|
Diepoxybutane
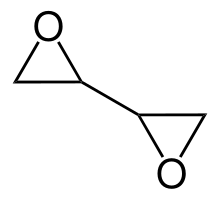
Diepoxybutane (also known as butane diepoxide, butadiene diepoxide, or 1,2:3,4-diepoxybutane) is an epoxide which is a colorless liquid at room temperature. Epoxides are very reactive due to ring strain and diepoxybutane contains two of these groups, so it is highly reactive, more than other ethers.[which?] It is hydrophilic, very flammable and easily ignited by heat or sparks.[citation needed] Diepoxybutane is used as a chemical intermediate, as a cross-linking agent for polymers and textiles, and as a preservative.[clarification needed][2][better source needed] Structure, reactivity, synthesisDiepoxybutane occurs as several enantiomers and a meso form.[citation needed] Diepoxybutane polymerizes in the presence of catalysts or when heated. These polymerization reactions can be violent.[3] Other UsesIn research diepoxybutane is used as a chemical intermediate, and in medicine for the diepoxybutane (DEB test) to screen for Fanconi anemia (FA) among patients with bone marrow failure syndromes.[4][better source needed] Although many chemicals are capable of DNA crosslinking, the DEB test is used because it gives fewer false negatives and positives than other chemicals.[5] ToxicityEffect on humansDiepoxybutane irritates the nose, throat and lungs, causing coughing and shortness of breath. Skin exposure can cause chemical burns. Longer exposure periods can cause pulmonary edema, and damage to the liver and kidneys.[6] Carcinogenicity
Effect on animalsIt is experimentally shown that diepoxybutane can cause tumors in rodent species at several different tissue sites and by several different exposure routes. Dermal contact with diepoxybutane caused skin tumors in mice.[quantify] Injection of diepoxybutane into mice and rats caused lung tumors. Furthermore, inhalation exposure to diepoxybutane caused benign Harderian-gland tumors in mice and also increased the size of benign or malignant tumors of the nasal cavity.[citation needed] References
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia