|
Hydrogen maser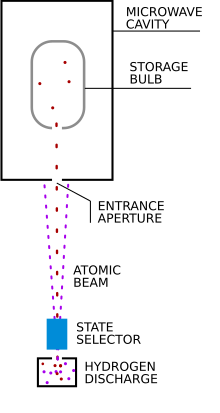 A hydrogen maser, also known as hydrogen frequency standard, is a specific type of maser that uses the intrinsic properties of the hydrogen atom to serve as a precision frequency reference. OverviewBoth the proton and electron of a hydrogen atom have spins. The atom has a higher energy if both are spinning in the same direction, and a lower energy if they spin in opposite directions. The amount of energy needed to reverse the spin of the electron is equivalent to a photon at the frequency of 1.420405751768 GHz,[1] which corresponds to the 21 cm line in the hydrogen spectrum. Hydrogen masers are very complex devices and sell for as much as US$235,000.[2] There are two types to be distinguished: active and passive. In both types, a small storage bottle of molecular hydrogen, H The storage bulb is inside a microwave cavity made from a precisely machined copper or silver-plated ceramic cylinder. This cavity is tuned to the 1.420 GHz resonance frequency of the atoms.[4] A weak static magnetic field is applied parallel to the cavity axis by a solenoid to lift the degeneracy of the magnetic Zeeman sublevels.[5] To decrease the influence of changing external magnetic fields on the transition line frequency and be compliant to electromagnetic interferences, the cavity is surrounded by several nested layers of shields.[3] In the active hydrogen maser, the cavity oscillates by itself. This requires a higher hydrogen atom density and a higher quality factor for the cavity. With advanced microwave cavities made out of silver-plated ceramic, the gain factor can be much higher, thereby requiring less hydrogen atom density.[3] The active maser is more complex and more expensive but has better short-term and long-term frequency stabilities. In the passive hydrogen maser, the cavity is fed from an external 1.420 GHz frequency. The external frequency is tuned to produce a maximum output in the cavity. This allows the use of lower hydrogen atom density and lower cavity quality factor, which reduces the cost.
See alsoReferences
Bibliography
External links
|
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia


