Star in the constellation Cassiopeia
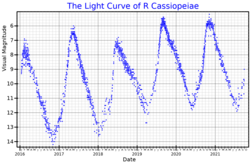
R Cassiopeiae is a variable star in the northern constellation of Cassiopeia . It is located approximately 574 light years distant from the Sun, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −23 km/s.[ 5] Mira-type variable star with a brightness that varies from magnitude +4.4 down to +13.5 over a period of 433.6 days.[ 3] naked eye as a faint, red-hued star.
Norman Robert Pogson discovered the star, in 1853.[ 9] [ 10] red giant star has a stellar classification that varies from M6e to M10e,[ 3] emission features in the spectrum . Currently on the asymptotic giant branch ,[ 11] [ 7] mass of the Sun with an oxygen rich chemical abundance.[ 12] core , the star has expanded to 263[ 7] Sun's radius . On average, the star is radiating 3,837[ 7] luminosity of the Sun from its swollen photosphere with an effective temperature ranging around 2,812 K.[ 7] × 10−6 M ☉ /yr−1 [ 6] ′ [ 12]
See also
References
^ "Download Data" . aavso.org . AAVSO. Retrieved 1 October 2021 .^ a b c d e Brown, A. G. A. ; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties" . Astronomy & Astrophysics 616 . A1. arXiv :1804.09365 Bibcode :2018A&A...616A...1G doi :10.1051/0004-6361/201833051 Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR .^ a b c d e Samus, N. N.; et al. (2017). "General Catalogue of Variable Stars". Astronomy Reports . 5.1. 61 (1): 80– 88. Bibcode :2017ARep...61...80S . doi :10.1134/S1063772917010085 . S2CID 125853869 . ^ a b Ducati, J. R. (2002). "Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues . 2237 : 0. Bibcode :2002yCat.2237....0D . ^ a b Famaey, B.; et al. (January 2005). "Local kinematics of K and M giants from CORAVEL/Hipparcos/Tycho-2 data. Revisiting the concept of superclusters". Astronomy and Astrophysics . 430 (1): 165– 186. arXiv :astro-ph/0409579 Bibcode :2005A&A...430..165F . doi :10.1051/0004-6361:20041272 . S2CID 17804304 . ^ a b c McDonald, I.; De Beck, E.; Zijlstra, A. A.; Lagadec, E. (2018). "Pulsation-triggered dust production by asymptotic giant branch stars" . Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society . 481 (4): 4984. arXiv :1809.07965 Bibcode :2018MNRAS.481.4984M . doi :10.1093/mnras/sty2607 S2CID 118969263 . ^ a b c d e f g Takeuti, Mine; et al. (2013). "A Method to Estimate the Masses of Asymptotic Giant Branch Variable Stars" . Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan . 65 (3): 60. Bibcode :2013PASJ...65...60T . doi :10.1093/pasj/65.3.60 ^ "R Cas" . SIMBAD Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg . Retrieved 2019-08-17 .^ Cannon, Annie J. (1907). "Second catalogue of variable stars" . Annals of Harvard College Observatory . 55 : 1– 94. Bibcode :1907AnHar..55....1C . Retrieved 12 January 2025 . ^ Toone, John (2010). "British variable star associations, 1848-1908" (PDF) . J. Br. Astron. Assoc . 120 (3): 135– 151. Retrieved 12 January 2025 . ^ Assaf, K. A. (December 2018). "Multi-epoch Proper Motion Magnetic Field Comparison of SiO Masers around R Cas" . The Astrophysical Journal . 869 (1): 19. Bibcode :2018ApJ...869...80A . doi :10.3847/1538-4357/aaea65 ^ a b Ueta, T.; et al. (May 2010). "The interface between the stellar wind and interstellar medium around R Cassiopeiae revealed by far-infrared imaging". Astronomy and Astrophysics . 514 : 6. arXiv :0911.4918 Bibcode :2010A&A...514A..16U . doi :10.1051/0004-6361/200913455 . S2CID 54745858 . A16.