|
Anti-ulcer agentsAnti-ulcer agents are medications or supplements used to cure the damage of mucosal layer on organs to prevent the damage from further extending to deeper regions to cause complications. An anti-ulcer medication for treating mouth ulcer is triamcinolone, a corticosteroid. Other anti-ulcer supplements include vitamin B2 and vitamin B12. Antibiotics and agents to reduce gastric acid secretion are used in combinations to treat Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)-induced peptic ulcer disease (PUD), an ulceration in the gastric region. Antibiotics include amoxicillin, clarithromycin and metronidazole. Bismuth subsalicylate is an antimicrobial agent of another drug class that can also be used to eradicate H. pylori for treating PUD. Agents for suppressing gastric acid secretion are proton-pump inhibitors (PPI), such as lansoprazole, pantoprazole, rabeprazole, omeprazole and esomeprazole. Anti-ulcer agents to treat mouth ulcerTriamcinolone, vitamin B2 and vitamin B12 can be used to treat mouth ulcers, which are confined, shallow, round to oval-shaped lesions that sometimes contain yellowish adherent central exudate and give a pain sensation.[1] Triamcinolone Triamcinolone is a corticosteroid, which can be applied on the ulcerated region to cure mouth ulcer by its anti-inflammatory action. Medical uses and available formsTriamcinolone is mainly used to treat recurrent mild to moderate aphthous stomatitis, also known as mouth ulcer.[2] This medication should show anti-ulcer effect or repair of oral tissues in seven days. This corticosteroid is available in the formulation of oral paste.[2] Mechanism of actionTriamcinolone exerts its anti-inflammatory effect by decreasing the formation, release and activity of inflammatory substances originated from human bodies.[3] By reducing the inflammation, it can achieve anti-ulcer effect.[3] Adverse effectsTriamcinolone commonly cause local side effects only. The undesirable effects may be oral mucosa changes that breaks the inner mouth mucosal layer. The damage in the mucosa may also cause redness and irritation on the application area.[4] In rare situations, systemic side effects may occur. Serious adverse drug reactions of this corticosteroid are Cushing's syndrome, symptoms and signs include high blood glucose level, excretion of glucose in urine and weight gain.[4] These undesirable effects can be prevented by not applying triamcinolone in large area.[4] ContraindicationsTriamcinolone should not be used if patients have hypersensitivity to triamcinolone.[5] Moreover, patients with fungal, viral, or bacterial infections in the mouth or throat should not consider using this medication.[5] InteractionsTriamcinolone may interact with medications which are CYP3A4 inhibitors. CYP3A4 inhibitor may decrease the break down of triamcinolone which increases its amount in patients' body to cause toxicity.[6] Examples of CYP3A4 inhibitors include clarithromycin, verapamil, ketoconazole and anti-viral drugs, including nirmatrelvir and ritonavir.[7] These medications should not be administered with triamcinolone as drug-drug interactions may result.[6][7] Vitamin B2 Vitamin B2 is a supplement for promoting cell growth.[8] It can treat mouth ulcer without causing serious side effects. Medical uses and available formsVitamin B2, also known as riboflavin, can cure mouth ulcer.[8] The common formulation of vitamin B2 is in tablet form for oral administration.[9] Mechanism of actionVitamin B2 is essential for mucosal growth. Sufficient intake of vitamin B2 can repair the damaged oral tissues efficiently.[8] This can heal the mouth ulcer. Adverse effectsAdverse effects of vitamin B2 are mild. A common side effect of taking vitamin B2 is the production of yellow-orange urine. To address this problem, drinking more water may help to reduce the colour intensity of urine.[10] ContraindicationsContraindications of vitamin B2 is uncommon. [11] InteractionsInteractions of vitamin B2 with other drugs is uncommon.[12] Vitamin B12Medical uses and available forms Vitamin B12 is a supplement that can heal mouth ulcer. [13] It exists in tablet formulation and can be taken orally. [14] Mechanism of actionVitamin B12 is essential for cell duplication and formation of blood cells.[13] It can promote cell growth to repair the ulcerated regions in the mouth.[13] Adverse effectsOral administration of vitamin B12 may increase infection risks.[15] Side effects in other body systems are uncommon for oral formulation.[15] ContraindicationsPatients with hypersensitivity to vitamin B12 should not take the vitamin B12 supplement.[16] InteractionsHeavy alcohol consumption over 2 weeks may decrease vitamin B12 absorption, which may reduce the effectiveness of this anti-ulcer agent.[14] Vitamin B12 may also interact with other medications. The therapeutic effect of this supplement may be reduced by chloramphenicol.[16] Anti-ulcer agents to treat peptic ulcer disease (PUD)Several anti-ulcer dosing regimens that combine antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors (PPI) to treat helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) induced peptic ulcer disease (PUD). The role of antibiotic in the therapies is to eradicate H. pylori, while the action of PPI is to reduce gastric acid secretion. The anti-ulcer dosing regimens generally repair the injury of gastric mucosal layer in PUD. Examples of dosing regimen: [17]
All therapies last for at least 2 weeks.[18] Ulcerations that remain active beyond 2 weeks may require longer treatment period.[18] AntibioticsFor all antibiotics, patients need to finish the whole course of treatment to prevent antimicrobial resistance.[19] Recurrent ulceration may occur if H. pylori is not eradicated.[19]  AmoxicillinAmoxicillin is an antibiotic that can be used in combination with other drugs to cure PUD.[20] Amoxicillin has a minimal resistance rate in H. Pylori of 2% worldwide.[21] This agent is used in first line treatment unless contraindicated.[20] Medical uses and available formsAmoxicillin is a penicillin antibiotic.[22] One of its indications is to eradicate H. pylori.[23] It is available as oral capsules.[24] Mechanism of actionAmoxicillin can inhibit cell wall mucopeptide biosynthesis, leading to bacterial death.[23] This can reduce the ulcer recurrence risk.[25] Adverse effectsAmoxicillin may cause gastrointestinal discomfort, namely nausea and vomiting.[26] To eliminate these adverse effects, take the medication after a meal. Besides, this antibiotic may disrupt bowel microflora and induce diarrhea.[27] In rare cases, amoxicillin may induce risk of Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea.[26][28] ContraindicationsPatients with hypersensitivity or drug allergy to amoxicillin or other beta-lactams should not use this drug.[29] InteractionsPatients using allopurinol may increase risk of allergic reactions.[30] Allergic responses range from skin rash to anaphylaxis.[30] ClarithromycinClarithromycin is an antibiotic used in combined therapies for treating PUD.[31] Given the resistance of clarithromycin is higher than 15% in all WHO regions, it is still being used for eradicating H. pylori.[32] Medical uses and available formsClarithromycin is an antibiotic under the class of macrolide.[33] It is indicated for the eradication of H. pylori to minimize the probability of duodenal ulcer recurrence by being a component of the combination therapy.[31][34] Clarithromycin is available as tablets which should be taken orally.[35][36][37] Mechanism of actionClarithromycin binds to the P site of 50S ribosomal subunit reversibly, which inhibits both the RNA-dependent protein synthesis and bacterial growth.[38] This reversible inhibition can kill the H. pylori in the gastric region.[38] Adverse effects Clarithromycin may cause gastrointestinal adverse effects including vomiting, nausea, taste alteration and abdominal pain.[39] This medication can also cause liver toxicity.[39] Symptoms of liver damage include anorexia, dark urine, jaundice, tender abdomen and pruritus.[39] To assess the liver function, ALT/AST should be closely monitored.[39] This antibiotic may also induce rare side effects in the cardiovascular system, such as QT prolongation, which may precipitate arrhythmia.[39][40] ContraindicationsPatients with hypersensitivity to clarithromycin, erythromycin, or any of the macrolide antibiotics should not take this medication.[41] Additionally, if patients are diagnosed with liver dysfunction before the treatment, clarithromycin is also contraindicated.[41] InteractionsClarithromycin should not be taken with CYP3A4 inhibitors, for instance, atorvastatin, amlodipine and warfarin.[42] Specifically, statins should be stopped for the period of therapy and resumed once H. Pylori is eradicated.[43] MetronidazoleMetronidazole is an antibiotic with an off-label use in eradicating H. pylori for treating gastric ulceration. Resistance of metronidazole is above 15% worldwide.[32] It is likely to be resistant so is not the first line choice of treatment.[44] However, resistance is variable, that can be overcome by high dosages and in combination with other antibiotics.[45] Medical uses and available formsMetronidazole is an nitroimidazole antibiotic which can treat PUD.[44] Metronidazole as available as tablets for oral administration. Mechanism of action Metronidazole inhibits nucleic acid synthesis by disrupting DNA and breaking the strand of the bacteria. This kills the H. pylori.[46] Adverse effectsThe metronidazole tablet may have an unpleasant metallic taste, deteriorating drug compliance.[47] This medication may also induce rare side effect in the central nervous system, including neurotoxicity (encephalopathy, peripheral neuropathy, seizure).[48][49][50][51] ContraindicationsPatients should not drink alcohol to prevent disulfiram-like reactions, with symptoms of flushing, tachycardia, palpitations, nausea, vomiting.[51] Alcohol should only be taken at least 3 days after the last dose of metronidazole.[52][53] InteractionsMetronidazole should not be used with carbocisteine due to the enhancement of carbocisteine toxicity.[54] Metronidazole also interacts with mebendazole to increase the risk of severe skin response like toxic epidermal necrolysis and Steven-Johnson syndrome[54] Other antimicrobial drugsBismuth subsalicylate Bismuth subsalicylate is an antimicrobial drug in the off-labelled dosing regimen for H. pylori-induced PUD.[55] Its indication is to eradicate H. Pylori.[56] Medical uses and available formsBismuth subsalicylate exists in the form of tablets and should be administered orally.[35][57] Mechanism of actionBismuth subsalicylate consists of the bismuth and subsalicylate moiety. The bismuth in bismuth subsalicylate has antibacterial activity against H pylori.[35] The salicylate moiety stimulates prostaglandins and exerts local gastroprotective effects.[56] Adverse effectsCommon side effect is darkening of the tongue and teeth.[58] It also causes darkening of faeces which may confuse with the signs of gastrointestinal bleeding.[59] In renal failure patients, long-term use of bismuth may cause toxicity, resulting in encephalopathy (ataxia, headache, confusion, seizures).[58] ContraindicationsPatients who are allergic to aspirin or taking other salicylates should not use bismuth salicylate.[59] InteractionsAs bismuth binds to food and experiences a reduction of efficacy, patients should take the medication on an empty stomach.[60] Proton pump inhibitor (PPI)Proton pump inhibitor (PPI) is a group of medications that reduce secretion of gastric acid to prevent further deterioration of gastric ulceration.[61] Medical uses and available formsPPI exist in the forms of oral enteric coated tablets or enteric granules capped within capsules. To ensure the effectiveness of the medication, patients should swallow the whole tablet.[62] They should not chew or cut the tablets, nor open the capsule and grind the granules.[62] To add on, patients should take the medicine 30 to 60 minutes before meals.[63]  Different medications in this class has different standard doses:[35][36]
Mechanism of action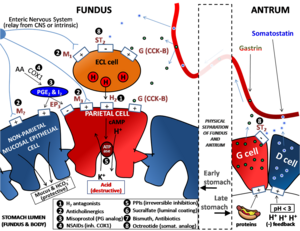 PPI irreversibly inhibits H+/K+ ATPase proton pump on gastric parietal cells to create a profound, long-lasting antisecretory effect on gastric acid.[61][64] Adverse effectsPPIs may induce common side effects including headache, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, and nausea. Taking PPI may rarely cause community-acquired pneumonia. Prolonged use of PPI may be associated with intestinal Clostridioides difficile infection, low magnesium level, Vitamin B12 and iron deficiency, osteoporosis, acute kidney inflammation, and gastric cancer.[65][66][67][68][69][70] ContraindicationsPatients who have hypersensitivity to PPIs, or using products containing rilpivirine concomitantly should not take PPI.[71] InteractionsDue to drug-drug interactions, patients taking clopidogrel, an antiplatelet drug, should not take PPI except rabeprazole.[72] Since PPI changes the acidity of the gastric content, patients taking ketoconazole, atazanavir, iron, erlotinib, and MMF should not take PPI at the same time.[72][73] References
|
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia