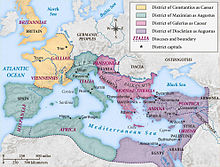
Nicomedia
| |||||||||||
Read other articles:

Terbang meluncur adalah penerbangan yang dilakukan oleh objek yang lebih berat dari udara tanpa menggunakan tenaga dorongan. Metode ini digunakan oleh beberapa jenis burung dan pesawat seperti glider. Contoh Penggunaan Karya Manusia Glider Layang gantung Paralayang Parasut Kapal terbang kertas Binatang Beberapa binatang memiliki kemampuan melakukan terbang dengan menggunakan teknik terbang melayang dan terbang membumbung untuk menempuh jarak yang jauh tanpa mengepakkan sayap. Hal ini dapat mengh…

提示:此条目页的主题不是沙菲宜阿都拉。 这是马来族人名,“阿达”是父名,不是姓氏,提及此人时应以其自身的名“莫哈末·沙菲益”为主。 尊敬的拿督斯里哈芝沙菲益阿达Mohd Shafie bin Hj. Apdal国会议员、州议员马来西亚国会下议院仙本那现任就任日期1995年4月26日前任山卡兰丹戴(馬來語:Sakaran Dandai)(国阵巫统)多数票12,218(1995)13,325(1999)13,319(2004)17,462…

2016年美國總統選舉 ← 2012 2016年11月8日 2020 → 538個選舉人團席位獲勝需270票民意調查投票率55.7%[1][2] ▲ 0.8 % 获提名人 唐納·川普 希拉莉·克林頓 政党 共和黨 民主党 家鄉州 紐約州 紐約州 竞选搭档 迈克·彭斯 蒂姆·凱恩 选举人票 304[3][4][註 1] 227[5] 胜出州/省 30 + 緬-2 20 + DC 民選得票 62,984,828[6] 65,853,514[6] 得…

American religious leader Francis M. LymanPresident of the Quorum of the Twelve ApostlesOctober 6, 1903 (1903-10-06) – November 18, 1916 (1916-11-18)PredecessorBrigham Young Jr.SuccessorHeber J. Grant Quorum of the Twelve ApostlesOctober 27, 1880 (1880-10-27) – November 18, 1916 (1916-11-18)Called byJohn Taylor LDS Church ApostleOctober 27, 1880 (1880-10-27) – November …

استسلم 42 من قوارب U الراسية في ليزاهالي ، أيرلندا الشمالية في يونيو 1945 مدمرة تابعة للبحرية البولندية ORP Krakowiak تقوم بسحب السفينة الألمانية نوع XXIII U-2337 إلى البحر لقرقتها في 28 نوفمبر 1945 عملية مصراع الكوة هي الاسم الرمزي لعملية قامت بها البحرية الملكية لإغراق غواصات يو بوت الألما�…

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع قائمة الدول حسب الناتج المحلي الإجمالي (توضيح). تتضمن هذه المقالة ثلاث قوائم لبلدان العالم مرتبة حسب ناتجها المحلي الإجمالي للفرد الواحد في القيم الاسمية، وتضم القيمة النهائية لجميع السلع والخدمات المنتجة داخل الدولة في سنة معينة وتحويلها بأسعار ال…

Greek city in ancient Caria For the town of ancient Laconia, Greece, see Iasos (Laconia). For the New Age musician, see Iasos (musician). IasosἸασός or Ἰασσός (in Greek)The hill with the acropolis, the bouleuterion (center) and a Hellenistic tower (right) near the agora of Iasos.Shown within TurkeyAlternative nameIassosLocationKıyıkışlacık, Muğla Province, TurkeyRegionCariaCoordinates37°16′40″N 27°35′11″E / 37.27778°N 27.58639°E / 37.27…

Luigi Agretti (La Spezia, 16 agosto 1877 – La Spezia, 17 novembre 1937) è stato un pittore e decoratore italiano. È stato artista le cui realizzazioni si valgono di un repertorio formale di tarda matrice neoclassica. Nella sua carriera ha alternato produzioni da cavalletto, affreschi e decorazioni ornamentali. Tutte le sue opere, sia ad olio che a fresco, rivelano un meticoloso studio di particolari, con estrema accuratezza nel disegno e molta originalità, trattando soggetti sia sacri che p…

Swiss rail project The NRLA project is the centrepiece of the Central European rail network. The New Railway Link through the Alps (NRLA; German: Neue Eisenbahn-Alpentransversale, NEAT, French: nouvelle ligne ferroviaire à travers les Alpes, NLFA, Italian: Nuova ferrovia transalpina, NFTA), is a Swiss construction project for faster north–south rail links across the Swiss Alps. It consists of two axes with several improvements along these rails including three new base tunnels several hundred…

Public school in Euless, Tarrant County, Texas, United StatesTrinity High SchoolAddress500 North Industrial BoulevardEuless, Tarrant County, Texas 76039United StatesInformationTypePublicMottoResponsibility, Pride, and Determination Make Trinity DifferentEstablished1968School districtHurst-Euless-Bedford Independent School DistrictNCES School ID482406002682[1]PrincipalMichael MartinakFaculty148.2 (FTE)[2]Grades10–12Number of students2,674 (2020–21)[2] • Gra…

Neighborhood of Los Angeles in California, United States of AmericaLittle EthiopiaNeighborhood of Los AngelesLittle Ethiopia neighborhood sign located at the intersection ofFairfax Avenue and Olympic BoulevardLittle EthiopiaLocation within Western Los AngelesCoordinates: 34°03′18″N 118°21′59″W / 34.055°N 118.366389°W / 34.055; -118.366389Country United States of AmericaState CaliforniaCounty Los AngelesTime zonePacificArea code323 Little Ethiopia is …

American science fiction television series This article is about the series. For the spaceship, see Starship Enterprise. Star Trek: EnterpriseAlso known asEnterpriseGenre Science fiction Action adventure Created by Rick Berman Brannon Braga Based onStar Trekby Gene RoddenberryShowrunners Brannon Braga Manny Coto Starring Scott Bakula John Billingsley Jolene Blalock Dominic Keating Anthony Montgomery Linda Park Connor Trinneer Opening themeFaith of the Heart, performed by Russell WatsonEnding the…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada April 2017. Shu NagaiInformasi pribadiNama lengkap Shu NagaiTanggal lahir 26 Mei 1980 (umur 44)Tempat lahir JepangPosisi bermain GelandangKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2001 Tokyo Verdy * Penampilan dan gol di klub senior hanya dihitung dari liga domestik Shu…

Green SwizzleCocktailTypeMixed drinkBase spirit Rum ServedFrozen: blended with iceStandard drinkware Collins glassCommonly used ingredientsfalernum, carypton A Green Swizzle is an alcohol-containing cocktail of the sour family. It was popular in Trinidad at the beginning of the 20th century but got lost during the course of the Second World War. Today's recipes usually constitute an often distinct divergence from the original. History The earliest written evidence for the existence of the Green …

Cassinetta di Lugagnano Kommun Villa Visconti Maineri Flagga Vapen Officiellt namn: Comune di Cassinetta di Lugagnano Land Italien Region Lombardiet Storstadsregion Milano Höjdläge 125 m ö.h. Koordinater 45°25′21″N 8°54′22″Ö / 45.42247°N 8.90604°Ö / 45.42247; 8.90604 Yta 3,32 km²[1] Folkmängd 1 870 (2018)[2] Befolkningstäthet 563 invånare/km² Tidszon CET (UTC+1) - sommartid CEST (UTC+2) P…

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع أذربيجان (توضيح). هذه المقالة عن دولة أذربيجان. لالمنطقة الواقعة في إيران، طالع أذربيجان (إيران). للصحيفة الحكومية، طالع أذربيجان (صحيفة). جمهورية أذربيجان Azərbaycan Respublikası (أذرية) أذربيجانعلم أذربيجان أذربيجانشعار أذربيجان موقع أذربيجا…

Cet article est une ébauche concernant les Îles Féroé. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. StreymoyGéographiePays îles FéroéCoordonnées 62° 00′ 42″ N, 6° 46′ 03″ ODémographiePopulation 24 781 hab. (2019)FonctionnementStatut Région des îles Féroémodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata Carte des îles Féroé indiquant leur décou…
Confédération Africaine de FootballLogo Discipline Calcio Calcio a 5 Fondazione8 febbraio 1957 GiurisdizioneAfrica Federazioni affiliate54 ConfederazioneFIFA (dal 1957) Sede 6 ottobre Presidente Patrice Motsepe Sito ufficialewww.cafonline.com Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale La giurisdizione del CAF La Confédération Africaine de Football (in inglese Confederation of African Football; in arabo الاتحاد الأفريقي لكرة القدم أو الكنفدرال�…

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 瓊·羅賓遜出生(1903-10-31)1903年10月31日 英格兰薩里郡坎伯利逝世1983年8月5日(1983歲—08—05)(79歲) 英格兰劍橋郡劍橋�…

Use of Cannabis in Burundi This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Cannabis in Burundi – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2018) Cannabis in Burundi is illegal. History A 1977 United States Congressional report noted that cannabis in Burundi was illegal, with cultivation, tr…