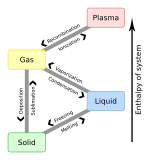
|
Superfluid helium-4Superfluid helium-4 (helium II or He-II) is the superfluid form of helium-4, an isotope of the element helium. A superfluid is a state of matter in which matter behaves like a fluid with zero viscosity. The substance, which resembles other liquids such as helium I (conventional, non-superfluid liquid helium), flows without friction past any surface, which allows it to continue to circulate over obstructions and through pores in containers which hold it, subject only to its own inertia.[1] The formation of the superfluid is a manifestation of the formation of a Bose–Einstein condensate of helium atoms. This condensation occurs in liquid helium-4 at a far higher temperature (2.17 K) than it does in helium-3 (2.5 mK) because each atom of helium-4 is a boson particle, by virtue of its zero spin. Helium-3, however, is a fermion particle, which can form bosons only by pairing with itself at much lower temperatures, in a weaker process that is similar to the electron pairing in superconductivity.[2] HistoryKnown as a major facet in the study of quantum hydrodynamics and macroscopic quantum phenomena, the superfluidity effect was discovered by Pyotr Kapitsa[3] and John F. Allen, and Don Misener[4] in 1937. Onnes possibly observed the superfluid phase transition on August 2, 1911, the same day that he observed superconductivity in mercury.[5] It has since been described through phenomenological and microscopic theories. In the 1950s, Hall and Vinen performed experiments establishing the existence of quantized vortex lines in superfluid helium.[6] In the 1960s, Rayfield and Reif established the existence of quantized vortex rings.[7] Packard has observed the intersection of vortex lines with the free surface of the fluid,[8] and Avenel and Varoquaux have studied the Josephson effect in superfluid helium-4.[9] In 2006, a group at the University of Maryland visualized quantized vortices by using small tracer particles of solid hydrogen.[10] In the early 2000s, physicists created a Fermionic condensate from pairs of ultra-cold fermionic atoms. Under certain conditions, fermion pairs form diatomic molecules and undergo Bose–Einstein condensation. At the other limit, the fermions (most notably superconducting electrons) form Cooper pairs which also exhibit superfluidity. This work with ultra-cold atomic gases has allowed scientists to study the region in between these two extremes, known as the BEC-BCS crossover. Supersolids may also have been discovered in 2004 by physicists at Penn State University. When helium-4 is cooled below about 200 mK under high pressures, a fraction (≈1%) of the solid appears to become superfluid.[11][12] By quench cooling or lengthening the annealing time, thus increasing or decreasing the defect density respectively, it was shown, via torsional oscillator experiment, that the supersolid fraction could be made to range from 20% to completely non-existent. This suggested that the supersolid nature of helium-4 is not intrinsic to helium-4 but a property of helium-4 and disorder.[13][14] Some emerging theories posit that the supersolid signal observed in helium-4 was actually an observation of either a superglass state[15] or intrinsically superfluid grain boundaries in the helium-4 crystal.[16] ApplicationsRecently[timeframe?] in the field of chemistry, superfluid helium-4 has been successfully used in spectroscopic techniques as a quantum solvent. Referred to as superfluid helium droplet spectroscopy (SHeDS), it is of great interest in studies of gas molecules, as a single molecule solvated in a superfluid medium allows a molecule to have effective rotational freedom, allowing it to behave similarly to how it would in the "gas" phase. Droplets of superfluid helium also have a characteristic temperature of about 0.4 K which cools the solvated molecule(s) to its ground or nearly ground rovibronic state. Superfluids are also used in high-precision devices such as gyroscopes, which allow the measurement of some theoretically predicted gravitational effects (for an example, see Gravity Probe B). The Infrared Astronomical Satellite IRAS, launched in January 1983 to gather infrared data was cooled by 73 kilograms of superfluid helium, maintaining a temperature of 1.6 K (−271.55 °C). When used in conjunction with helium-3, temperatures as low as 40 mK are routinely achieved in extreme low temperature experiments. The helium-3, in liquid state at 3.2 K, can be evaporated into the superfluid helium-4, where it acts as a gas due to the latter's properties as a Bose–Einstein condensate. This evaporation pulls energy from the overall system, which can be pumped out in a way completely analogous to normal refrigeration techniques. (See dilution refrigerator) Superfluid-helium technology is used to extend the temperature range of cryocoolers to lower temperatures. So far the limit is 1.19 K, but there is a potential to reach 0.7 K.[17] PropertiesSuperfluids, such as helium-4 below the lambda point (known, for simplicity, as helium II), exhibit many unusual properties. A superfluid acts as if it were a mixture of a normal component, with all the properties of a normal fluid, and a superfluid component. The superfluid component has zero viscosity and zero entropy. Application of heat to a spot in superfluid helium results in a flow of the normal component which takes care of the heat transport at relatively high velocity (up to 20 cm/s) which leads to a very high effective thermal conductivity. Film flowMany ordinary liquids, like alcohol or petroleum, creep up solid walls, driven by their surface tension. Liquid helium also has this property, but, in the case of He-II, the flow of the liquid in the layer is not restricted by its viscosity but by a critical velocity which is about 20 cm/s. This is a fairly high velocity so superfluid helium can flow relatively easily up the wall of containers, over the top, and down to the same level as the surface of the liquid inside the container, in a siphon effect. It was, however, observed, that the flow through nanoporous membrane becomes restricted if the pore diameter is less than 0.7 nm (i.e. roughly three times the classical diameter of helium atom), suggesting the unusual hydrodynamic properties of He arise at larger scale than in the classical liquid helium.[18] RotationAnother fundamental property becomes visible if a superfluid is placed in a rotating container. Instead of rotating uniformly with the container, the rotating state consists of quantized vortices. That is, when the container is rotated at speeds below the first critical angular velocity, the liquid remains perfectly stationary. Once the first critical angular velocity is reached, the superfluid will form a vortex. The vortex strength is quantized, that is, a superfluid can only spin at certain "allowed" values. Rotation in a normal fluid, like water, is not quantized. If the rotation speed is increased more and more quantized vortices will be formed which arrange in nice patterns similar to the Abrikosov lattice in a superconductor. Comparison with helium-3Although the phenomenologies of the superfluid states of helium-4 and helium-3 are very similar, the microscopic details of the transitions are very different. Helium-4 atoms are bosons, and their superfluidity can be understood in terms of the Bose–Einstein statistics that they obey. Specifically, the superfluidity of helium-4 can be regarded as a consequence of Bose–Einstein condensation in an interacting system. On the other hand, helium-3 atoms are fermions, and the superfluid transition in this system is described by a generalization of the BCS theory of superconductivity. In it, Cooper pairing takes place between atoms rather than electrons, and the attractive interaction between them is mediated by spin fluctuations rather than phonons. (See fermion condensate.) A unified description of superconductivity and superfluidity is possible in terms of gauge symmetry breaking. Macroscopic theoryThermodynamics 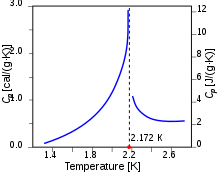  Figure 1 is the phase diagram of 4He.[19] It is a pressure-temperature (p-T) diagram indicating the solid and liquid regions separated by the melting curve (between the liquid and solid state) and the liquid and gas region, separated by the vapor-pressure line. This latter ends in the critical point where the difference between gas and liquid disappears. The diagram shows the remarkable property that 4He is liquid even at absolute zero. 4He is only solid at pressures above 25 bar. Figure 1 also shows the λ-line. This is the line that separates two fluid regions in the phase diagram indicated by He-I and He-II. In the He-I region the helium behaves like a normal fluid; in the He-II region the helium is superfluid. The name lambda-line comes from the specific heat – temperature plot which has the shape of the Greek letter λ.[20][21] See figure 2, which shows a peak at 2.172 K, the so-called λ-point of 4He. Below the lambda line the liquid can be described by the so-called two-fluid model. It behaves as if it consists of two components: a normal component, which behaves like a normal fluid, and a superfluid component with zero viscosity and zero entropy. The ratios of the respective densities ρn/ρ and ρs/ρ, with ρn (ρs) the density of the normal (superfluid) component, and ρ (the total density), depends on temperature and is represented in figure 3.[22] By lowering the temperature, the fraction of the superfluid density increases from zero at Tλ to one at zero kelvins. Below 1 K the helium is almost completely superfluid. It is possible to create density waves of the normal component (and hence of the superfluid component since ρn + ρs = constant) which are similar to ordinary sound waves. This effect is called second sound. Due to the temperature dependence of ρn (figure 3) these waves in ρn are also temperature waves.   Superfluid hydrodynamicsThe equation of motion for the superfluid component, in a somewhat simplified form,[23] is given by Newton's law
The mass is the molar mass of 4He, and is the velocity of the superfluid component. The time derivative is the so-called hydrodynamic derivative, i.e. the rate of increase of the velocity when moving with the fluid. In the case of superfluid 4He in the gravitational field the force is given by[24][25]
In this expression is the molar chemical potential, the gravitational acceleration, and the vertical coordinate. Thus we get the equation which states that the thermodynamics of a certain constant will be amplified by the force of the natural gravitational acceleration
Eq. (1) only holds if is below a certain critical value, which usually is determined by the diameter of the flow channel.[26][27] In classical mechanics the force is often the gradient of a potential energy. Eq. (1) shows that, in the case of the superfluid component, the force contains a term due to the gradient of the chemical potential. This is the origin of the remarkable properties of He-II such as the fountain effect.  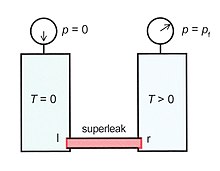  Fountain pressureIn order to rewrite Eq.(1) in more familiar form we use the general formula
Here is the molar entropy and the molar volume. With Eq.(2) can be found by a line integration in the – plane. First we integrate from the origin to , so at . Next we integrate from to , so with constant pressure (see figure 6). In the first integral and in the second . With Eq.(2) we obtain
We are interested only in cases where is small so that is practically constant. So
where is the molar volume of the liquid at and . The other term in Eq.(3) is also written as a product of and a quantity which has the dimension of pressure
The pressure is called the fountain pressure. It can be calculated from the entropy of 4He which, in turn, can be calculated from the heat capacity. For the fountain pressure is equal to 0.692 bar. With a density of liquid helium of 125 kg/m3 and g = 9.8 m/s2 this corresponds with a liquid-helium column of 56 meter height. So, in many experiments, the fountain pressure has a bigger effect on the motion of the superfluid helium than gravity. With Eqs.(4) and (5), Eq.(3) obtains the form
Substitution of Eq.(6) in (1) gives
with the density of liquid 4He at zero pressure and temperature. Eq.(7) shows that the superfluid component is accelerated by gradients in the pressure and in the gravitational field, as usual, but also by a gradient in the fountain pressure. So far Eq.(5) has only mathematical meaning, but in special experimental arrangements can show up as a real pressure. Figure 7 shows two vessels both containing He-II. The left vessel is supposed to be at zero kelvins () and zero pressure (). The vessels are connected by a so-called superleak. This is a tube, filled with a very fine powder, so the flow of the normal component is blocked. However, the superfluid component can flow through this superleak without any problem (below a critical velocity of about 20 cm/s). In the steady state so Eq.(7) implies
where the indexes and apply to the left and right side of the superleak respectively. In this particular case , , and (since ). Consequently,
This means that the pressure in the right vessel is equal to the fountain pressure at . In an experiment, arranged as in figure 8, a fountain can be created. The fountain effect is used to drive the circulation of 3He in dilution refrigerators.[28][29]  Heat transportFigure 9 depicts a heat-conduction experiment between two temperatures and connected by a tube filled with He-II. When heat is applied to the hot end a pressure builds up at the hot end according to Eq.(7). This pressure drives the normal component from the hot end to the cold end according to
Here is the viscosity of the normal component,[30] some geometrical factor, and the volume flow. The normal flow is balanced by a flow of the superfluid component from the cold to the hot end. At the end sections a normal to superfluid conversion takes place and vice versa. So heat is transported, not by heat conduction, but by convection. This kind of heat transport is very effective, so the thermal conductivity of He-II is very much better than the best materials. The situation is comparable with heat pipes where heat is transported via gas–liquid conversion. The high thermal conductivity of He-II is applied for stabilizing superconducting magnets such as in the Large Hadron Collider at CERN. Microscopic theoryLandau two-fluid approachL. D. Landau's phenomenological and semi-microscopic theory of superfluidity of helium-4 earned him the Nobel Prize in physics, in 1962. Assuming that sound waves are the most important excitations in helium-4 at low temperatures, he showed that helium-4 flowing past a wall would not spontaneously create excitations if the flow velocity was less than the sound velocity. In this model, the sound velocity is the "critical velocity" above which superfluidity is destroyed. (Helium-4 actually has a lower flow velocity than the sound velocity, but this model is useful to illustrate the concept.) Landau also showed that the sound wave and other excitations could equilibrate with one another and flow separately from the rest of the helium-4, which is known as the "condensate". From the momentum and flow velocity of the excitations he could then define a "normal fluid" density, which is zero at zero temperature and increases with temperature. At the so-called Lambda temperature, where the normal fluid density equals the total density, the helium-4 is no longer superfluid. To explain the early specific heat data on superfluid helium-4, Landau posited the existence of a type of excitation he called a "roton", but as better data became available he considered that the "roton" was the same as a high momentum version of sound. The Landau theory does not elaborate on the microscopic structure of the superfluid component of liquid helium.[31] The first attempts to create a microscopic theory of the superfluid component itself were done by London[32] and subsequently, Tisza.[33][34] Other microscopical models have been proposed by different authors. Their main objective is to derive the form of the inter-particle potential between helium atoms in superfluid state from first principles of quantum mechanics. To date, a number of models of this kind have been proposed, including: models with vortex rings, hard-sphere models, and Gaussian cluster theories. Vortex ring modelLandau thought that vorticity entered superfluid helium-4 by vortex sheets, but such sheets have since been shown to be unstable. Lars Onsager and, later independently, Feynman showed that vorticity enters by quantized vortex lines. They also developed the idea of quantum vortex rings. Arie Bijl in the 1940s,[35] and Richard Feynman around 1955,[36] developed microscopic theories for the roton, which was shortly observed with inelastic neutron experiments by Palevsky. Later on, Feynman admitted that his model gives only qualitative agreement with experiment.[37][38] Hard-sphere modelsThe models are based on the simplified form of the inter-particle potential between helium-4 atoms in the superfluid phase. Namely, the potential is assumed to be of the hard-sphere type.[39][40][41] In these models the famous Landau (roton) spectrum of excitations is qualitatively reproduced. Gaussian cluster approachThis is a two-scale approach which describes the superfluid component of liquid helium-4. It consists of two nested models linked via parametric space. The short-wavelength part describes the interior structure of the fluid element using a non-perturbative approach based on the logarithmic Schrödinger equation; it suggests the Gaussian-like behaviour of the element's interior density and interparticle interaction potential. The long-wavelength part is the quantum many-body theory of such elements which deals with their dynamics and interactions.[42] The approach provides a unified description of the phonon, maxon and roton excitations, and has noteworthy agreement with experiment: with one essential parameter to fit one reproduces at high accuracy the Landau roton spectrum, sound velocity and structure factor of superfluid helium-4.[43] This model utilizes the general theory of quantum Bose liquids with logarithmic nonlinearities[44] which is based on introducing a dissipative-type contribution to energy related to the quantum Everett–Hirschman entropy function.[45][46] See alsoReferences
Further reading
External links
|
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia