|
Magnesium permanganate
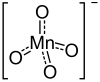
Magnesium permanganate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Mg(MnO4)2. It can be used as an oxidant.[1] PreparationMagnesium permanganate hexahydrate was prepared by E. Mitserlich and H. Aschoff by reacting barium permanganate with magnesium sulfate:[2]
It can be obtained by the reaction of magnesium chloride and silver permanganate:
The hexahydrate Mg(MnO4)2·6H2O can be crystallized from the solution, which is slightly hygroscopic.[3] The anhydrous form can be obtained by decomposing the hexahydrate by heating it. Chemical propertiesMagnesium permanganate hexahydrate is a blue-black solid.[4] It decomposes at 130 °C with the evolution of oxygen in an autocatalytic decomposition process. The tetrahydrate decomposes above 150 °C. The crystals are practically insoluble in carbon trichloride, carbon tetrachloride, benzene, toluene, nitrobenzene ether, ligroin and carbon disulfide, but soluble in pyridine and glacial acetic acid. It dissolves in water and dissociates completely in dilute solutions. It oxidizes a range of organic compounds and reacts instantly (in some cases with fire) with common solvents such as tetrahydrofuran, ethanol, methanol, t-butanol, acetone and acetic acid.[2] ApplicationsMagnesium permanganate is used in various branches of industry and technology, such as:[2]
References
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia