|
Maxillary nerve
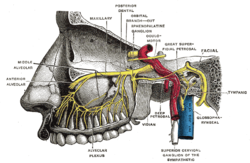
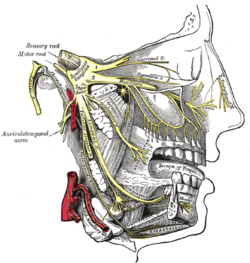
In neuroanatomy, the maxillary nerve (V2) is one of the three branches or divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth (CN V) cranial nerve. It comprises the principal functions of sensation from the maxilla, nasal cavity, sinuses, the palate and subsequently that of the mid-face,[1] and is intermediate, both in position and size, between the ophthalmic nerve and the mandibular nerve.[2] StructureIt begins at the middle of the trigeminal ganglion as a flattened plexiform band then it passes through the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus. It leaves the skull through the foramen rotundum, where it becomes more cylindrical in form, and firmer in texture. After leaving foramen rotundum it gives two branches to the pterygopalatine ganglion. It then crosses the pterygopalatine fossa, inclines lateralward on the back of the maxilla, and enters the orbit through the inferior orbital fissure. It then runs forward on the floor of the orbit, at first in the infraorbital groove and then in the infraorbital canal remaining outside the periosteum of the orbit. It then emerges on the face through the infraorbital foramen and terminates by dividing into inferior palpebral, lateral nasal and superior labial branches. The nerve is accompanied by the infraorbital branch of (the third part of) the maxillary artery and the accompanying vein. BranchesIts branches may be divided into four groups, depending upon where they branch off: in the cranium, in the pterygopalatine fossa, in the infraorbital canal, or on the face. In the cranium
From the pterygopalatine fossa
In the infraorbital canalOn the face
FunctionThe Maxillary nerve gives cutaneous branches to the face. It also carries parasympathetic preganglionic fibers (sphenopalatine) and postganglionic fibers (zygomatic, greater and lesser palatine and nasopalatine) to and from the pterygopalatine ganglion. Additional images
See alsoReferences
Books
External links
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia