Sautrāntika
|
Read other articles:

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Politeknik APP Jakarta – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Politeknik APP JakartaNama sebelumnyaAkademi Pimpinan Perusahaan JakartaDidirikan1957DirekturAmrin Rapi[1]LokasiJakarta Sel…

نيشان الصوفة الذهبيةمعلومات عامةالبداية 26 يونيو 1998 الاسم الأصل ოქროს საწმისის ორდენი (بالجورجية) البلد جورجيا الرتبة الأعلى التالية Order of Saint Nicholas (en) الرتبة الأدنى التالية نيشان فاختانغ جورجاسالي تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات نيشان الصوف الذهبي نيشان الص…

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要編修,以確保文法、用詞、语气、格式、標點等使用恰当。 (2013年8月6日)請按照校對指引,幫助编辑這個條目。(幫助、討論) 此條目剧情、虛構用語或人物介紹过长过细,需清理无关故事主轴的细节、用語和角色介紹。 (2020年10月6日)劇情、用語和人物介紹都只是用於了解故事主軸,輔助讀�…

Bulgarian politician (1938–1996) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Andrey Lukanov – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Andrey LukanovАндрей ЛукановLukanov in 199040th Prime Minister of BulgariaIn office3 February 19…

Events at the2001 World ChampionshipsTrack events100 mmenwomen200 mmenwomen400 mmenwomen800 mmenwomen1500 mmenwomen5000 mmenwomen10,000 mmenwomen100 m hurdleswomen110 m hurdlesmen400 m hurdlesmenwomen3000 msteeplechasemen4 × 100 m relaymenwomen4 × 400 m relaymenwomenRoad eventsMarathonmenwomen20 km walkmenwomen50 km walkmenField eventsHigh jumpmenwomenPole vaultmenwomenLong jumpmenwomenTriple jumpmenwomenShot putmenwomenDiscus throwmenwomenHammer throwmenwomenJavelin throwmenwomenCombined even…

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Дворец спорта. Дворец спорта Местоположение Минск Построен 1963—1966 Архитектор Сергей Дмитриевич Филимонов[вд] и Валентин Николаевич Малышев[вд] Вместимость 3311 Домашняя команда МХК «Минские зубры» Размеры поля 61×30 Сайт s…

1990 single by Janet Jackson EscapadeSingle by Janet Jacksonfrom the album Janet Jackson's Rhythm Nation 1814 ReleasedJanuary 8, 1990 (1990-01-08)Recorded1988–1989[1]StudioFlyte Tyme (Minneapolis, Minnesota)Genre Dance-pop new jack swing Length4:44LabelA&MSongwriter(s) Janet Jackson James Harris III Terry Lewis Producer(s) Jimmy Jam and Terry Lewis Janet Jackson Janet Jackson singles chronology Rhythm Nation (1989) Escapade (1990) Alright (1990) Music videoEscapade o…

British epidemiologist (1807–1883) For other people named William Farr, see William Farr (disambiguation). William Farr William Farr CB (30 November 1807 – 14 April 1883) was a British epidemiologist, regarded as one of the founders of medical statistics. Early life William Farr was born in Kenley, Shropshire, to poor parents. He was effectively adopted by a local squire, Joseph Pryce, when Farr and his family moved to Dorrington. In 1826 he took a job as a dresser (surgeon's assistant) in t…

American consumer electronics company Bose CorporationCompany typePrivateIndustryAudio electronicsFounded1964; 60 years ago (1964)FounderAmar Bose[1]HeadquartersFramingham, Massachusetts, U.S.Key peopleLila Snyder, CEO[2] Jim Scammon, President and COO[3]Bob Maresca, Chairman, former CEO[4]ProductsAudio equipmentRevenueUS$3.2 billion (FY 2021)[5]OwnerMassachusetts Institute of Technology (majority)Number of employees7,000 (FY 2021)[5&…

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Hari Kemerdekaan Republik Indonesia atau Tujuhbelasan. Soekarno membacakan naskah Proklamasi Kemerdekaan Republik Indonesia yang sudah diketik oleh Sayuti Melik dan telah ditandatangani oleh Soekarno-Hatta Rumah Proklamasi lengkap dengan Tugu Proklamasi sekitar tahun 1950-1960 di Jalan Pegangsaan Timur (sekarang Jalan Proklamasi). Rumah Proklamasi kini telah hancur, sementara Tugu Proklamasi masih berdiri di Taman Proklamasi sekarang. Proklamasi Kemerdekaan Indonesia d…

Universitas Islam Negeri Sumatera Utara (disingkat: UINSU) adalah Perguruan Tinggi Keagamaan Islam Negeri yang berada di Medan, Sumatera Utara, Indonesia. UINSU awalnya berdiri dengan nama Institut Agama Islam Negeri (IAIN SU) pada tahun 1973. Kemudian alih status IAIN SU menjadi Universitas Islam Negeri (UIN) Sumatera Utara telah disetujui dengan Perpres No. 131/2014 tanggal 16 Oktober 2014 oleh Presiden ke-6 Indonesia Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono.[1] Universitas Islam NegeriSumatera UtaraJ…

British new wave band For other uses, see Ultravox (disambiguation). UltravoxUltravox at the end of a concert in Berlin in 2012 (l-r): Warren Cann, Chris Cross, Midge Ure, Billy CurrieBackground informationAlso known asTiger Lily (1974–1975)Ultravox! (1976–1978)OriginLondon, EnglandGenresSynth-popnew wavepost-punkYears active1974–19871992–19962008–2013LabelsIslandChrysalisEMIPolyGramSpinoffsVisageSpinoff ofTiger LilyPast members Chris Cross John Foxx Stevie Shears Warren Cann Billy Cur…

Kejuaraan Eropa UEFA 2024UEFA Euro 2024 (Inggris)Fußball-Europameisterschaft 2024 (Jerman)United by Football. Vereint im Herzen Europas.(Disatukan oleh sepak bola. Bersatu di jantung Eropa.)Informasi turnamenTuan rumahJermanJadwalpenyelenggaraan14 Juni – 14 JuliJumlahtim peserta24Tempatpenyelenggaraan10 (di 10 kota)Statistik turnamenJumlahpertandingan8Jumlah gol25 (3,13 per pertandingan)Jumlahpenonton448.745 (56.093 per pertandingan)Pencetak golterbanyak24 pemain(masing-masing …

2015 Kentucky elections ← 2014 November 3, 2015 2016 → Elections in Kentucky Federal government Presidential elections 1792 1796 1800 1804 1808 1812 1816 1820 1824 1828 1832 1836 1840 1844 1848 1852 1856 1860 1864 1868 1872 1876 1880 1884 1888 1892 1896 1900 1904 1908 1912 1916 1920 1924 1928 1932 1936 1940 1944 1948 1952 1956 1960 1964 1968 1972 1976 1980 1984 1988 1992 1996 2000 2004 2008 2012 2016 2020 2024 Presidential primaries Democratic 2000 2004 2008 2012 2016 2020 …
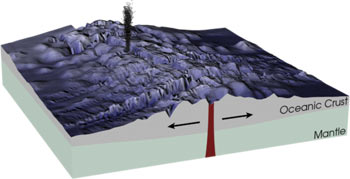
خريطة تبين التضاريس تحت الماء (قياس الأعماق) لقاع المحيط. تشبه التضاريس في قاع المحيط تضاريس الأرض حيث تتكون من تلال ووديان وسهول وبراكين. إن قاع البحر (المعروف أيضًا باسم قعر البحر أو أرضية البحر, أو قاع المحيط) بأنه الجزء السفلي من المحيط. بنية المحيط أكبر أقسام المحيط تتميز …

American jazz musician This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: James Williams musician – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (N…

Alat penyiksaan the rack di kastil Rothschildschloss, Austria The rack adalah alat penyiksaan yang terdiri dari bingkai persegi panjang, biasanya berbahan kayu, dengan posisi sedikit terangkat dari tanah,[1] dengan rol di salah satu atau kedua ujungnya. Pergelangan kaki korban diikat ke salah satu gelinding dan pergelangan tangan dirantai ke gelinding lainnya. Saat interogasi berlangsung, mekanisme pegangan dan ratchet yang dipasang pada gelinding atas digunakan untuk menarik rantai seca…

Cet article est une ébauche concernant l’astronomie. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Cycle solaire 11 Généralités Début 1867 Fin 1878 Durée ~11 a Cycle solaire 10 Cycle solaire 12 modifier Le cycle solaire 11 est le onzième cycle solaire depuis 1755, date du début du suivi intensif de l'activité et des taches solaires. Il a commencé en 1867 et s'est achevé en 1878. Références v&#…

Rugby teamFairfield Yankees RFCFull nameFairfield Yankees Rugby Football ClubUnionEmpire Geographical UnionFounded1975 Ground(s)Staples High School Football Field Westport, Connecticut Team kit Official websitewww.fairfieldyankeesrugby.org The Fairfield Yankees Rugby Football Club is a Division II and IV Men's and Division II Women's Rugby Club based in Fairfield, Connecticut. Founded in 1975, the club consists of many teams, two Men's sides and one Women's side, as well as teams for Summer Seve…

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: General Zuazua – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Municipality and townGeneral Zuazua MunicipalityMunicipality and townMunicipal PalaceCoordinates: 25°54′N 100°07′W / 25.900°…

