|
| Strukturformel
|

|
| Allgemeines
|
| Name
|
1,3-Indandion
|
| Andere Namen
|
- 1,3-Dioxoindan
- 1,3-Diketohydrinden
- 1,3-Hydrindendion
|
| Summenformel
|
C9H6O2
|
| Kurzbeschreibung
|
gelbes Pulver[1]
|
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken
|
|
|
| Eigenschaften
|
| Molare Masse
|
146,14 g·mol−1
|
| Aggregatzustand
|
fest
|
| Dichte
|
1,37 g·cm−3[2]
|
| Schmelzpunkt
|
129–132 °C[3]
|
| Dampfdruck
|
- 0,864 Pa (322,95 K)[4]
- 23,543 Pa (357,71 K)[4]
|
| pKS-Wert
|
7,2 (18 °C)[5]
|
| Löslichkeit
|
|
| Sicherheitshinweise
|
|
|
Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet.
Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen (0 °C, 1000 hPa).
|
1,3-Indandion ist ein Diketon aus der Gruppe der bicyclischen aromatischen Kohlenwasserstoffe.
Gewinnung und Darstellung
1,3-Indandion kann durch eine Claisen-Kondensation mit Diethylphthalat oder Dibutylphthalat als Ausgangsmaterial mit anschließender Hydrolyse und Decarboxylierung gewonnen werden.[6]
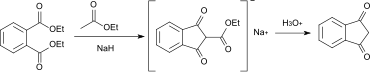
Die Oxidation von Indan mit Oxidationsmitteln wie z. B. Wasserstoffperoxid oder tert-Butylhydroperoxid verläuft nur mit schlechten Ausbeuten, als Hauptprodukt entsteht dabei 1-Indanon.[7]

Eigenschaften
Physikalische Eigenschaften
Die Bildungsenthalpie von 1,3-Indandion in der Gasphase bei 298,15 K beträgt −165,0 ± 2,6 kJ/mol, die Schmelzenthalpie 17,2 kJ/mol und die Verdampfungsenthalpie 72,6 kJ/mol.[4]
Chemische Eigenschaften
Im 1,3-Indandion-Molekül liegt eine Keto-Enol-Tautomerie vor[8]
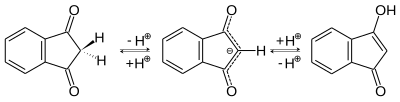
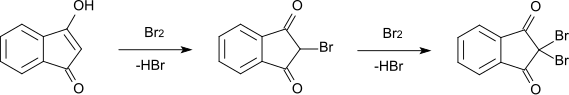
Die Bromierung von 1,3-Indandion zu 2-Brom-1,3-indandion (Schmelzpunkt 118–120 °C) verläuft über die Enolform unter Abspaltung von Bromwasserstoff. Auch eine weitere Bromierung zu 2,2-Dibrom-1,3-indandion[S 1] (Schmelzpunkt 181–182 °C) verläuft nach dem gleichen Mechanismus über die Enolform des Monobromderivats.[8]
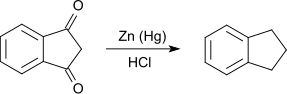
Die Reduktion von 1,3-Indandion nach Clemmensen mit amalgamiertem Zink in Salzsäure führt zum Indan. Als Nebenprodukt entsteht Inden.[9]
Katalytische ionische Hydrierung mit Triethylsilan und Trifluoressigsäure führt ebenfalls zum Indan.[10]
Wird die Reduktion mit Natriumborhydrid und Palladium als Katalysator durchgeführt, so geht die Reduktion nur bis zum 3-Hydroxy-1-indanon,[S 2] bzw. in weiterer Folge zum 1,3-Indandiol.[S 3][11]
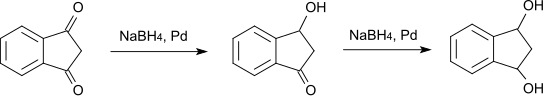
Auch die Reduktion mit Zinkstaub in Eisessig liefert 3-Hydroxy-1-indanon.[12]
Verwendung
1,3-Indandion kann durch Reaktion mit 1,1-Diphenylaceton[S 4] zu Diphacinon (einem Rodentizid) weiterverarbeitet werden.[13]

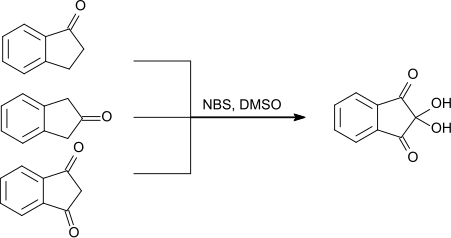
1,3-Indandion kann neben 1-Indanon und 2-Indanon[S 5] als Ausgangsstoff zur Herstellung von Ninhydrin eingesetzt werden. Als weitere Reagenzien werden N-Bromsuccinimid und Dimethylsulfoxid eingesetzt.[14]
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ a b c Datenblatt 1,3-Indanedione, 97% bei Alfa Aesar, abgerufen am 1. Dezember 2019 (Seite nicht mehr abrufbar).
- ↑ David R. Lide: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics A Ready-reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data. CRC Press, 1995, ISBN 978-0-8493-0595-5, S. 330 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- ↑ a b c Datenblatt 1,3-Indandione, 97% bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 1. Dezember 2019 (PDF).
- ↑ a b c M. A. Matos, M. S. Miranda, M. J. Monte, L. M. Santos, V. M. Morais, J. S. Chickos, P. Umnahanant, J. F. Liebman: Calorimetric and computational study of indanones (PDF-Datei; 102 kB), in: J. Phys. Chem. A, 2007, 111 (43), S. 11153–11159.
- ↑ C. F. Bernasconi, P. Paschalis: "Kinetics of ionization of 1,3-indandione in methyl sulfoxide-water mixtures. Solvent effect on intrinsic rates and Broensted coefficients", in: J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1986, 108 (11), S. 2969–2977, doi:10.1021/ja00271a027.
- ↑ cnki: Synthesis of 1,3-indandione
- ↑ J. Muzart: Homogeneous CrVI-Catalyzed Benzylic, Allylic and Propargylic Oxidations by tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide, in: Mini-Reviews in Organic Chemistry, 2009, (6), S. 9–20. doi:10.2174/157019309787316120
- ↑ a b D. Nematollahi, N. Akaberi: Electrochemical Study of Bromide in the Presence of 1,3-Indandione. Application to the Electrochemical Synthesis of Bromo Derivatives of 1,3-Indandione, in: Molecules, 2001, 6, S. 639–646.
- ↑ S. A. Galton, M. Kalafer, F. M. Beringer: Rearrangements in the Clemmensen reduction of 1-indanones and, 1,3-indandiones, in: J. Org. Chem., 1970, 35 (1), S. 1–6. doi:10.1021/jo00826a001
- ↑ O. K. Popova, Z. N. Parnes, M. I. Katinkin, S. M. Markosyan, N. I. Kopteva, L. P. Zalukaev, D. N. Kursanov: Ionic hydrogenation of 1,3-indanedione derivatives, in: Russian Chemical Bulletin, 1981, 30 (9), S. 1709–1711. doi:10.1007/BF00949478
- ↑ Patent US3992450A: 2,3-Disubstituted-1-indanones. Angemeldet am 30. April 1971, veröffentlicht am 16. November 1976, Anmelder: Du Pont, Erfinder: John Fred Neumer.
- ↑ S. M. Resnick, D. S. Torock, K. Lee, J. M. Brand, D. T. Gibson: Regiospecific and Stereoselective Hydroxylation of 1-Indanone and 2-Indanone by Naphthalene Dioxygenase and Toluene Dioxygenase (PDF-Datei; 1,34 MB) in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1994, 60 (9), S. 3323–3328.
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook, Verlag William Andrew, 1996. ISBN 978-0-8155-1401-5. S. 900 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- ↑ J. L. Hallman: Synthesis of Naphtho(f)ninhydrin and Synthesis of Polymer-supported Crown Ethers. Dissertation, 1991.
Anmerkungen
- ↑ Externe Identifikatoren von bzw. Datenbank-Links zu 2,2-Dibrom-1,3-indandion: CAS-Nr.: 1685-97-8, PubChem: 267415, Wikidata: Q82036250.
- ↑ Externe Identifikatoren von bzw. Datenbank-Links zu 3-Hydroxy-1-indanon: CAS-Nr.: 26976-59-0, PubChem: 176448, Wikidata: Q82927683.
- ↑ Externe Identifikatoren von bzw. Datenbank-Links zu 1,3-Indandiol: CAS-Nr.: 112166-53-7, Wikidata: Q131389099.
- ↑ Externe Identifikatoren von bzw. Datenbank-Links zu 1,1-Diphenylaceton: CAS-Nr.: 781-35-1, EG-Nr.: 212-307-9, ECHA-InfoCard: 100.011.189, PubChem: 69907, Wikidata: Q72472996.
- ↑ Externe Identifikatoren von bzw. Datenbank-Links zu 2-Indanon: CAS-Nr.: 615-13-4, EG-Nr.: 210-410-3, ECHA-InfoCard: 100.009.465, PubChem: 11983, ChemSpider: 11488, Wikidata: Q15906443.
|








