|
Typhoon Nina (1975)
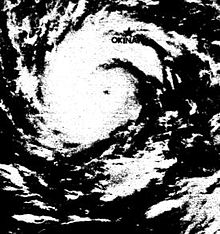
Typhoon Nina, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Bebeng, was a deadly tropical cyclone in the summer of 1975. It formed on July 30 and gradually intensified as it moved generally to the west. On August 2, Nina reached peak intensity, and a day later the typhoon struck Taiwan. It weakened before moving ashore southeastern China. While moving slowly through central China, it dropped heavy rainfall and caused several dam failures, including the Banqiao Dam. It is one of the deadliest typhoons in the Pacific. Flooding from the Banqiao Dam collapse killed 26,000 people, with 100,000 more dying from subsequent famine and diseases. Meteorological history Map key Tropical depression (≤38 mph, ≤62 km/h) Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h) Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h) Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h) Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h) Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h) Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h) Unknown Storm type A well defined trough line extending southeastward into the Philippine Sea spawned a disturbance on July 29. After its initial status as a disturbance, Tropical Depression 04W was designated and moved southwestward for 36 hours as the structure of the system began to organize. On July 31, the depression slowed and began to rapidly intensify, becoming a tropical storm and was named "Nina". It began to turn to the northwest afterward. A subtropical ridge prevented Nina from turning further north and it began to track west-northwest just before reaching typhoon intensity. Nina underwent explosive development in the late hours of August 1. Aircraft reconnaissance reported a 65 hPa drop of pressure, with winds increasing from a mere 65 to 130 knots (75 to 150 mph; 120 to 241 km/h) the day after. During that period, it attained its peak intensity of 135 knots (155 mph; 250 km/h). The typhoon began to weaken as it approached Taiwan, making landfall near the coastal city of Hualien as a Category 3 storm with 100 kn (120 mph; 190 km/h) winds.[1] The storm began to weaken as it went across the island's central mountain range, sparing the most populated areas from the eyewall. It entered the Formosa Straits as a weak typhoon, making another landfall near Jinjiang, Fujian.[2] After moving northwest and crossing Jiangxi, it turned north on the night of August 5 near Changde, Hunan. A day later, the storm moved over Xinyang, Henan, and was later blocked by a cold front near Zhumadian, Henan for three days.[3] The stationary thunderstorm system brought heavy rainfall, causing the infamous collapse of the Banqiao Dam. The storm moved southwest on August 8, and dissipated soon afterwards.[4] Impact
TaiwanUpon making landfall in Taiwan, the storm brought winds of 185 km/h (115 mph) to places near the storm's eye.[9] Wind gusts were also measured up to 222 km/h (138 mph).[10] Widespread heavy rainfall, peaking around 700 mm (28 in),[11] from the storm triggered deadly flooding and landslides which killed 29 people and injured 168 others. Reports from the island indicate that 3,000 homes were damaged or destroyed by the typhoon.[9] In the city of Hualien alone, four people were killed, 561 homes were destroyed, and 1,831 more homes were damaged.[12] Across the island, domestic flights, trains, and bus services were all suspended due to the storm; however, Taipei Songshan Airport remained open for international flights.[13] ChinaDue to the interaction with the mountains of Taiwan, Nina weakened to a tropical storm before making landfall in China. The storm crossed the coastline with winds of 110 km/h (70 mph); however, little damage resulted near where the system struck land.[9] Further inland, the remnants of the storm produced widespread torrential rainfall, with more than 400 mm (16 in) falling across an area of 19,410 km2 (7,490 sq mi). The heaviest rainfall was recorded along the Banqiao Dam where 1,631 mm (64.2 in) of rain fell, 830 mm (33 in) of which fell in a six-hour span.[14] These rains led to the collapse of the Banqiao Dam, which received 1-in-2000-year flood conditions. In all, 62 dams failed during the disaster, causing large temporary lakes and US$1.2 billion (equivalent to $5.3 billion in 2023) in damage.[15] The floods killed 26,000 people, while another 100,000 people died from subsequent famine and disease. Some online sources suggest a higher total death toll of 230,000.[16] See also
References
External linksWikimedia Commons has media related to Typhoon Nina (1975). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia