|
Geography of Anguilla
Anguilla is an island in the Leeward Islands. It has numerous bays, including Barnes, Little, Rendezvous, Shoal, and Road Bays. StatisticsLocation: Caribbean, island in the Caribbean Sea, east of Puerto Rico Geographic coordinates: 18°15′ N, 63°10′ W Map references: Central America and the Caribbean Area:
Area – comparative: about half the size of Washington, D.C. Coastline: 61 km Maritime claims:
Climate: tropical moderated by northeast trade winds Terrain: flat and low-lying island of coral and limestone Elevation extremes:
Natural resources: salt, fish, lobster Land use:
Natural hazards: frequent hurricanes and other tropical storms (July to October) Environment – current issues: supplies of potable water sometimes cannot meet increasing demand largely because of poor distribution system. Islands and cays The territory of Anguilla consists of the island of Anguilla itself (by far the largest), as well as numerous other islands and cays, most of which are very small and uninhabited. These include:
DistrictsAnguilla is divided into fourteen districts: 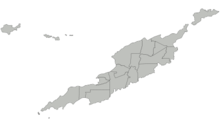
ClimateAnguilla features a tropical wet and dry climate under the Köppen climate classification. The island has a rather dry climate, moderated by northeast trade winds. Temperatures vary little throughout the year. Average daily maxima range from about 27 °C (80.6 °F) in December to 30 °C (86 °F) in July. With no mountains to slow or trap clouds, rainfall is erratic, averaging about 900 mm (35.4 in) per year, the wettest months being September and October, and the driest February and March. Anguilla is vulnerable to hurricanes from June to November, peak season August to mid-October. The island suffered damage from Hurricane Luis in 1995, severe flooding of 1.5 to 6 metres (5 to 19.5 feet) from Hurricane Lenny in 1999 and severe damage from Hurricane Irma in 2017, which remains the most powerful hurricane to hit the island.
VegetationAnguilla's coral and limestone terrain provide no subsistence possibilities for forests, woodland, pastures, crops, or arable lands. Its dry climate and thin soil hamper commercial agricultural development. In Anguilla forest cover is around 61% of the total land area, equivalent to 5,500 hectares (ha) of forest in 2020, which was unchanged from 1990.[3][4] See alsoReferences
External links
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia