|
Okavirus
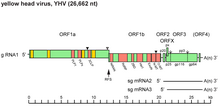
Okavirus is a genus of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which infect crustaceans.[1] Host organisms are mostly shrimp. It is the only genus in the family Roniviridae.[2] Viruses associated with the genus include: gill-associated virus (GAV) which causes reddening, biofouling with exoparasites, emaciation, and massive mortality; and yellow head virus (YHV) which causes yellow head, arrest of feeding, and massive mortality.[1][3] The name is derived from the 'Oka' or lymphoid organ in which the viruses are commonly detected and in which pathology occurs during acute infections. Lymphoid organs are anatomical structures common to penaeid shrimp. There are three species in this genus.[1] StructureViruses in the genus Okavirus are enveloped, with bacilliform geometries, and helical symmetry. The diameter is around 20–30 nm.[1][3] GenomeGenomes are linear and non-segmented, around 26 kb in length.[1][3] Life cycleEntry into the host cell is achieved by attachment to host receptors, which mediates endocytosis. Replication follows the positive stranded RNA virus replication model. Positive stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. Crustaceans and mostly prawns serve as the natural host. Transmission routes are ingestion.[1][3] Taxonomy The genus contains one subgenus with three species:[4] References
External links |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||