|
立毛肌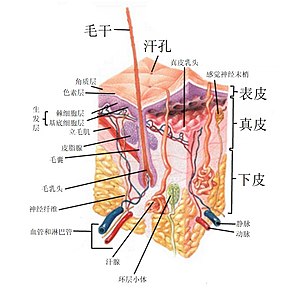 立毛肌,亦稱為豎毛肌 (Arrector pili muscle)是哺乳動物附著在毛囊上的小塊肌肉,這些肌肉的收縮會使毛髮直立[1],俗稱雞皮疙瘩(Goose bumps)。目前認為立毛肌在毛囊幹細胞微環境的組成中具有重要作用。立毛肌的離斷可能是與其連接的毛囊bulge區受損,以及毛囊前體細胞丟失的表現,可以被稱為是毛髮不可再生的標誌[2][3]。此外,毛囊單位中立毛肌的改變與雄激素源性脫髮(Androgenetic alopecia、AGA)病程演進的關係受到越來越多的關注[4],而AGA是一種雄激素依賴性疾病,表現為逐漸顯著的額顳部和頂部頭髮細軟、密度降低,以及髮際線後移[5]。 功能立毛肌由平滑肌纖維以束狀組成,受到自律神經系統的交感神經支配,故其收縮為非自主行為,例如寒冷、恐懼等壓力可能會刺激交感神經系統,從而引起收縮。立毛肌的收縮有許多目的。對於大部分的哺乳動物,其主要功能是提供絕緣。空氣被截留在直立的毛髮之間,從而幫助動物保持熱量。豪豬長而濃密的毛髮直立使它變得更具威嚇性,嚇走肉食性動物。皮脂因為立毛肌所施加的壓力,被迫沿著毛囊向表面移動,因而保護了頭髮。 除此之外,目前已有研究發現與立毛肌接觸面積越大的毛囊越能持久保持,而與立毛肌接觸面積越小的毛囊則更容易受到雄激素的刺激而轉變為毫毛[6]。 參考資料
|
Index:
pl ar de en es fr it arz nl ja pt ceb sv uk vi war zh ru af ast az bg zh-min-nan bn be ca cs cy da et el eo eu fa gl ko hi hr id he ka la lv lt hu mk ms min no nn ce uz kk ro simple sk sl sr sh fi ta tt th tg azb tr ur zh-yue hy my ace als am an hyw ban bjn map-bms ba be-tarask bcl bpy bar bs br cv nv eml hif fo fy ga gd gu hak ha hsb io ig ilo ia ie os is jv kn ht ku ckb ky mrj lb lij li lmo mai mg ml zh-classical mr xmf mzn cdo mn nap new ne frr oc mhr or as pa pnb ps pms nds crh qu sa sah sco sq scn si sd szl su sw tl shn te bug vec vo wa wuu yi yo diq bat-smg zu lad kbd ang smn ab roa-rup frp arc gn av ay bh bi bo bxr cbk-zam co za dag ary se pdc dv dsb myv ext fur gv gag inh ki glk gan guw xal haw rw kbp pam csb kw km kv koi kg gom ks gcr lo lbe ltg lez nia ln jbo lg mt mi tw mwl mdf mnw nqo fj nah na nds-nl nrm nov om pi pag pap pfl pcd krc kaa ksh rm rue sm sat sc trv stq nso sn cu so srn kab roa-tara tet tpi to chr tum tk tyv udm ug vep fiu-vro vls wo xh zea ty ak bm ch ny ee ff got iu ik kl mad cr pih ami pwn pnt dz rmy rn sg st tn ss ti din chy ts kcg ve
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia