Homathko River
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

هنودمعلومات عامةنسبة التسمية الهند التعداد الكليالتعداد قرابة 1.21 مليار[1][2]تعداد الهند عام 2011ق. 1.32 مليار[3]تقديرات عام 2017ق. 30.8 مليون[4]مناطق الوجود المميزةبلد الأصل الهند البلد الهند الهند نيبال 4,000,000[5] الولايات المتحدة 3,982,398[6] الإمارا�…

Державний комітет телебачення і радіомовлення України (Держкомтелерадіо) Приміщення комітетуЗагальна інформаціяКраїна УкраїнаДата створення 2003Керівне відомство Кабінет Міністрів УкраїниРічний бюджет 1 964 898 500 ₴[1]Голова Олег НаливайкоПідвідомчі орг�…

泰国陆军元帅他侬·吉滴卡宗ถนอม กิตติขจรPChW SR MPCh MWM第10任泰國總理任期1963年12月9日—1973年10月14日君主拉玛九世前任沙立·他那叻元帥继任訕耶·探瑪塞任期1958年1月1日—1958年10月20日君主拉玛九世前任乃朴·沙拉信继任沙立·他那叻元帥第32任泰國國防部長任期1957年9月23日—1973年10月14日前任鑾披汶·頌堪继任他威·尊拉塞(英语:Dawee Chullasapya) 个人资料出生(…

TaurierscomuneTauriers – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Francia RegioneAlvernia-Rodano-Alpi Dipartimento Ardèche ArrondissementLargentière CantoneVallon-Pont-d'Arc TerritorioCoordinate44°33′N 4°17′E / 44.55°N 4.283333°E44.55; 4.283333 (Tauriers)Coordinate: 44°33′N 4°17′E / 44.55°N 4.283333°E44.55; 4.283333 (Tauriers) Superficie4,46 km² Abitanti189[1] (2009) Densità42,38 ab./km² Altre informazioniCod. postale07110 Fuso …
Kenyan steeplechase runner Not to be confused with Paul Koech. Kipsiele Koech running on the 2010 Diamond League circuit Paul Kipsiele Koech (born 10 November 1981) is a Kenyan runner who specializes in the 3000 metres steeplechase. He won the 2004 Olympic bronze medal in this event. His personal best of 7:54.31 minutes is the third fastest of all time.[1] He was born in 1981 in Kapchepkoro, near Sotik town, Sotik District. He graduated from Cheplanget Secondary School in 1999. He did we…

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要編修,以確保文法、用詞、语气、格式、標點等使用恰当。 (2013年8月6日)請按照校對指引,幫助编辑這個條目。(幫助、討論) 此條目剧情、虛構用語或人物介紹过长过细,需清理无关故事主轴的细节、用語和角色介紹。 (2020年10月6日)劇情、用語和人物介紹都只是用於了解故事主軸,輔助讀�…

Book by Thomas Jefferson Notes was the only full-length book published by Thomas Jefferson in his lifetime. Notes on the State of Virginia (1785) is a book written by the American statesman, philosopher, and planter Thomas Jefferson. He completed the first version in 1781 and updated and enlarged the book in 1782 and 1783. It originated in Jefferson's responses to questions about Virginia, part of a series of questions posed to each of the thirteen states in 1780 by François Barbé-Marbois, the…

علم الضحاياصنف فرعي من psychotraumatology (en) — علم الجريمة المواضيع تضحية — Victim of crime or civil wrong (en) تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات علم الضحايا (بالإنجليزية: Victimology) هو علم دراسة الإيذاء، بما في ذلك العلاقة بين الضحايا والجناة، والتفاعلات بين الضحايا ونظام العدالة الجنائية - أي �…
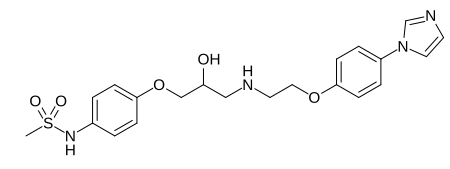
Ersentilide Names IUPAC name N-[4-[2-Hydroxy-3-[2-(4-imidazol-1-ylphenoxy)ethylamino]propoxy]phenyl]methanesulfonamide Identifiers CAS Number 125228-82-2 3D model (JSmol) Interactive image ChEMBL ChEMBL99585 ChemSpider 115376 PubChem CID 130400 InChI InChI=1S/C21H26N4O5S/c1-31(27,28)24-17-2-6-21(7-3-17)30-15-19(26)14-22-11-13-29-20-8-4-18(5-9-20)25-12-10-23-16-25/h2-10,12,16,19,22,24,26H,11,13-15H2,1H3Key: QZWUQVSQIFFFKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N SMILES CS(=O)(=O)NC1=CC=C(C=C1)OCC(CNCCOC2=CC=C(C=C2)N3C=…

Armed wing of the Communist Party of the Philippines This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article relies excessively on references to primary sources. Please improve this article by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Find sources: New People's Army – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2021) (Learn how and when to …

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Maret 2016. SMP Negeri 3 PaluInformasiRentang kelasVII, VIII, IXKurikulumKurikulum Tingkat Satuan PendidikanAlamatLokasiJl. Kemiri 35, Palu, Sulawesi TengahMoto SMP Negeri (SMPN) 3 Palu, merupakan salah satu Sekolah Menengah Pertama Negeri yang ada di Provinsi Sulawesi…

Respuesta de la Unión Europea a la invasión rusa de Ucrania Parte de la refundación de la Unión Europea y la construcción del relato europeo. La Torre Eiffel durante la presidencia francesa del Consejo de la UE en 2022.Fecha 24 de febrero de 2022 – presente (2 años, 3 meses y 17 días)Lugar Unión EuropeaAcción Aumento de las sanciones impuestas por la UE a Rusia Aumento de la ayuda (humanitaria, política, económica y militar) de la UE a Ucrania.Causas Invasión r…

This article is about fuel coke derived from coal. For fuel coke derived from petroleum, see Petroleum coke. For other uses, see Coke (disambiguation). Coal product used in making steel Raw coke Coke is a grey, hard, and porous coal-based fuel with a high carbon content. It is made by heating coal or oil in the absence of air. Coke is an important industrial product, used mainly in iron ore smelting, but also as a fuel in stoves and forges. The unqualified term coke usually refers to the product…

ملعب أرثر أشArthur Ashe Stadium (بالإنجليزية) معلومات عامةسمّي باسم أرثر أش[1] المنطقة الإدارية كوينز البلد الولايات المتحدة التشييد والافتتاحالافتتاح الرسمي 1997 المهندس المعماري Rossetti Architects (en) المقاول الرئيسي USTA Billie Jean King National Tennis Center (en) الاستعمالالرياضة كرة المضرب المستضيف …

1984 US television film directed by Clive Donner A Christmas Carol1984 posterGenreDramaFamilyFantasyBased onA Christmas Carol by Charles DickensScreenplay byRoger O. HirsonDirected byClive DonnerStarringGeorge C. ScottFrank FinlayDavid WarnerSusannah YorkEdward WoodwardRoger ReesLiz SmithMusic byNick BicâtCountry of originUnited KingdomUnited StatesOriginal languageEnglishProductionExecutive producerRobert E. FuiszProducersGeorge F. StorkeAlfred R. KelmanProduction locationsShrewsbury, Shropshi…

Alessandro Scarlatti Alessandro Scarlatti (Palermo, 2 maggio 1660 – Napoli, 24 ottobre 1725) è stato un compositore italiano di musica barocca. Considerato dai musicologi come uno dei più importanti rappresentanti della scuola musicale napoletana, fu il maggiore compositore d'opera italiano tra la fine del XVII e l'inizio del XVIII secolo. Soprannominato dai suoi contemporanei “l'Orfeo italiano”, divise la sua carriera tra Napoli e Roma, dove ricevette la sua formazione; proprio alla cit…

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) 1841 في المملكة المتحدةمعلومات عامةالسنة 1841 1840 في المملكة المتحدة 1842 في المملكة المتحدة تعديل - تعديل مصدري -…

Hino 日野町Kota kecil BenderaLambangLokasi Hino di Prefektur TottoriNegara JepangWilayahChūgokuPrefektur TottoriDistrikHinoLuas • Total134 km2 (52 sq mi)Populasi (Oktober 1, 2015) • Total3.278 • Kepadatan24,46/km2 (6,340/sq mi)Zona waktuUTC+9 (JST)Kode pos689-4503Simbol • PohonCryptomeria japonica• BungaRhododendron• BurungAix galericulataNomor telepon0859-72-0331Alamat101 Neu, Hino-chō,Hino-gun, Tottori-…

Una donna di Ramallah, Palestina in abiti ricamati, 1929-1946 Il ricamo è stata un'arte importante nel mondo islamico, dall'inizio dell'Islam fino alla rivoluzione industriale che ha sconvolto gli stili di vita tradizionali. Indice 1 Panoramica 2 Tecniche 3 Simbolismo 4 Declino 5 Note 6 Bibliografia 7 Collegamenti esterni Panoramica Maschera da donna ricamata con filo d'argento. Fès, Marocco . XVIII-XIX secolo Il primo Islam prese il controllo delle società quando il ricamo di abiti, per entr…

American rock band SuperchunkSuperchunk in 2019Background informationOriginChapel Hill, North Carolina, United StatesGenresIndie rock, alternative rock, punk rock, emoYears active1989–presentLabelsMatador, MergeMembers Mac McCaughan Laura Ballance Jim Wilbur Jason Narducy Laura King Past members Chuck Garrison Jack McCook Jon Wurster Websitesuperchunk.com Superchunk is an American indie rock band from Chapel Hill, North Carolina, United States, consisting of singer-guitarist Mac McCaughan, gui…

