.no
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando la regione biogeografica, vedi Corno d'Africa (regione biogeografica). Corno d'AfricaBaraawe, Somalia Stati Gibuti Eritrea Etiopia Somalia Somaliland (non riconosciuto da nessuno stato al mondo) TerritorioAfrica Orientale Superficie1 882 757 km² Abitanti122 618 170 (2016) Lingueamarico, oromonico, somalo, arabo, francese, inglese, italiano, tigrino, sidamigno, afar, wolaytto Fusi orariUTC+3 La posizione del C…

Town in the state of Maine, United States Town in Maine, United StatesMonson, MaineTownMonson Village, c. 1905 SealMotto: By the Shores of Lake HebronLocation in Piscataquis County and the state of Maine.Coordinates: 45°17′11″N 69°30′21″W / 45.28639°N 69.50583°W / 45.28639; -69.50583CountryUnited StatesStateMaineCountyPiscataquisArea[1] • Total49.10 sq mi (127.17 km2) • Land46.78 sq mi (121.16…

Achaemenide burial The grave as it appears in the exacvation report Torc with lion head The Acropole Tomb was excavated on 6 February 1901 by Jacques de Morgan on the so called acropolis in Susa. The Achaemenide burial was found intact and contained a high number of personal adornments, many of them made in gold. The burial dates around 350 to 332 BC. Most of the objects are now on display in the Louvre in Paris.[1] It is one of the most important Achaemenide treasures ever found. The bu…

Military boarding school in Pakistan Cadet College PetaroLocationPetaro-76120, Sindh. Petaro is situated about 30 km from Hyderabad.Coordinates25°32′28″N 68°19′34″E / 25.541°N 68.326°E / 25.541; 68.326InformationMottoA Petaro Cadet Does Not Cheat, Lie Or StealOpenedAugust 1957 at MirpurkhasAugust 1959 at PetaroPrincipalCommodore Mushtaq Ahmed Siyal (SI)MAdjutantLieutenant Commander Abu Bakr Siddique, Pakistan NavyAreaover 700 acresHouses8Colour(s) &…

Digital motion picture camera system by Arri This article contains content that is written like an advertisement. Please help improve it by removing promotional content and inappropriate external links, and by adding encyclopedic content written from a neutral point of view. (March 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Arri Alexa camera The Arri Alexa is a digital motion picture camera system developed by Arri. The Arri Alexa was introduced in April 2010 and was Arri's first major tr…

حزب الاتحاد الديمقراطي البلد مصر تاريخ التأسيس 1990 المقر الرئيسي القاهرة الأيديولوجيا علمانية تعديل مصدري - تعديل هذه المقالة عن حزب الاتحاد الديمقراطي في مصر. لالحزب الاتحادي الديمقراطي في السودان، طالع الحزب الاتحادي الديمقراطي. حزب الاتحاد الديمق…

Biển IrelandẢnh vệ tinhVị trígiữa đảo Anh và đảo IrelandTọa độ53°B 5°T / 53°B 5°T / 53; -5LoạiBiểnLưu vực quốc giaVương quốc Liên hiệp Anh và Bắc Ireland; Cộng hòa Ireland; Đảo ManDiện tích bề mặt46,007 km2 (17,763 dặm vuông Anh)Thể tích nước2,800 km3 (2.270.000 acre⋅ft)Các đảoAnglesey và đảo Holy, đảo Man và Calf of Man, đảo Bardsey, Walney, Lambay, Ire…

Team position in Australian rules football The Carlton interchange bench in a match against St Kilda, 2011. Interchange (or, colloquially, the bench or interchange bench) is a team position in Australian rules football, consisting of players who are part of the selected team but are not currently on the field of play. Interchange numbers AFL As of the 2023 season, at AFL level, each team is permitted four interchange players, and a maximum of seventy-five total player interchanges during a game;…
La isla Programa de televisiónGénero Reality showDirigido por Luz AldamaPresentado por Pedro García AguadoPaís de origen EspañaIdioma(s) original(es) EspañolN.º de temporadas 2N.º de episodios 16ProducciónDuración 75 minutos (aprox.)Empresa(s) productora(s) Atresmedia TelevisiónShine IberiaLanzamientoMedio de difusión La SextaHorario Miércoles, a las 22h30 (T1)Jueves, a las 22h45 (T2)Fecha de lanzamiento 17 de mayo de 2017Enlaces externos Sitio web oficial Ver todos los créditos (I…
Public health strategy Measures such as hand washing, social distancing and face masks reduce and delay the peak of active cases, allowing more time for healthcare capacity to increase and better cope with patient load.[1] Time gained through thus flattening the curve can be used to raise the line of healthcare capacity to better meet surging demand.[2]Without pandemic containment measures—such as social distancing, vaccination, and use of face masks—pathogens can spread expo…

County in Oregon, United States County in OregonWallowa CountyCountyWallowa County Courthouse in EnterpriseLocation within the U.S. state of OregonOregon's location within the U.S.Coordinates: 45°35′N 117°10′W / 45.58°N 117.17°W / 45.58; -117.17Country United StatesState OregonFoundedOctober 14, 1887Named forWallowa RiverSeatEnterpriseLargest cityEnterpriseArea • Total3,152 sq mi (8,160 km2) • Land3,146 sq …

Argentines of Ukrainian birth or descent Ethnic group Ukrainian ArgentinesУкраїнці aргентини (Ukrainian)Ucraniano-argentinos (Spanish) Ukrainian Argentines in parade in Misiones ProvinceTotal population4,811 (by birth, 2023)[1]+ 470,000 (by ancestry)[2][3][4][5]1% of Argentina's populationRegions with significant populationsPredominantly in the Pampas, the North and the PatagoniaLanguages Spanish Ukrainian Religion Ukrainian Catho…

German professional ice hockey team Eisbären BerlinCityBerlin, GermanyLeagueDeutsche Eishockey LigaFounded1954; 70 years ago (1954)Home arenaUber Arena(capacity: 14,200)Colours Owner(s)Anschutz Entertainment Group(Philip Anschutz, chairman)General managerPeter-John LeeHead coachSerge AubinCaptainKai WissmannWebsiteeisbaeren.deFranchise history1954–1990SC Dynamo Berlin1990–1992EHC Dynamo Berlin Current season Eisbären Berlin (pronunciationⓘ; Engli…
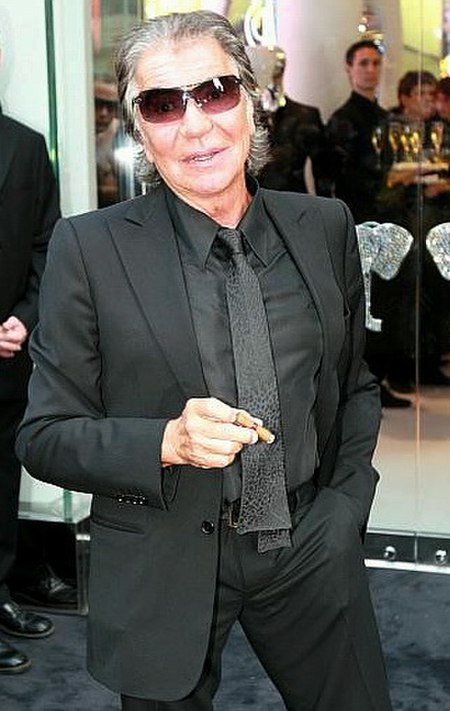

Italian fashion designer and inventor (1940–2024) Roberto CavalliCavalli in 2009Born(1940-11-15)15 November 1940[1]Florence, Kingdom of ItalyDied12 April 2024(2024-04-12) (aged 83)Florence, ItalyOccupationFounder of Roberto CavalliLabelsRoberto CavalliJustcavalliRoberto Cavalli JuniorRoberto Cavalli ParfumsRoberto Cavalli HomeSpouse(s)Silvanella Giannoni (1964–1974)Eva Düringer (1980–2010)PartnerSandra NilssonChildren6 Roberto Cavalli (Italian pronunciation: [roˈbɛrto k…

French lawyer Pierre-Henri TeitgenMinister of StateIn office22 January 1947 – 22 October 1947PresidentVincent AuriolPrime MinisterPaul Ramadier Personal detailsBorn(1908-05-29)29 May 1908Rennes, FranceDied6 April 1997(1997-04-06) (aged 88)Paris, FrancePolitical partyPopular Republican MovementAlma materUniversity of NancyProfessionLawyer Pierre-Henri Teitgen (29 May 1908 – 6 April 1997) was a French lawyer, professor and politician.[1] Teitgen was born in Rennes, Britta…

2014 biographical film This article is about the 2014 film. For the 2012 book on which the film is based, see American Sniper (book). American SniperTheatrical release posterDirected byClint EastwoodScreenplay byJason HallBased onAmerican Sniperby Chris KyleScott McEwenJim DeFeliceProduced by Clint Eastwood Robert Lorenz Andrew Lazar Bradley Cooper Peter Morgan Starring Bradley Cooper Sienna Miller CinematographyTom SternEdited by Joel Cox Gary D. Roach Productioncompanies Village Roadshow Pictu…

City in Chūbu, JapanMakinohara 牧之原市CityTea plantations in Makinohara FlagSealLocation of Makinohara in Shizuoka PrefectureMakinohara Coordinates: 34°44′N 138°13′E / 34.733°N 138.217°E / 34.733; 138.217CountryJapanRegionChūbu (Tōkai)PrefectureShizuokaFirst official recorded6 BCSagara Town settledApril 1, 1889Haibara Town settledApril 1, 1955Both town merged and city settledOctober 11, 2005Government • MayorKikuo Sugimoto (from October 20…

For information on the 2006 Delaware race for the United States Senate, see Delaware United States Senate election, 2006. 2006 United States House of Representatives election in Delaware ← 2004 November 7, 2006 2008 → Nominee Mike Castle Dennis Spivack Party Republican Democratic Popular vote 143,897 97,565 Percentage 57.2% 38.8% County results House district resultsCastle: 40–50% 50–60% …

Varian tekstual adalah variasi bacaan yang ditemukan dalam berbagai naskah kuno yang memuat bagian Perjanjian Baru dalam Alkitab Kristen. Varian tekstual muncul ketika seorang penyalin membuat sebuah perubahan yang disengaja atau tidak disengaja pada teks yang sedang direproduksi olehnya. Beberapa perubahan yang umum termasuk penghapusan, penataan ulang, pengulangan, atau penggantian satu atau beberapa kata ketika mata si penyalin beralih kembali dari salinannya ke naskah asli tetapi pada kata y…

特雷西納[1](葡萄牙語:Teresina,巴西葡萄牙語發音:[teɾeˈzinɐ])是巴西的城鎮,位於該國東部,也是皮奧伊州的首府,面積1,392平方公里,海拔高度72米,受熱帶氣候影響,每年平均降雨量約1,500毫米,2011年人口822,363。 参考文献 ^ 民政部地名研究所 (编). Teresina 特雷西纳. 世界地名译名词典. 北京: 中国社会出版社: 2832. 2017-05. ISBN 978-7-5087-5525-0. OCLC 1121629943. OL …

