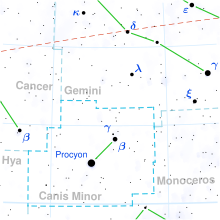
Star in the constellation Canis Minor
Delta1 Canis Minoris , Latinized from δ1 Canis Minoris, is a solitary,[ 11] star in the constellation Canis Minor . It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +5.25.[ 2] parallax shift of 4.29 mas as seen from Earth,[ 1] light years from the Sun .
Houk and Swift (1999) list a stellar classification of F0 V[ 4] 1 Canis Minoris, indicating it is an F-type main-sequence star . However, Cowley et al. (1969) gave it a class of F0 III, which would suggest it is instead an evolved giant star .[ 3] spectrum displays a higher than solar metallicity – a term indicating the abundance of elements other than hydrogen and helium compared to the Sun. The star is spinning with a projected rotational velocity of 50[ 9] [ 7] Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 7,623 K.[ 8]
References
^ a b c d e f van Leeuwen, F. (2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics , 474 (2): 653– 664, arXiv :0708.1752 Bibcode :2007A&A...474..653V , doi :10.1051/0004-6361:20078357 , S2CID 18759600 . ^ a b c d Johnson, H. L.; et al. (1966), "UBVRIJKL photometry of the bright stars", Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory , 4 (99): 99, Bibcode :1966CoLPL...4...99J . ^ a b Cowley, A.; et al. (April 1969), "A study of the bright A stars. I. A catalogue of spectral classifications", Astronomical Journal , 74 : 375– 406, Bibcode :1969AJ.....74..375C , doi :10.1086/110819 . ^ a b Houk, N.; Swift, C. (1999), "Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD Stars", Michigan Spectral Survey , 5 , Bibcode :1999MSS...C05....0H . ^ de Bruijne, J. H. J.; Eilers, A.-C. (October 2012), "Radial velocities for the HIPPARCOS-Gaia Hundred-Thousand-Proper-Motion project", Astronomy & Astrophysics , 546 : 14, arXiv :1208.3048 Bibcode :2012A&A...546A..61D , doi :10.1051/0004-6361/201219219 , S2CID 59451347 , A61. ^ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters , 38 (5): 331, arXiv :1108.4971 Bibcode :2012AstL...38..331A , doi :10.1134/S1063773712050015 , S2CID 119257644 . ^ a b McDonald, I.; et al. (2012), "Fundamental Parameters and Infrared Excesses of Hipparcos Stars", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society , 427 (1): 343– 57, arXiv :1208.2037 Bibcode :2012MNRAS.427..343M , doi :10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21873.x S2CID 118665352 . ^ a b c d Prugniel, Ph.; et al. (2011), "The atmospheric parameters and spectral interpolator for the MILES stars", Astronomy & Astrophysics , 531 : 25, arXiv :1104.4952 Bibcode :2011A&A...531A.165P , doi :10.1051/0004-6361/201116769 , S2CID 54940439 , A165. ^ a b Jasniewicz, G.; et al. (July 2006), "Lithium abundances for early F stars: new observational constraints for the Li dilution", Astronomy and Astrophysics , 453 (2): 717– 722, Bibcode :2006A&A...453..717J , doi :10.1051/0004-6361:20054421 ^ "del01 CMi" . SIMBAD Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg . Retrieved 2017-09-03 .{{cite web }}: CS1 maint: postscript (link )^ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008), "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 389 (2): 869– 879, arXiv :0806.2878 Bibcode :2008MNRAS.389..869E , doi :10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x S2CID 14878976 .
External links