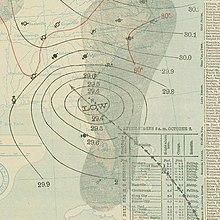
1898 Georgia hurricane
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Le Carnet B est l'instrument principal de surveillance des « suspects », français ou étrangers, sous la Troisième République en France. Il est créé en 1886 par le général Boulanger, pour lutter contre les activités d'espionnage. Géré par le ministère de l'Intérieur, il est progressivement étendu à tous les individus pouvant troubler l'ordre public ou antimilitaristes qui pourraient s'opposer à la mobilisation nationale. Le 1er août 1914, le ministre de l'Intérieur L…

le Gaduet Pont médiéval sur le Gaduet à Bransat. Caractéristiques Longueur 17,7 km Bassin collecteur Loire Régime pluvial Cours Source près du hameau du Rigotty · Localisation Le Theil · Altitude 428 m · Coordonnées 46° 21′ 29″ N, 3° 07′ 19″ E Confluence la Sioule · Localisation Saint-Pourçain-sur-Sioule · Altitude 235 m · Coordonnées 46° 18′ 28″ N, 3° 17′ 39″ E Géographie Pays travers�…

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「弐」…

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁地�…

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁地�…

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut). …
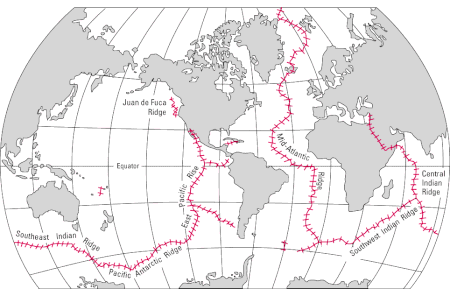
Mid-ocean ridge in the South Atlantic between the South American Plate and the Antarctic Plate Bathymetric map of the South American-Antarctic Ridge The South American–Antarctic Ridge or simply American-Antarctic Ridge (SAAR or AAR) (in Spanish: Dorsal Antártico-Americana) is the tectonic spreading center between the South American Plate and the Antarctic Plate. It runs along the sea-floor from the Bouvet Triple Junction in the South Atlantic Ocean south-westward to a major transform fault bo…

Nunavut ᓄᓇᕗᑦcode: iu is deprecated (Inuktitut)Wilayah BenderaLambang kebesaranMotto: ᓄᓇᕗᑦ ᓴᙱᓂᕗᑦ (Nunavut Sannginivut)Our land, our strengthNotre terre, notre force BC AB SK MB ON QC NB PE NS NL YT NT NU Koordinat: 70°10′00″N 90°44′00″W / 70.16667°N 90.73333°W / 70.16667; -90.73333Koordinat: 70°10′00″N 90°44′00″W / 70.16667°N 90.73333°W / 70.16667; -90.73333NegaraKanadabergabung deng…

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府與�…

BabysitterPoster promosiSkenarioChoi Hyo-bi (최효비)SutradaraKim Yong-su (김용수)PemeranShin Yoon-joo Kim Min-joon Cho Yeo-jeong Lee Seung-joonPenata musikPark Seong-jin (박성진)Negara asalKorea SelatanBahasa asliKoreaJmlh. episode4ProduksiDurasi61-65 menit per episodeRumah produksiL&HoldingsDistributorKBSRilis asliJaringanKBS2Rilis14 Maret 2016 (2016-03-14) Babysitter adalah serial televisi Korea Selatan tahun 2016, disiarkan di KBS2 dari tanggal 14 Maret 2016, dibintang…

Військово-музичне управління Збройних сил України Тип військове формуванняЗасновано 1992Країна Україна Емблема управління Військово-музичне управління Збройних сил України — структурний підрозділ Генерального штабу Збройних сил України призначений для плануван�…

Season of television series The X-Files Season of television series The X-FilesSeason 2DVD coverStarring David Duchovny Gillian Anderson No. of episodes25ReleaseOriginal networkFoxOriginal releaseSeptember 16, 1994 (1994-09-16) –May 19, 1995 (1995-05-19)Season chronology← PreviousSeason 1Next →Season 3List of episodes The second season of the science fiction television series The X-Files commenced airing on the Fox network in the United States on September 16, 1994…

Aneurisma AortaGambar A menunjukkan aorta normal. Gambar B menunjukkan aneurisma aorta torakalis (posisinya di belakang jantung). Gambar C menunjukkan aneurisma aorta abdominalis yang posisinya di bawah arteri yang menyuplai darah ke ginjal.Informasi umumSpesialisasiBedah vaskularTipeAneurisma aorta abdominalis, aneurisma aorta torakalis, aneurisma aorta torakoabdominalisPenyebabAterosklerosis, hipertensi, trauma, infeksi aortaFaktor risikoMerokok, hipertensi, diabetes melitus, riwayat keluarga …

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Lineation geology – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Spanish. Click [show] for important translation ins…

2003 Sri Lankan filmClean Out ක්ලීන් අවුට්Directed byRoy de SilvaWritten byRoy de SilvaProduced byAruna Kanthi FilmsStarringRodney Warnakula Priyantha Seneviratne Ananda Wickramage Wasanthi GunarathnaCinematographyG. NandasenaEdited byElmo HallidayMusic bySangeeth WickramasingheProductioncompaniesPrasad Color Lab, IndiaRelease date 6 February 2003 (2003-02-06) CountrySri LankaLanguageSinhala Clean Out (Sinhala: ක්ලීන් අවුට්) is a 2003 Sr…

Scottish football player and manager (1934–2015) For other people named Dave Mackay, see David McKay. Dave Mackay Mackay in 2006Personal informationFull name David Craig Mackay[1]Date of birth (1934-11-14)14 November 1934Place of birth Edinburgh, ScotlandDate of death 2 March 2015(2015-03-02) (aged 80)Place of death Nottingham, EnglandHeight 5 ft 8 in (1.73 m)[2][3][4]Position(s) Left-half / SweeperSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)1953–19…

Banchi di Sopra vicino a piazza Tolomei, con la lupa senese su una colonna Banchi di Sopra (il nome generico della strada è banchi, senza l'aggiunta di via) è una delle direttrici principali del centro storico di Siena, spina dorsale del Terzo di Camollia. Indice 1 Storia 2 Descrizione 3 Note 4 Bibliografia 5 Voci correlate 6 Altri progetti Storia Proveniente da Porta Camollia corrisponde al segmento centrale urbano di Siena della via Francigena, fino alla confluenza della Croce del Travaglio …

See also: List of Jains Idol of Kundakunda, the most revered Digambara acharya Part of a series onJainism Jains History Timeline Index Philosophy Anekantavada Cosmology Ahimsa Karma Dharma Mokṣa Kevala Jnana Dravya Tattva Brahmacarya Aparigraha Gunasthana Saṃsāra EthicsEthics of Jainism Mahavratas (major vows) Ahiṃsā (non-violence) Satya (truth) Asteya (non-stealing) Brahmacarya (chastity) Aparigraha (non-possession) Anuvratas (further vows) Sāmāyika Sallekhana Jain prayers Bhaktamara …

Japanese light novel series and its adaptations Reign of the Seven SpellbladesFirst light novel volume cover七つの魔剣が支配する(Nanatsu no Maken ga Shihai Suru)GenreFantasy[1] Light novelWritten byBokuto UnoIllustrated byRuria MiyukiPublished byASCII Media WorksEnglish publisherNA: Yen PressImprintDengeki BunkoDemographicMaleOriginal runSeptember 7, 2018 – presentVolumes13 + 1 MangaWritten byBokuto UnoIllustrated bySakae EsunoPublished byKadokaw…

氷彫刻の白鳥 2011年NHLウィンター・クラシックのロゴ 氷像製作時の様子 氷像(ひょうぞう)、もしくは氷彫刻とは、氷を原材料に作られた像のことである。 大型の氷像は、寒冷地の観光振興やイベント、芸術を目的に作られる。 氷 個人や氷屋(業者)が製造した氷、天然の池や湖から天然氷を切り出して使用する[1]。魚や花等を氷に閉じ込める例があるが、魚の�…