National Presbyterian Church in Mexico
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Indoor stadium at the Dallas Cowboys headquarters Ford Center at The StarTostitos Championship Plaza, at the entrance to Ford Center at the Star. The plaza's field is a miniature 3⁄5 representation of an official field.Address9 Cowboys WayLocationFrisco, TexasCoordinates33°06′38″N 96°49′41″W / 33.1105°N 96.8281°W / 33.1105; -96.8281OperatorDallas CowboysCapacity12,000SurfaceHellas Matrix Helix TurfConstructionBroke groundAugust 22, 2014Opened2016Construc…

Coppa delle Alpi 1967 Competizione Coppa delle Alpi Sport Calcio Edizione 7ª Luogo Svizzera Partecipanti 8 Risultati Vincitore Eintracht Francoforte(1º titolo) Statistiche Incontri disputati 20 Gol segnati 57 (2,85 per incontro) Cronologia della competizione 1966 1968 Manuale La Coppa delle Alpi 1967 è stata la settima edizione del torneo a cui hanno partecipato le squadre dei campionati italiano, svizzero e (per la prima volta) tedesco occidentale. A vincere la coppa fu l'Ei…

Italian basketball coach Sergio ScarioloSergio Scariolo at EuroBasket 2011Personal informationBorn (1961-04-01) 1 April 1961 (age 63)Brescia, ItalyNationalityItalianPositionHead coachCoaching career1989–presentCareer historyAs coach:1989–1991Scavolini Pesaro1991–1993Aurora Desio1993–1997Fortitudo Bologna1997–1999Saski Baskonia1999–2002Real Madrid2003–2008Unicaja Málaga2008–2010Khimki Moscow2009–2012Spain2011–2013Olimpia Milano2013–2014Saski Baskonia2015–presentSpain…

Single by Ramji Gulati ft. Team07 This article may need to be rewritten to comply with Wikipedia's quality standards. You can help. The talk page may contain suggestions. (February 2020) Nazar Na Lag JayeSingle by Ramji GulatiLanguageHindiPunjabiReleased21 September 2019 (2019-09-21)Genre Indian pop Filmi Length3:43LabelUnited White FlagSongwriter(s) Moody Akkhar Producer(s)United White Flag StudiosMusic videoNazar Na Lag Jaye on YouTube Nazar Na Lag Jaye is a song by Indian singe…

Військово-музичне управління Збройних сил України Тип військове формуванняЗасновано 1992Країна Україна Емблема управління Військово-музичне управління Збройних сил України — структурний підрозділ Генерального штабу Збройних сил України призначений для плануван�…

Politics of Denmark Constitution Fundamental laws Act of Succession Freedom of Speech Freedom of the Press The Crown Monarch Frederik X Crown Prince Christian Royal family Privy Council Purveyors to the Royal Court The unity of the Realm Denmark proper Faroe Islands Greenland Executive Government Frederiksen II Prime Minister (list) Mette Frederiksen Government Offices Ministries High Commissioners Faroe Islands Greenland Legislature Folketinget (parliament) Speaker: Søren Gade Members Judiciar…

فيصل بن فهد بن عبد الله آل سعود معلومات شخصية مكان الميلاد الرياض مواطنة السعودية الأب فهد بن عبد الله بن محمد بن عبد الرحمن آل سعود عائلة آل سعود الحياة العملية المهنة صاحب أعمال اللغة الأم العربية اللغات العربية تعديل مصدري - تعديل يفتقر محتوى هذه…

American college football season 2002 LSU Tigers footballSEC Western Division co-championCotton Bowl Classic, L 20–35 vs. TexasConferenceSoutheastern ConferenceDivisionWestern DivisionRecord8–5 (5–3 SEC)Head coachNick Saban (3rd season)Offensive coordinatorJimbo Fisher (3rd season)Defensive coordinatorWill Muschamp (1st season)Home stadiumTiger Stadium(Capacity: 91,600)Seasons← 20012003 → 2002 Southeastern Conference football standings vte Conf Ove…

German family business Fichtel & SachsCompany typePrivateIndustryAutomotiveFoundedAugust 1895; 128 years ago (1895-08)Schweinfurt,Germany (as Schweinfurt Precision Ball Bearing factories)FounderErnst SachsKarl Fichtel Defunct2011SuccessorMannesmannZF Friedrichshafen HeadquartersSchweinfurt, GermanyArea served Worldwide ProductsMotorsBicyclesBall bearingsAutomotive partsRevenue Euro 1.832 billion (2009)[1]Number of employees16,488 [1] (200…

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (نوفمبر 2020) سفارة مصر في تونس مصر تونس البلد تونس المكان تونس السفير إيهاب فهمي تعديل مصدري - تعديل سفارة مصر في …

Russian and Ukrainian beers In Russia, beer (Russian: пиво pivo) is tied with vodka as the most popular alcoholic drink in the country. The average Russian person drank about 11.7 liters of pure alcohol in 2016, with beer and vodka accounting for 39% each.[1] Russians categorize beer by color rather than fermentation process: Light, Red or Semi-Dark and Dark. [2] Until 2011, anything containing less than 10% alcohol was classified as food in Russia, and sale of beer was there…

Excavation of sediment, usually under water Dredge redirects here. For other uses, see Dredge (disambiguation). Dredgers redirects here. Not to be confused with Dreggers. Dragger redirects here. For the fishing boat, see Fishing trawler. A grab dredge Dredging is the excavation of material from a water environment. Possible reasons for dredging include improving existing water features; reshaping land and water features to alter drainage, navigability, and commercial use; constructing dams, dike…
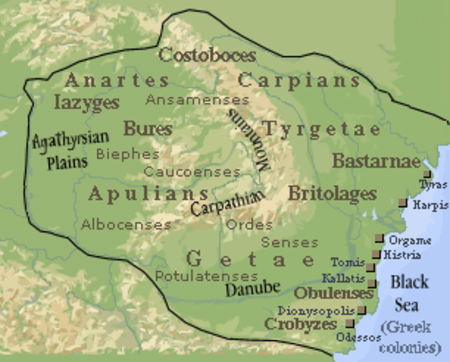
Historical region in Central Europe For other uses, see Transylvania (disambiguation). Siebenbürgen redirects here. For the band, see Siebenbürgen (band). TransylvaniaTransilvania / Ardeal (Romanian)Erdély (Hungarian)Siebenbürgen (German)Siweberjen (German)[a] Flag Coat of arms Transylvania Banat, Crișana and Maramureș Bukovina, Dobruja, Moldavia, Muntenia, and OlteniaLargest cityCluj-NapocaOfficial languagesRomanian[1&…

← 152 153 154 → ← 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 → Daftar angka — Bilangan bulat ← 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 →Kardinalseratus lima puluh tigaOrdinalke-153(keseratus lima puluh tiga)Faktorisasi32· 17 Pembagi1, 3, 9, 17, 51, 153RomawiCLIIIBiner100110012Ternari122003Kuaternari21214Quinary11035Senary4136Oktal2318Duodesimal10912Heksadesimal9916Vigesimal7D20Basis 364936 153 (dibaca seratus lima puluh tiga) adalah sebuah angka dan sistem bilangan yang mewakil…

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Bastrop. Cet article est une ébauche concernant le Texas. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Comté de Bastrop(en) Bastrop County Le palais de justice de Bastrop, siège du comté. Administration Pays États-Unis État Texas Chef-lieu Bastrop Fondation 1836 Démographie Population 97 216 hab. (2020) Densité 42 hab./km2 Géographie Coordonnées 30° …

Sporting event delegationBrazil at the1964 Summer OlympicsIOC codeBRANOCBrazilian Olympic CommitteeWebsitewww.cob.org.br (in Portuguese)in TokyoCompetitors61 (60 men and 1 woman) in 11 sportsFlag bearer Wlamir MarquesMedalsRanked 35th Gold 0 Silver 0 Bronze 1 Total 1 Summer Olympics appearances (overview)1920192419281932193619481952195619601964196819721976198019841988199219962000200420082012201620202024 Brazil competed at the 1964 Summer Olympics in Tokyo, Japan. 61 competitors, 60 men…

Madonna col Bambino, Museo nazionale di Villa Guinigi, Lucca Matteo Civitali (Lucca, 1436 – Lucca, 1502) è stato uno scultore italiano del XV secolo; come molti artisti del suo tempo, fu anche architetto ed ingegnere. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Opere 3 Gli eredi di Matteo Civitali 4 Omaggi 5 Note 6 Altri progetti 7 Collegamenti esterni Biografia Il nome deriva dall'essere il di lui padre, Giovanni da Civitale, friulano, proveniente da Cividale. Matteo nacque a Lucca e si formò alla scuola fiorenti…

Besart Berisha was the first player to score 100 A-League goals and is the highest scorer in the competition's history Since the A-League Men's formation, at the start of the 2005–06 season, a total of 17 players have scored 50 or more goals in the competition. During the 2010–11 season, Archie Thompson became the first player to score 50 goals. Meanwhile, during the 2016–17 season, Besart Berisha became the first player to score 100 goals in the competition.[1] Bruno Fornaroli is …

San Diego Film Critics Society Award for Best Supporting ActressCurrent recipient: Rachel McAdamsAwarded forBest Performance by an Actress in a Supporting RoleCountryUnited StatesPresented bySan Diego Film Critics SocietyFirst awarded1996Currently held byRachel McAdams Are You There God? It's Me, Margaret. (2023)Websitesdfcs.org The San Diego Film Critics Society Award for Best Supporting Actress is an award given by the San Diego Film Critics Society to honor supporting female acting achievemen…

Cat having fur of two colors Chelsea Clinton's cat Socks (1989–2009) lived in the White House from 1993 to 2001. Socks was a bicolor cat with low-grade spotting, or tuxedo cat. A bicolor cat (also bicolour cat, or a more specific term such as black-and-white cat) is a cat with white fur combined with fur of some other color, for example solid black, tabby, or colorpointed.[1] There are various patterns of a bicolor cat. These range from the Van-patterned (color on the crown of the head…








