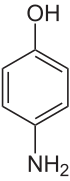
4-Aminophenol
Names
Preferred IUPAC name
Other names
p -Aminophenolpara -Aminophenol
Identifiers
385836
ChEBI
ChEMBL
ChemSpider
ECHA InfoCard 100.004.198
EC Number
2926
KEGG
MeSH
Aminophenols
UNII
UN number
2512
InChI=1S/C6H7NO/c7-5-1-3-6(8)4-2-5/h1-4,8H,7H2
Y Key: PLIKAWJENQZMHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Y InChI=1/C6H7NO/c7-5-1-3-6(8)4-2-5/h1-4,8H,7H2
Key: PLIKAWJENQZMHA-UHFFFAOYAD
Properties
C 6 H 7 N O
Molar mass
−1
Appearance
Colorless to reddish-yellow crystals
Density
1.13 g/cm3
Melting point
187.5 °C (369.5 °F; 460.6 K)
Boiling point
284 °C (543 °F; 557 K)
1.5 g/100 mL
Solubility
log P
0.04
Acidity (pK a )
5.48 (amino; H2 O) 10.30 (phenol; H2 O)[ 2]
Structure
orthorhombic
Thermochemistry
-190.6 kJ/mol
Hazards
GHS labelling
Warning
H302 , H332 , H341 , H410
P201 , P202 , P261 , P264 , P270 , P271 , P273 , P281 , P301+P312 , P304+P312 , P304+P340 , P308+P313 , P312 , P330 , P391 , P405 , P501
NFPA 704
Flash point
195 °C (383 °F; 468 K) (cc)
Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC):
671 mg/kg
Related compounds
Related aminophenols
2-Aminophenol 3-Aminophenol
Related compounds
Aniline Phenol
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Chemical compound
4-Aminophenol (or para -aminophenolp -aminophenolorganic compound with the formula H2 NC6 H4 OH. Typically available as a white powder,[ 3] developer for black-and-white film , marketed under the name Rodinal .
Reflecting its slightly hydrophilic character, the white powder is moderately soluble in alcohols and can be recrystallized from hot water. In the presence of a base, it oxidizes readily. The methylated derivatives N -methylaminophenolN ,N -dimethylaminophenol
The compound is one of three isomeric aminophenols, the other two being 2-aminophenol and 3-aminophenol .
Preparation
From phenol
It is produced from phenol by nitration followed by reduction with iron. Alternatively, the partial hydrogenation of nitrobenzene affords phenylhydroxylamine , which rearranges primarily to 4-aminophenol (Bamberger rearrangement ).[ 4]
C6 H5 NO2 + 2 H2 → C6 H5 NHOH + H2 O C6 H5 NHOH → HOC6 H4 NH2
From nitrobenzene
It can be produced from nitrobenzene by electrolytic conversion to phenylhydroxylamine , which spontaneously rearranges to 4-aminophenol.[ 5]
From 4-nitrophenol
4-nitrophenol can be reduced through a variety of methods, to yield 4-aminophenol. One method involves hydrogenation over a Raney Nickel catalyst . A second method involves selective reduction of the nitro group by Tin(II) Chloride in anhydrous ethanol or ethyl ethanoate . [ 6] [ 7]
Uses
4-Aminophenol is a building block used in organic chemistry. Prominently, it is the final intermediate in the industrial synthesis of paracetamol . Treating 4-aminophenol with acetic anhydride gives paracetamol:[ 8] [ 9] [ 10]
It is a precursor to amodiaquine , mesalazine , AM404 , parapropamol , B-86810 & B-87836 (c.f. WO 2001042204
4-Aminophenol converts readily to the diazonium salt .[ 11]
References
^ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book) . Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry . 2014. p. 690. doi :10.1039/9781849733069-FP001 . ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4 ^ Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics CRC Press . pp. 5– 89. ISBN 978-1498754286 ^ CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 65th Ed.^ Mitchell, S.C. & Waring, R.H. "Aminophenols." In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; 2002 Wiley-VCH, doi :10.1002/14356007.a02_099
^ Polat, K.; Aksu, M.L.; Pekel, A.T. (2002), "Electroreduction of nitrobenzene to p-aminophenol using voltammetric and semipilot scale preparative electrolysis techniques", Journal of Applied Electrochemistry , 32 (2), Kluwer Academic Publishers: 217– 223, doi :10.1023/A:1014725116051 , S2CID 54499902 ^ US2998450A , Godfrey, Wilbert & De, Angelis John, "Process of preparing nu-acetyl-p-amino phenol", issued 1961-08-29 ^ Bellamy, F. D.; Ou, K. (1984-01-01). "Selective reduction of aromatic nitro compounds with stannous chloride in non acidic and non aqueous medium" . Tetrahedron Letters . 25 (8): 839– 842. doi :10.1016/S0040-4039(01)80041-1 . ISSN 0040-4039 . ^ Ellis, Frank (2002). Paracetamol: a curriculum resource . Cambridge: Royal Society of Chemistry. ISBN 0-85404-375-6 ^ Anthony S. Travis (2007). "Manufacture and uses of the anilines: A vast array of processes and products". In Zvi Rappoport (ed.). The chemistry of Anilines Part 1 764 . ISBN 978-0-470-87171-3 ^ Elmar Friderichs; Thomas Christoph; Helmut Buschmann. "Analgesics and Antipyretics". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry doi :10.1002/14356007.a02_269.pub2 . ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2 ^ F. B. Dains, Floyd Eberly (1935). "p-Iodophenol". Organic Syntheses . 15 : 39. doi :10.15227/orgsyn.015.0039 .