|
ʻŪkēkē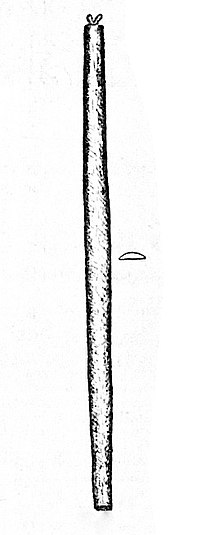 The ʻūkēkē is a musical bow made of koa wood, 16 to 24 inches long and about 11⁄2 inches wide with two or three strings fastened through and around either end, tuned to an A major triad. Prior to the introduction of steel strings, gut or sennit (coconut fibre) was used. The strings were strummed with one hand while the other hand kept the ʻūkēkē in position. The mouth would then act as a resonating chamber.Unlike the African stick zither and Berimbau
The ʻūkēkē is the only stringed instrument indigenous to Hawaii, with other Hawaiian string instruments like the ukulele and slack-key guitar having been introduced by European sailors and settlers. Modern usageThe 19th-century Hawaiian kumu hula ʻIoane ʻŪkēkē played the ʻūkēkē. Hawaiian artists such as Palani Vaughan and Ranga Pae have incorporated the ʻūkēkē into their compositions. Meaning of ʻūkēkēIn Hawaiian ʻūkēkē means to quiver. The instrument nearly went extinct until Mahi La Pierre studies old Hawaiian music and attempted to make one. He was successful in the recreation of the instrument, and the Papahan Kuaola organization is now devoted to preserving the memory of the ʻūkēkē and its effect on the Hawaiian culture. Papahana KuaolaPapahana Kuaola is a native Hawaiian project dedicated to preserving lifelong learning of Hawaiian history and tradition. This project is supported by the Institute of Museum and Library Services (IMLS). The goal is to provide activities for classrooms and people of all ages to connect to their heritage. ʻūkēkē soundThe steel strings of the ʻūkēkē are tuned to the three A major notes (A, C#, E). It was played in the evening so it could be properly heard in the quiet. The sound was labeled as devil music when two women playing the instrument to each other were first heard by a foreign missionary. Bibliography
External links
|
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia