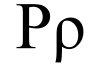|
Rho
Rho (/ˈroʊ/; uppercase Ρ, lowercase ρ or ϱ; Greek: ρο or ρω) is the seventeenth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 100. It is derived from Phoenician letter res Uses GreekRho is classed as a liquid consonant (together with Lambda and sometimes the nasals Mu and Nu), which has important implications for morphology. In both Ancient and Modern Greek, it represents an alveolar trill IPA: [r], alveolar tap IPA: [ɾ], or alveolar approximant IPA: [ɹ]. In polytonic orthography, a rho at the beginning of a word is written with a rough breathing, equivalent to h (ῥ rh), and a double rho within a word is written with a smooth breathing over the first rho and a rough breathing over the second (ῤῥ rrh). That apparently reflected an aspirated or voiceless pronunciation in Ancient Greek, which led to the various Greek-derived English words starting with rh or containing rrh. The name of the letter is written in Greek as ῥῶ (polytonic) or ρω/ρο (monotonic). Other alphabetsLetters that arose from rho include Roman R and Cyrillic Er (Р). Mathematics and scienceThe characters ρ and ϱ are also conventionally used outside the Greek alphabetical context in science and mathematics.
Chi Rho (☧) The letter rho overlaid with chi forms the Chi Rho symbol, used to represent Jesus Christ. It was first used by Emperor Constantine the Great. A can be seen on his standard known as the Labarum. Rho with stroke (ϼ)The rho with a stroke through its tail is used for abbreviations involving rho, most notably in γϼ for γράμμα as a unit of measurement.[4] Unicode
These characters are used only as mathematical symbols. Stylized Greek text should be encoded using the normal Greek letters, with markup and formatting to indicate text style:
See alsoReferences
|
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia