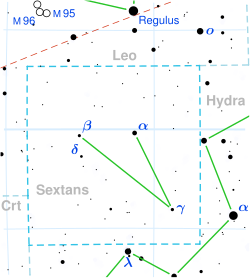
م‚چمپڈمپ¶م‚“مپژه؛§مƒ™مƒ¼م‚؟وکں
م‚چمپڈمپ¶م‚“مپژه؛§βوکں(م‚چمپڈمپ¶م‚“مپژمپ–مƒ™مƒ¼م‚؟مپ›مپ„م€پβ Sextantisم€پβ Sex)مپ¯م€پم‚چمپڈمپ¶م‚“مپژه؛§مپ®وپ’وکںمپ§مپ‚م‚‹[7]م€‚見مپ‹مپ‘مپ®ç‰ç´ڑمپ¯5.08مپ¨م€پو·،مپ„مپŒè‚‰çœ¼مپ§مپ؟مپˆم‚‹وکژم‚‹مپ•مپ§مپ‚م‚‹[1]م€‚ه¹´ه‘¨è¦–ه·®م‚’هں؛مپ«è¨ˆç®—مپ—مپںه¤ھ陽مپ‹م‚‰مپ®è·é›¢مپ¯م€پمپٹم‚ˆمپ367ه…‰ه¹´مپ§مپ‚م‚‹[3][و³¨ 1]م€‚
特ه¾´
م‚چمپڈمپ¶م‚“مپژه؛§βوکںمپ¯م€پè،¨é¢مپ®وœ‰هٹ¹و¸©ه؛¦مپ¯مپٹم‚ˆمپ13,800Kم€په…‰ه؛¦مپ¯ه¤ھ陽مپ®330ه€چ程ه؛¦مپ§م€پهچٹه¾„مپ¯ه¤ھ陽مپ®3.3ه€چم€پè³ھé‡ڈمپ¯ه¤ھ陽مپ®4ه€چ程ه؛¦مپ¨è¦‹ç©چم‚‚م‚‰م‚Œم‚‹[5][4]م€‚
و¨™و؛–وکں
م‚چمپڈمپ¶م‚“مپژه؛§βوکںمپ¯م€پé’مپ؟مپŒمپ‹مپ£مپںBه‹ن¸»ç³»هˆ—وکںمپ§م€پم‚¹مƒڑم‚¯مƒˆمƒ«ه‹مپ¯B6 Vمپ¨هˆ†é،مپ•م‚Œم‚‹[7][1]م€‚م‚چمپڈمپ¶م‚“مپژه؛§βوکںمپ¯م€پMKم‚¹مƒڑم‚¯مƒˆمƒ«هˆ†é،مپ«مپٹمپ„مپ¦م€پB6 Vه‹وکںمپ®ن¸€و¬،و¨™و؛–وکںمپ«éپ¸مپ°م‚Œمپ¦مپ„م‚‹[8]م€‚مپ¾مپںم€پم‚¹مƒˆمƒ¬مƒ م‚°مƒ¬مƒ³و¸¬ه…‰م‚·م‚¹مƒ†مƒ (英èھ版)مپ§م‚‚uvby4色و¸¬ه…‰م‚·م‚¹مƒ†مƒ م€پهڈٹمپ³βم‚·م‚¹مƒ†مƒ مپ®و¨™و؛–وکںمپ«ن½چç½®ن»کمپ‘م‚‰م‚Œمپ¦مپ„م‚‹[9][10]م€‚و›´مپ«م€پ視ç·ڑé€ںه؛¦و¸¬ه®ڑمپ®و¨™و؛–وکںمپ«م‚‚مپھمپ£مپ¦مپ„م‚‹[11]م€‚
ه¤‰ه…‰
و¨™و؛–وکںمپ§مپ‚مپ£مپںم‚چمپڈمپ¶م‚“مپژه؛§βوکںمپ¯م€پو•°ه¤ڑمپڈمپ®و¸¬ه…‰è¦³و¸¬مپŒè،Œم‚ڈم‚ŒمپںمپŒم€پو¸¬ه®ڑمپ•م‚Œمپںç‰ç´ڑمپ«مپ¯و–‡çŒ®مپ«م‚ˆمپ£مپ¦مپ°م‚‰مپ¤مپچمپŒمپ‚مپ£مپں[12]م€‚مپ°م‚‰مپ¤مپچمپ¯è¦³و¸¬è€…é–“مپ®éپ•مپ„مپ«م‚‚م‚ˆم‚‹مپ®مپ§م€پوکژم‚‹مپ•مپ®ه¤‰هŒ–مپ¯م€پمƒ‡مƒ¼م‚؟و•´ç´„ن¸ٹمپ®ه•ڈé،Œمپ‹مپ¨م‚‚و€م‚ڈم‚ŒمپںمپŒم€پن¸€é€£مپ®è¦³و¸¬مپ‹م‚‰ه…‰ه؛¦ه¤‰هŒ–م‚’و±‚م‚پم‚‹مپ¨م€پé–“éپ•مپ„مپھمپڈه¤‰ه…‰مپ—مپ¦مپ„م‚‹مپ“مپ¨مپŒم‚ڈمپ‹م‚ٹم€پç¢؛ه®ڑمپ—مپںه¤‰ه…‰وکںمپ¨مپ—مپ¦و‰±م‚ڈم‚Œمپ¦مپ„م‚‹[12][13][2]
م‚چمپڈمپ¶م‚“مپژه؛§βوکںمپ¯م€په¤‰ه…‰وکںç·ڈهگˆم‚«م‚؟مƒم‚°مپ§مپ¯م‚ٹم‚‡مپ†مپ‘م‚“ه؛§α2ه‹ه¤‰ه…‰وکںمپ‹م‚‚مپ—م‚Œمپھمپ„مپ¨مپ•م‚Œمپ¦مپ„م‚‹[2]م€‚مپ—مپ‹مپ—م€په¤‰ه…‰مپ®ه‘¨وœںم‚’هˆ†وگمپ™م‚‹مپ¨م€په‘¨وœںمپ¯ç´„15.4و—¥مپ¨مپھم‚ٹم€پè‡ھ転é€ںه؛¦مپ®و¸¬ه®ڑه€¤ï¼ˆ≥80 km/s)مپ‹م‚‰è¦‹ç©چم‚‚م‚‰م‚Œم‚‹è‡ھ転ه‘¨وœںمپ¨é£ںمپ„éپ•مپ†[13]م€‚م‚ٹم‚‡مپ†مپ‘م‚“ه؛§α2وکںمپ¯è‡ھ転مپ«ن¼´مپ£مپ¦ه¤‰و›´مپ™م‚‹ه›è»¢ه¤‰ه…‰وکںمپ®1種مپ§مپ‚م‚‹مپŒم€په¤‰ه…‰ه‘¨وœںمپŒو£مپ—مپ‘م‚Œمپ°م€په¤‰ه…‰مپ®مپ—مپڈمپ؟م‚’è‡ھ転مپ§èھ¬وکژمپ™م‚‹مپ“مپ¨مپ«مپ¯çں›ç›¾مپŒç”ںمپکم‚‹[14][13]م€‚
è„ڑو³¨
و³¨é‡ˆ
- ^ a b c مƒ‘مƒ¼م‚»م‚¯مپ¯1 أ· ه¹´ه‘¨è¦–ه·®ï¼ˆç§’)م‚ˆم‚ٹ計算م€په…‰ه¹´مپ¯1أ·ه¹´ه‘¨è¦–ه·®ï¼ˆç§’)أ—3.2615638م‚ˆم‚ٹ計算
- ^ 視ç‰ç´ڑ + 5 + 5أ—log(ه¹´ه‘¨è¦–ه·®ï¼ˆç§’))م‚ˆم‚ٹ計算م€‚ه°ڈو•°ç¬¬1ن½چمپ¾مپ§è،¨è¨ک
ه‡؛ه…¸
- ^ a b c d e f ESA (1997), The HIPPARCOS and TYCHO catalogues. Astrometric and photometric star catalogues derived from the ESA HIPPARCOS Space Astrometry Mission, ESA SP Series, 1200, Noordwijk, Netherlands: ESA Publications Division, Bibcode: 1997ESASP1200.....E, ISBN 9290923997
- ^ a b c Samus, N. N.; et al. (2009-01), “General Catalogue of Variable Starsâ€, VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/gcvs, Bibcode: 2009yCat....102025S
- ^ a b c d e f g “bet Sex -- alpha2 CVn Variableâ€. SIMBAD. CDS. 2023ه¹´8وœˆ2و—¥é–²è¦§م€‚
- ^ a b c Underhill, A. B. (1973), “A study of B6 starsâ€, Astronomy & Astrophysics 25: 161-174, Bibcode: 1973A&A....25..161U
- ^ a b c d e Zorec, J.; Royer, F. (2012-01), “Rotational velocities of A-type stars. IV. Evolution of rotational velocitiesâ€, Astronomy & Astrophysics 537: 120, Bibcode: 2012A&A...537A.120Z, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201117691
- ^ a b Hempel, M.; Holweger, H. (2003-09), “Abundance analysis of late B stars. Evidence for diffusion and against weak stellar windsâ€, Astronomy & Astrophysics 408: 1065-1076, Bibcode: 2003A&A...408.1065H, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20030889
- ^ a b Kaler, James B. (2012ه¹´4وœˆ6و—¥). “BETA SEX (Beta Sextantis)â€. Stars. University of Illinois. 2023ه¹´8وœˆ2و—¥é–²è¦§م€‚
- ^ Lesh, Janet Rountree (1968-12), “The Kinematics of the Gould Belt: an Expanding Group?â€, Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 17 (151): 371-444, Bibcode: 1968ApJS...17..371L, doi:10.1086/190179
- ^ Grأ¸nbech, B.; Olsen, E. H.; Strأ¶mgren, B. (1976-10), “Standard stars for uvby photoelectric photometry south of declination +10°â€, Astronomy & Astrophysics Supplement Series 26: 155-176, Bibcode: 1976A&AS...26..155G
- ^ Crawford, D. L.; Mander, J. (1966-03), “Standard stars for photoelectric Hβ photometryâ€, Astronomical Journal 71: 114-118, Bibcode: 1966AJ.....71..114C, doi:10.1086/109865
- ^ Slettebak, A.; et al. (1975-05), “A system of standard stars for rotational velocity determinationsâ€, Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 29 (281): 137-159, Bibcode: 1975ApJS...29..137S, doi:10.1086/190338
- ^ a b Heck, A.; Manfroid, J. (1982-09), “Is HD 90994 a "Reduction Variable"?â€, Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 2199: 1, Bibcode: 1982IBVS.2199....1H
- ^ a b c Mathys, G.; Manfroid, J.; Renson, P. (1986-03), “Photometric variability of some early-type starsâ€, Astronomy & Astrophysics Supplement Series 63 (3): 403-416, Bibcode: 1986A&AS...63..403M
- ^ “GCVS Variability Types and Distribution Statistics of Designed Variable Stars According to their Types of Variabilityâ€. Sternberg Astronomical Institute. 2023ه¹´8وœˆ2و—¥é–²è¦§م€‚
é–¢é€£é …ç›®
ه¤–部مƒھمƒ³م‚¯
ه؛§و¨™:  10h 30m 17.4802898904s, −00آ° 38′ 13.314537996″ 10h 30m 17.4802898904s, −00آ° 38′ 13.314537996″
|