|
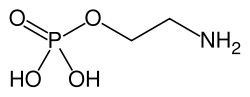
Phosphoethanolamin
Phosphoethanolamin ist der Phosphorsäureester des Monoethanolamins. Es tritt als Strukturausschnitt beispielsweise in Phosphatidylethanolaminen auf und ist Abbauprodukt des Sphingosin-1-phosphates. DarstellungPhosphoethanolamin kann durch die Reaktion von Oxazolidin-2-on mit Phosphorsäure hergestellt werden.[2]  Ein weiterer Syntheseweg ist die Ringöffnung von Aziridin durch Phosphorsäure.[3]  Einzelnachweise
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Index:
pl ar de en es fr it arz nl ja pt ceb sv uk vi war zh ru af ast az bg zh-min-nan bn be ca cs cy da et el eo eu fa gl ko hi hr id he ka la lv lt hu mk ms min no nn ce uz kk ro simple sk sl sr sh fi ta tt th tg azb tr ur zh-yue hy my ace als am an hyw ban bjn map-bms ba be-tarask bcl bpy bar bs br cv nv eml hif fo fy ga gd gu hak ha hsb io ig ilo ia ie os is jv kn ht ku ckb ky mrj lb lij li lmo mai mg ml zh-classical mr xmf mzn cdo mn nap new ne frr oc mhr or as pa pnb ps pms nds crh qu sa sah sco sq scn si sd szl su sw tl shn te bug vec vo wa wuu yi yo diq bat-smg zu lad kbd ang smn ab roa-rup frp arc gn av ay bh bi bo bxr cbk-zam co za dag ary se pdc dv dsb myv ext fur gv gag inh ki glk gan guw xal haw rw kbp pam csb kw km kv koi kg gom ks gcr lo lbe ltg lez nia ln jbo lg mt mi tw mwl mdf mnw nqo fj nah na nds-nl nrm nov om pi pag pap pfl pcd krc kaa ksh rm rue sm sat sc trv stq nso sn cu so srn kab roa-tara tet tpi to chr tum tk tyv udm ug vep fiu-vro vls wo xh zea ty ak bm ch ny ee ff got iu ik kl mad cr pih ami pwn pnt dz rmy rn sg st tn ss ti din chy ts kcg ve
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia