Christopher T. Hill
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

ASD Torrino C5Calcio a 5 Segni distintivi Uniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Colori sociali blu/rosso/verde acqua Dati societari Città Roma Nazione Italia Confederazione UEFA Federazione FIGC Fondazione 1988 Rifondazione 2012 Rifondazione 2018 Presidente Piero Cucunato Palmarès Scudetti 2 Titoli nazionali 1 Coppa Italia di Serie A2, 1 Scudetto Femminile, 1 Scudetto Juniores, 1 Vice Campione d'Italia Allievi, 1 Vice Campione d'Italia Juniores Trofei nazionali 5 Coppe Italia10 Impianto Centro…

1981 Catholic Church document on marriage and the family Familiaris consortioLatin for 'The fellowship of the family' Apostolic exhortation of Pope John Paul IISignature date 22 November 1981Number2 of 15 of the pontificateTextIn English← Catechesi tradendae Redemptionis donum →Part of a series on theCatholic ChurchSt. Peter's Basilica, Vatican City Overview Pope: Francis Hierarchy History (timeline) Theology Liturgy Sacraments Mary Background Jesus Crucifixion R…

Ранний буддизмПисьменные источники Палийский канон Агамы Гандхара Соборы 1-й буддийский собор 2-й буддийский собор 3-й буддийский собор 4-й буддийский собор Школы Досектантский буддизм Махасангхика Экавьявахарика Локоттаравада Чайтика Апара Шайла Уттара Шайла Гокулика Б…

Election for Governor of Texas 1886 Texas gubernatorial election ← 1884 November 2, 1886 1888 → Candidate Lawrence Sullivan Ross Archelaus M. Cochran Ebenezer L. Dohoney Party Democratic Republican Prohibition Popular vote 228,776 65,236 65,236 Percentage 73.0% 20.8% 6.1% Governor before election John Ireland Democratic Governor-elect Lawrence Sullivan Ross Democratic Elections in Texas Federal government Presidential elections 1848 1852 1856 1860 1872 1876 1880…

State highway in New Mexico, United States State Road 6NM 6 highlighted in redRoute informationMaintained by NMDOTLength36.360 mi[1] (58.516 km)Major junctionsWest end I-40 on the Laguna Indian ReservationMajor intersections I-25 / US 85 in Los Lunas NM 314 in Los Lunas NM 263 in ValenciaEast end NM 47 in Valencia LocationCountryUnited StatesStateNew MexicoCountiesCibola, Valencia Highway system New Mexico State Highway System Inters…
Lokasi di Vietnam Mán Bạc merupakan situs arkeologi Neolitikum yang terletak di Distrik Yên Mô, Provinsi Ninh Bình, Vietnam,[1] berasal dari sekitar 1.850–1.650 SM. Mán Bạc dihubungkan dengan kebudayaan Phùng Nguyên. Dengan 95 pemakaman ditemukan di situs tersebut, Mán Bạc adalah situs terbesar dan paling utuh yang terkait dengan kebudayaan Phùng Nguyên, melampaui situs di Lung Hoa.[2] Referensi Kutipan ^ Oxenham 2011, hlm. 2. ^ Oxenham 2016, hlm. 111.…

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、蘭&…

Political system of Kazakhstan This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Politics of Kazakhstan – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Politics of Kazakhstan CIS member state Constitution Human rights President (list) Kassym-Jomart Tokayev Pr…

Standard RGB color space For the ancillary chunk in the PNG file format, see PNG § Ancillary chunks. sRGBIEC 61966-2-1 Default RGB Colour Space - sRGBsRGB colors situated at calculated position in CIE 1931 chromaticity diagram. Luminance Y {\displaystyle Y} set so that R + G + B = 1 {\displaystyle R+G+B=1} to avoid mach bands.AbbreviationsRGBStatusPublishedYear started1996First publishedOctober 18, 1999; 24 years ago (1999-10-18)[1]OrganizationIEC[1]Commit…

1998 single by Touch and Go Would You...?Single by Touch and Gofrom the album I Find You Very Attractive Released26 October 1998 (1998-10-26)[1]Genre Pop[2] jazz[2] Length3:12LabelV2Songwriter(s)David LoweProducer(s)David LoweTouch and Go singles chronology Would You...? (1998) Straight to... Number One (1999) AudioWould You...? on YouTube Would You...? is a song by British electronic group Touch and Go. Written and produced by band member David Lowe, it wa…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Januari 2023. SMK Al-MubarokInformasiAlamatLokasiJalan KH Abdul Latif No. 07, Kota Serang, Banten, IndonesiaMoto SMK Al-Mubarok adalah sebuah sekolah yang terletak di Kota Serang, provinsi Banten, Indonesia. Sejarah Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan (SMK) Al-Mubarok dibangun d…

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要編修,以確保文法、用詞、语气、格式、標點等使用恰当。 (2013年8月6日)請按照校對指引,幫助编辑這個條目。(幫助、討論) 此條目剧情、虛構用語或人物介紹过长过细,需清理无关故事主轴的细节、用語和角色介紹。 (2020年10月6日)劇情、用語和人物介紹都只是用於了解故事主軸,輔助讀�…

Species of amphibian Incilius bocourti Male and female in amplexus Conservation status Least Concern (IUCN 3.1)[1] Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Amphibia Order: Anura Family: Bufonidae Genus: Incilius Species: I. bocourti Binomial name Incilius bocourti(Brocchi, 1877) Synonyms Bufo bocourti Brocchi, 1877 Cranopsis bocourti (Brocchi, 1877) Ollotis bocourti (Brocchi, 1877) Incilius bocourti (formerly Bufo bocourti; common n…

1762 book by Jean-Jacques Rousseau This article is about Jean-Jacques Rousseau's 1762 treatise. For social contract as a political and philosophical concept, see Social contract. For other uses, see Social Contract (disambiguation). The Social Contract; or, Principles of Political Right Title page of the first octavo editionAuthorJean-Jacques RousseauOriginal titleDu contrat social; ou, Principes du droit politiqueCountryFrance (edited in Amsterdam)LanguageFrenchPublication date1762Original…

For other uses, see 116th Street. New York City Subway station in Manhattan New York City Subway station in Manhattan, New York 116 Street New York City Subway station (rapid transit)Platform viewStation statisticsAddressWest 116th Street & Frederick Douglass BoulevardNew York, NYBoroughManhattanLocaleHarlemCoordinates40°48′16″N 73°57′19″W / 40.804389°N 73.955412°W / 40.804389; -73.955412DivisionB (IND)[1]Line IND…

Windows ist eine Weiterleitung auf diesen Artikel. Weitere Bedeutungen sind unter Windows (Begriffsklärung) aufgeführt. Microsoft Windows Windows 11 Startmenü Entwickler Microsoft Lizenz(en) proprietär: Microsoft EULA Erstveröff. 20. November 1985 Akt. Version Windows 11 Architektur(en) IA-32, x64, ARM64historisch: x86 (16-Bit), MIPS, Alpha, PPC, IA-64, ARM32 Chronik siehe: ZeitleisteWindows 1.0Windows 2.xWindows 3.0Windows 3.1Windows 95Windows 98Windows Me Windows NT 3.1 Windows …
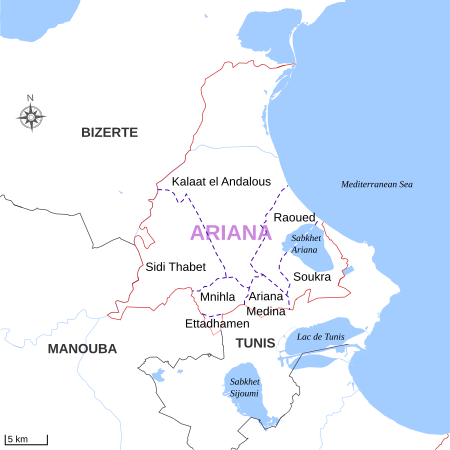
Governorate of Tunisia Governorate in TunisiaAriana Governorate ولاية أريانةGovernorateMap of Tunisia with Ariana highlightedSubdivisions of Ariana GovernorateCoordinates: 36°51′45″N 10°11′44″E / 36.86250°N 10.19556°E / 36.86250; 10.19556Country TunisiaCreatedMarch 1983[1]CapitalArianaGovernment • GovernorKhaled Nouri (since 2022)Area • Total482 km2 (186 sq mi) • RankRanked 23rd of 24Po…

この記事の正確性に疑問が呈されています。問題箇所に信頼できる情報源を示して、記事の改善にご協力ください。議論はノートを参照してください。(2009年2月) 粒子・反粒子振動(りゅうしはんりゅうししんどう、particle-antiparticle oscillation)または中性粒子振動(ちゅうせいりゅうししんどう、Neutral particle oscillation)とは素粒子物理学において、非ゼロの内部量子数�…

Self-similar growth curve Spira mirabilis redirects here. For the orchestra, see Spira Mirabilis (orchestra). For the Italian film, see Spira Mirabilis (film). Logarithmic spiral (pitch 10°) A section of the Mandelbrot set following a logarithmic spiral A logarithmic spiral, equiangular spiral, or growth spiral is a self-similar spiral curve that often appears in nature. The first to describe a logarithmic spiral was Albrecht Dürer (1525) who called it an eternal line (ewige Linie).[1]…

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento attori italiani non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Franco Citti nel film Il Decameron (1971) Franco Citti (Roma, 23 aprile 1935 – Fiumicino, 14 gennaio 2016) è stato un attore italiano. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Filmografia 2.1 Attore 2.1.1 Cinema 2.1.2 Televisi…













