|
Monoethanolamine oleate
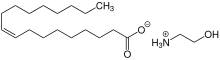
Monoethanolamine oleate (ethanolammonium oleate) is an organic compound with the formula [CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7CO2][H3NCH2CH2OH].. A colorless oily liquid, it is an example of a protic ionic liquid.[1] It is a salt formed by the reaction between monoethanolamine and oleic acid.[2] Antivaricose agentAs an antivaricose agent, it is injected topically into varicosities to cause sclerosis (closure) of the abnormal vein. It is indicated for the treatment of patients with esophageal varices that have recently bled, to prevent rebleeding. Ethanolamine is not indicated for the treatment of patients with esophageal varices that have not bled. There is no evidence that treatment of this population decreases the likelihood of bleeding. Sclerotherapy with ethanolamine has no beneficial effect upon portal hypertension, the cause of esophageal varices, so that recanalization and collateralization may occur, necessitating reinjection.[3] References
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia