operators selling to Mexican and foreign tourists. The site The market is located i…

阿尔莫罗斯Almorox市镇阿尔莫罗斯在西班牙的位置坐标:40°13′57″N 4°23′31″W / 40.2325°N 4.3919444444444°W / 40.2325; -4.3919444444444国家西班牙自治区卡斯蒂利亚-拉曼恰省托莱多省面积 • 总计65 平方公里(25 平方英里)人口(2001) • 總計2,166人 • 密度33.3人/平方公里(86.3人/平方英里)时区CET(UTC+1) • 夏时制CEST(UTC+2) 阿�…

Sporting event delegationBotswana at theParalympicsIPC codeBOTNPCParalympic Association of BotswanaMedals Gold 1 Silver 0 Bronze 0 Total 1 Summer appearances200420082012201620202024 Botswana made its Paralympic Games début at the 2004 Summer Paralympics in Athens, sending a single representative (Tshotlego Morama) to compete in athletics. Morama entered only the women's 400m T46 sprint, and won gold, setting a world record time of 55.99. No further athletes from Botswana have competed at the Su…

第三十二届夏季奥林匹克运动会女子87公斤以上級舉重比賽比賽場館東京國際論壇日期2021年8月2日参赛选手14位選手,來自14個國家和地區冠军成绩320 kg OR奖牌获得者01 ! 李雯雯 中国02 ! 埃米莉·坎贝尔 英国03 ! 萨拉·罗布尔斯 美国← 20162024 → 2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会举重比赛男子女子61公斤级49公斤级67公斤级55公斤级73公斤级59公斤级81公斤�…

University of Durhambahasa Latin: Universitas Dunelmensīs Lambang kebesaran Universitas Durham Tampilkan peta yang diperbesarTampilkan peta yang diperkecil InformasiNama lainThe Warden, Masters and Scholars of the University of Durham[1]Motobahasa Latin: Fundamenta eius super montibus sanctis (dari Mazmur 87:1)Moto dalam bahasa InggrisHer foundations are upon the holy hills (Landasannya berada di atas bukit-bukit suci)JenisRiset publik kolegiatDidirikan1832; 1…

撒奇萊雅族Sakizaya火神祭(Palamal)總人口約1,099人(2024年5月)[1]分佈地區花蓮縣豐濱鄉磯奇部落語言撒奇萊雅語、中華民國國語宗教信仰撒奇萊雅族傳統信仰相关族群 噶瑪蘭族、阿美族 和其他「臺灣原住民」都屬於「台灣南島民族」 和島嶼東南亞、非洲馬達加斯加島、以及大洋洲密克羅尼西亞、美拉尼西亞、波里尼西亞的「南島民族」相關 撒奇萊雅族 (撒奇萊雅語:Saki…

Indian actress Not to be confused with Padmapriya, yesteryear Kannada actress. This biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification. Please help by adding reliable sources. Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately from the article and its talk page, especially if potentially libelous.Find sources: Padmapriya Janakiraman – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (…



