|
Supraorbital artery
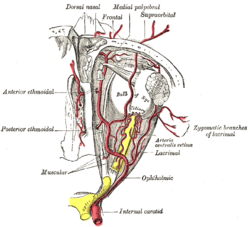
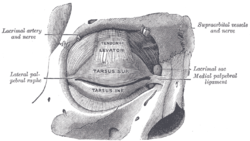
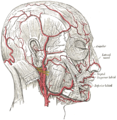
The supraorbital artery is a branch of the ophthalmic artery. It passes anteriorly within the orbit to exit the orbit through the supraorbital foramen or notch alongside the supraorbital nerve, splitting into two terminal branches which go on to form anastomoses with arteries of the head. StructureOriginThe supraorbital artery arises from the ophthalmic artery.[1][2] Course and relationsIt travels anteriorly in the orbit by passing superior to the eye and medial to the superior rectus and levator palpebrae superioris.[citation needed] It then joins the supraorbital nerve to jointly pass between the periosteum of the roof of the orbit and the levator palpebrae superioris towards the supraorbital foramen or notch.[3] After passing through the supraorbital foramen or notch, it often splits into a superficial branch and a deep branch.[1] DistributionThe supraorbital artery contributes arterial supply to: the superior rectus muscle, superior oblique muscle, levator palpebrae muscles, periorbita,[1] the diploë of the frontal bone, frontal sinus, upper eyelid,[citation needed] and the skin and musculature of the forehead and scalp.[1] AnastomosesIts terminal branches anastomose with the supratrochlear artery, frontal branch of superficial temporal artery, and the contralateral supraorbital artery.[1] VariationThis artery may be absent in 10% to 20% of individuals.[4] Additional images
References
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia