United Colonies
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

2019 film The WhistlersFilm posterDirected byCorneliu PorumboiuWritten byCorneliu PorumboiuProduced byMarcela UrsuStarringVlad Ivanov Catrinel MenghiaCinematographyTudor MirceaEdited byRoxana SzelProductioncompanies42 Km FilmKomplizen FilmLes Films du Worsomk2Release dates 18 May 2019 (2019-05-18) (Cannes) 13 September 2019 (2019-09-13) (Romania) Running time97 minutesCountriesRomaniaFranceGermanyLanguagesRomanianEnglishEl SilboSpanishBox office$808,743[…

American seafood restaurant chain Bubba Gump Shrimp CompanyCompany typeSubsidiaryIndustrySeafood restaurantFoundedMonterey, California (1996; 28 years ago (1996))HeadquartersHouston, TexasNumber of locations35 restaurants[1]Area servedUnited States Canada United Kingdom Mexico Mainland China Hong Kong Indonesia Japan Qatar Egypt (Future) Kuwait (Future) ParentLandry's, Inc.(2010–present)Websitewww.bubbagump.com The Bubba Gump Shrimp Co. restaurant in Long Beach, Calif…

AngeloAutoreRaffaello Sanzio Data1500-1501 TecnicaOlio su tavola Dimensioni58×36 cm UbicazioneLouvre, Parigi Angelo è un dipinto a olio su tavola (58x36 cm) di Raffaello, databile al 1500-1501 e conservato nel Museo del Louvre a Parigi. Si tratta di uno dei frammenti della Pala Baronci. Indice 1 Storia 2 Descrizione e stile 3 Bibliografia 4 Voci correlate 5 Altri progetti 6 Collegamenti esterni Storia La pala eseguita per la cappella Baronci nella chiesa di Sant'Agostino a Città di Caste…

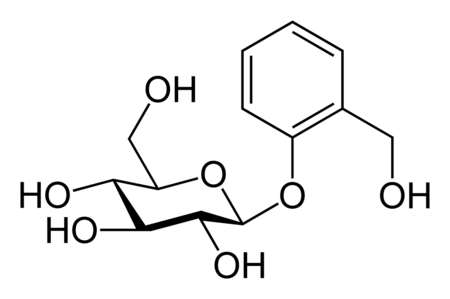
Phenyl glycidyl ether Names IUPAC name 2-(phenoxymethyl)oxirane Other names Phenyl glycidyl ether; Phenylglycidyl ether; Phenol glycidyl ether; Phenol-glycidaether; Phenoxypropene oxide; Phenoxypropylene oxide; Phenyl 2,3-epoxypropyl ether; Phenylglycydyl ether; Propane, 1,2-epoxy-3-phenoxy-; Oxirane, 2-(phenoxymethyl)- Identifiers CAS Number 122-60-1 3D model (JSmol) Interactive image ChEBI CHEBI:82367 ChEMBL ChEMBL1568222 ChemSpider 28958 ECHA InfoCard 100.004.144 EC Number 204-557-2 KEGG C192…

Questa voce sull'argomento società calcistiche rumene è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Fotbal Club Unirea DejCalcio Uniriștii (Gli unionisti) Segni distintiviUniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Colori socialiGiallo, blu, rosso Dati societariCittàDej Nazione Romania ConfederazioneUEFA Federazione FRF Campionatoliga II Fondazione1921 Presidente Gabriel Magdaș Allenatore Dragos Militaru StadioStadionul Unirea(6 000 posti) PalmarèsDa…

1972 European Athletics Indoor ChampionshipsTrack events50 mmenwomen400 mmenwomen800 mmenwomen1500 mmenwomen3000 mmen50 m hurdlesmenwomen4 × 180 m relaywomen4 × 360 m relaymenwomen4 × 720 m relaymenField eventsHigh jumpmenwomenPole vaultmenLong jumpmenwomenTriple jumpmenShot putmenwomenvte The men's pole vault event at the 1972 European Athletics Indoor Championships was held on 12 March in Grenoble.[1][2] Results [3] Rank Name Nationality 4.60 4.70 4.80 4.90 5.00 5.10…

Village in Estonia Village in Saare County, EstoniaKõigusteVillageKõiguste rear daymarkCountry EstoniaCountySaare CountyParishSaaremaa ParishTime zoneUTC+2 (EET) • Summer (DST)UTC+3 (EEST) Kõiguste is a village in Saaremaa Parish, Saare County in western Estonia.[1] Before the administrative reform in 2017, the village was in Laimjala Parish.[2] References ^ Lisa. Asustusüksuste nimistu (PDF). haldusreform.fin.ee (in Estonian). Rahandusministeerium. Retrieved…

Banjir Pakistan 2010Satelit NASA menampilkan sungai Indus saat banjir terjadiTanggal26 Juli 2010 – [per kapan?]2010LokasiKhyber Pakhtunkhwa, Punjab, Sindh, Balochistan dan Gilgit-BaltistanTewas1,781+[1]Kerugian harta benda$43 billion[2] (estimated) Daerah yang terkena Banjir Pakistan 2010 Banjir Pakistan 2010 adalah sebuah banjir besar yang melanda Pakistan tepatnya di Daerah Aliran Sungai Indus. Banjir ini berlangsung sejak 26 Juli 2010 . Bencana ini membunuh setidakny…

This article is about the pretender to the Moroccan throne. For the Egytian archeological site, see El Hiba. Ahmed al-HibaThe French periodical Le Petit Journal's portrayal of al-Hiba's call to arms to his partisans. 1 September 1912.Native nameأحمد الهيبةBorn9 September 1877Died26 June 1919Years of service1910–1919Battles/warsBattle of Sidi Bou Othman Ahmed al-Hiba (Arabic: أحمد الهيبة, also known as The Blue Sultan; 9 September 1877 – 26 June 1919), was a leader of…

1993 Eeuwen: 19e eeuw · 20e eeuw · 21e eeuw Decennia: 1980-1989 · 1990-1999 · 2000-2009 Jaren: << · < · 1992 · 1993 · 1994 · > · >> Maanden: jan · feb · mrt · apr · mei · jun jul · aug · sep · okt · nov · dec Jaartelling in verschillende culturen Ab urbe condita: 2746 MMDCCXLVI Armeense jaartelling: 1442 – 1443ԹՎ ՌՆԽԲ – ՌՆԽԳ Chinese jaartelling: …

Saron-sur-AubecomuneSaron-sur-Aube – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Francia RegioneGrand Est Dipartimento Marna ArrondissementÉpernay CantoneVertus-Plaine Champenoise TerritorioCoordinate48°34′N 3°44′E48°34′N, 3°44′E (Saron-sur-Aube) Superficie16,86 km² Abitanti299[1] (2009) Densità17,73 ab./km² Altre informazioniCod. postale51260 Fuso orarioUTC+1 Codice INSEE51524 CartografiaSaron-sur-Aube Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Saron-sur-Aube è un comun…
Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne cite pas suffisamment ses sources (septembre 2020). Si vous disposez d'ouvrages ou d'articles de référence ou si vous connaissez des sites web de qualité traitant du thème abordé ici, merci de compléter l'article en donnant les références utiles à sa vérifiabilité et en les liant à la section « Notes et références ». En pratique : Quelles sources sont attendues ? Co…

In this Spanish name, the first or paternal surname is Augustín and the second or maternal family name is Dávila. The Most ExcellentBasilio Augustín113th Governor-General of the PhilippinesIn officeApril 11 – July 24, 1898Preceded byFernando Primo de RiveraSucceeded byFermín Jáudenes Personal detailsBorn(1840-02-12)February 12, 1840Cádiz, Province of CádizDiedAugust 7, 1910(1910-08-07) (aged 70)Vitoria-Gasteiz, Álava Basilio Augustín y Dávila (February 12, 1840 …

Cet article est une ébauche concernant les Jeux olympiques et l’Allemagne. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Allemagne aux Jeux olympiques d'été de 1912 Code CIO GER Comité Comité olympique allemand Lieu Stockholm Participation 5e Athlètes 185 (dans 14 sport) Porte-drapeau Karl Halt MédaillesRang : 6e Or5 Arg.13 Bron.7 Total25 Historique Jeux olympiques d'été 1896 1900 1904 1908 1912 19…

United States historic placeFarnam BuildingU.S. National Register of Historic Places Farnam Building, view from 17th and FarnamShow map of NebraskaShow map of the United StatesLocation1613 Farnam Street,Omaha, NebraskaCoordinates41°15′27″N 95°56′16″W / 41.25750°N 95.93778°W / 41.25750; -95.93778Built1929ArchitectGeorge B. PrinzArchitectural styleGothic RevivalNRHP reference No.00000171[1]Added to NRHPMarch 9, 2000 The Farnam Building is …

Bienes económicos apilados en un almacén. Los bienes económicos o bienes escasos, por oposición a los bienes libres, son aquellos que se adquieren en el mercado, generalmente pagando un precio por ellos y que satisface directa o indirectamente una necesidad.[1] Es decir, son bienes materiales e inmateriales que poseen un valor económico y que, por esto son susceptibles de ser evaluados en términos monetarios. En este sentido, el término bien se utiliza para nombrar cosas que son ú…

Men's 400 metres hurdles at the 2023 World ChampionshipsThe final underway.VenueNational Athletics CentreDates20 August (heats)21 August (semi-finals)23 August (final)Competitors43 from 31 nationsMedalists Karsten Warholm Norway Kyron McMaster British Virgin Islands Rai Benjamin United States← 20222025 →Events at the2023 World ChampionshipsTrack events100 mmenwomen200 mmenwomen400 mmenwomen800 mmenwomen…

بينت فريسي الاسم الرسمي (باليونانية: Πέντε Βρύσαι) الإحداثيات 40°48′30″N 23°09′18″E / 40.8083°N 23.155°E / 40.8083; 23.155 تقسيم إداري البلد اليونان[1] عدد السكان عدد السكان 302 (2021)337 (2001)359 (1991)322 (2011) معلومات أخرى 572 00 رمز جيونيمز 734716 تعديل مصدري - تعدي�…

United States Capitol cornerstone layingGeorge Washington depicted in a mural by Allyn CoxDateSeptember 18, 1793 (1793-09-18)VenueUnited States CapitolLocationWashington, D.C., U.S.Patron(s)George Washington The United States Capitol cornerstone laying was the Freemasonry ceremonial placement of the cornerstone of the United States Capitol on September 18, 1793. The cornerstone was laid by president of the United States George Washington Leder of the Lodge of the Continental Army,…

此條目可能包含不适用或被曲解的引用资料,部分内容的准确性无法被证實。 (2018年2月28日)请协助校核其中的错误以改善这篇条目。详情请参见条目的讨论页。 古巴协会Federación Cubana De Voleibol大洲联合会北美、中美和加勒比排球联合会總教練Nicolás Vives球衣 主場 客場 夏季奧運參賽次數7(首次參賽:1972年)最佳成績 季軍:(1976)世界排球锦标赛參賽次數14(首次�…




