Battle of Grenada
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
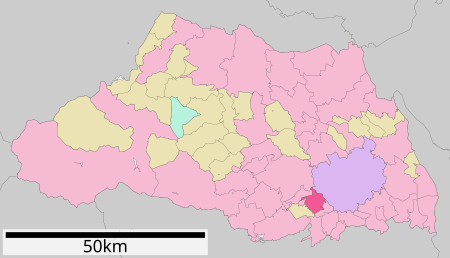
Fujimi 富士見市KotaNegaraJepangWilayahKantōPrefekturSaitamaPopulasi • Total104.937 • Kepadatan5.327/km2 (13,800/sq mi)Zona waktuUTC+9 (JST) Fujimi adalah kota yang terletak di Prefektur Saitama, Jepang. Jumlah penduduk kota ini pada tahun 2005 sebesar 104,937 jiwa. Pranala luar situs resmi Diarsipkan 2007-02-24 di Wayback Machine. lbs Prefektur SaitamaSaitama (ibu kota)Distrik kota (Saitama) Chūō Iwatsuki Kita Midori Minami Minuma Nishi Ōmiya Sakura Urawa Kot…

Частина серії проФілософіяLeft to right: Plato, Kant, Nietzsche, Buddha, Confucius, AverroesПлатонКантНіцшеБуддаКонфуційАверроес Філософи Епістемологи Естетики Етики Логіки Метафізики Соціально-політичні філософи Традиції Аналітична Арістотелівська Африканська Близькосхідна іранська Буддійсь…

Nội chiến LàoMột phần của Chiến tranh Việt NamCác khu vực của Lào do Pathet Lào kiểm soát và bị Không quân Hoa Kỳ ném bom để hỗ trợ Vương quốc Lào.Thời gian23 tháng 5 năm 1959 (1959-05-23) – 2 tháng 12 năm 1975 (1975-12-02)(16 năm, 6 tháng, 1 tuần và 2 ngày)Địa điểmVương quốc LàoKết quả Pathet Lào chiến thắng và thành lập Cộng hòa Dân chủ Nhân dân Lào.Tham chiến Vươ…

بريانكا (بالأوكرانية: Брянка) بريانكا بريانكا تاريخ التأسيس 1889 تقسيم إداري البلد أوكرانيا (1991–) روسيا (2022–) [1] التقسيم الأعلى جمهورية لوغانسك الشعبية (2022–) خصائص جغرافية إحداثيات 48°30′48″N 38°38′35″E / 48.513333333333°N 38.643055555556°E / 48.513333333333; 38.6430555…

American politician Joe GallegosJoe Gallegos in 2014Member of the Oregon House of Representativesfrom the 30th[1] districtIn officeJanuary 14, 2013 – January 9, 2017Preceded byShawn LindsaySucceeded byJaneen Sollman Personal detailsBorn (1941-11-28) November 28, 1941 (age 82)San Antonio, Texas, U.S.[2]Political partyDemocraticResidence(s)Hillsboro, Oregon, U.S.EducationPortland State University (BS, MSW)University of Denver (PhD)Websiteelectjoegallegos…

Mexican pole vaulter For the Mexican weightlifter, see Rigoberto Pérez (weightlifter). Rigoberto Pérez Medal record Men's athletics Representing Mexico Central American and Caribbean Games 1938 Panama Pole vault Rigoberto Pérez Identity Card for Berlin 1936 Olympic Games In this Spanish name, the first or paternal surname is Pérez and the second or maternal family name is Amavisca. Rigoberto Pérez Amavisca (born 26 November 1912, date of death unknown) was a Mexican pole vault…

سيركل الإحداثيات 47°25′01″N 105°35′19″W / 47.416944444444°N 105.58861111111°W / 47.416944444444; -105.58861111111 [1] تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[2] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة ماكوني عاصمة لـ مقاطعة ماكوني خصائص جغرافية المساحة 2.029183 كيلومتر مربع2.027651 كيلومتر م�…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Ida Odinga Istri of the Perdana Menteri KenyaMasa jabatan17 April 2008 – 9 April 2013PendahuluNgina Kenyatta (1964)PenggantiTessie Mudavadi (2022) Informasi pribadiLahirIda Anyango Oyoo24 Agustus 1950 (umur 73)Migori, KenyaSuami/istriRaila…

Kastel Edinburgh Edinburgh, Skotlandia Kastel Edinburgh Letak Istana Edinburgh di Edinburgh Koordinat 55°56′55″N 3°12′03″W / 55.948611°N 3.200833°W / 55.948611; -3.200833Koordinat: 55°56′55″N 3°12′03″W / 55.948611°N 3.200833°W / 55.948611; -3.200833 Dibangun Telah diduduki semenjak Zaman Perunggu akhir; bangunan istana saat ini berasal dari abad ke-12 hingga abad ke-21 Digunakan Masih digunakan Pemiliksaat ini Pemerintah Sko…

Welsh politician (born 1943) The Right HonourableThe Lord WigleyPCWigley in 2006Member of the House of Lords Lord TemporalIncumbentAssumed office 24 January 2011Life PeerageMember of the Welsh Assemblyfor CaernarfonIn office6 May 1999 – 1 May 2003Preceded byOffice CreatedSucceeded byAlun Ffred JonesMember of Parliamentfor CaernarfonIn office28 February 1974 – 14 May 2001Preceded byGoronwy RobertsSucceeded byHywel Williams Personal detailsBornDavid Wigley (1943-04-01) 1 …

1981 Hunt-class mine countermeasures vessel of the Royal Navy For other ships with the same name, see HMS Ledbury. HMS Ledbury on Operation Kipion, 2020 History United Kingdom NameHMS Ledbury Ordered31 March 1977[1] BuilderVosper Thornycroft LaunchedDecember 1979 Sponsored byLady Elizabeth Berthan[2] Commissioned11 June 1981 HomeportHMS Jufair, Bahrain Identification IMO number: 4906587 MMSI number: 232002833 Callsign: GWAE Pennant number: M30 MottoMors Mina (Death to Mines)…

Benedetto CroceBenedetto Croce negli anni 30 (fotografia di Mario Nunes Vais) Ministro della pubblica istruzione del Regno d'ItaliaDurata mandato15 giugno 1920 –4 luglio 1921 Capo del governoGiovanni Giolitti PredecessoreAndrea Torre SuccessoreOrso Mario Corbino Ministro senza portafoglio del Regno d'Italia (periodo costituzionale transitorio)Durata mandato22 aprile 1944 –27 luglio 1944 PresidentePietro BadoglioIvanoe Bonomi Senatore del Regno d'ItaliaDurata …

المحكمة الاجتماعية الاتحادية (ألمانيا)الشعارالتاريخالتأسيس 1954 المدير Christine Fuchsloch (en) (2024 – ) الإطارالاختصار BSG (بالألمانية)[1] النوع محكمة علياFederal courts (Germany) (en) منطقة الاختصاص ألمانيا المقر الرئيسي Dienstgebäude für das Wehrkreiskommando IX (de) على الخريطة البلد ألمانيا التنظيمالأجهزة ال…

National Gendarmerie force of the Republic of Turkey Law enforcement agency Gendarmerie General CommandJandarma Genel KomutanlığıEmblem of the Gendarmerie General CommandFlag of the Gendarmerie General CommanderAgency overviewFormed1839[1]Preceding agenciesGendarmerie OrganisationOttoman GendarmerieEmployees198,317 active personnel[2]Jurisdictional structureOperations jurisdictionTurkeyGeneral natureGendarmerieOperational structureHeadquartersAnkaraElected officer responsibleA…

Ninth and last major release of the classic Mac OS This article is about the ninth major release of the classic Mac OS. For version 10.9 of macOS (formerly OS X), see OS X Mavericks. Operating system Mac OS 9Version of the classic Mac OS operating systemScreenshot of Mac OS 9.0.4DeveloperApple ComputerOS familyMacintoshWorking stateHistoric, not supportedSource modelClosed sourceReleased tomanufacturingOctober 23, 1999; 24 years ago (October 23, 1999)[1][2][3]…

Argentine Public University This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (July 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) National University of General San MartínUniversidad Nacional de General San MartínOther nameUNSAMMottoLa Potencia de Talento (Spanish)Motto in EnglishThe Power of TalentTypePublic and Nation…

1634–1757 Oirat Mongol khanate in Dzungaria Dzungar Khanate1634–1758Dzungar Khanate in the early 18th century[1][2]StatusNomadic empireCapitalGhulja[3]Common languagesOirat, Chagatai[4]Religion Tibetan BuddhismGovernmentMonarchyKhan or Khong Tayiji • 1632-1653 Erdeni Batur (first)• 1671-1697 Galdan Boshugtu Khan• 1745-1750 Tsewang Dorji Namjal Legislature Customary rules Mongol-Oirat Code of 1640 Historical eraEarly modern period…

مسافر بلا طريق[1] هو فيلم مصري تم إنتاجه عام 1978، بطولة صلاح ذو الفقار، محمود ياسين، عفاف شعيب، وماجدة الخطيب، إخراج علي عبد الخالق.[2] مسافر بلا طريقمعلومات عامةتاريخ الصدور 1978مدة العرض 95 دقيقةاللغة الأصلية اللغة المصرية الحديثةالبلد مصرالطاقمالمخرج علي عبد الخا�…

Act of seeking safety in the building one is in For the quarantine order, see Stay-at-home order. Shelter-in-place (SIP; also known as a shelter-in-place warning, SAME code SPW) is the act of seeking safety within the building one already occupies, rather than evacuating the area or seeking a community emergency shelter. The American Red Cross says the warning is issued when chemical, biological, or radiological contaminants may be released accidentally or intentionally into the environment and …
République démocratique du Viêt Nam(vi) Việt Nam Dân Chủ Cộng Hòa 1945–1976 Hymne Tiến Quân CaLes troupes avancent Territoire contrôlé (vert foncé)Territoire revendiqué mais incontrôlé (vert clair)Informations générales Statut République marxiste-léniniste État communiste à parti unique sous dictature Capitale Hanoï Langue(s) Vietnamien Religion Athéisme d'État Monnaie đồng nord-vietnamien Superficie Superficie 155 751 km² Histoire et événements 2 septem…

