N170
|
Read other articles:

United States historic placeMeridian HighwayU.S. National Register of Historic Places Bridge on the Meridian Highway in Pierce County, Nebraska; seen from the southwestNearest cityPierce, NebraskaArea36 acres (15 ha)Built1911 (1911)NRHP reference No.01001273[1]Added to NRHPNovember 29, 2001 Meridian Highway was a United States auto trail in the early twentieth century. It roughly followed the path of present-day U.S. Route 81 from Pembina, North Dakota to Fort Worth, …
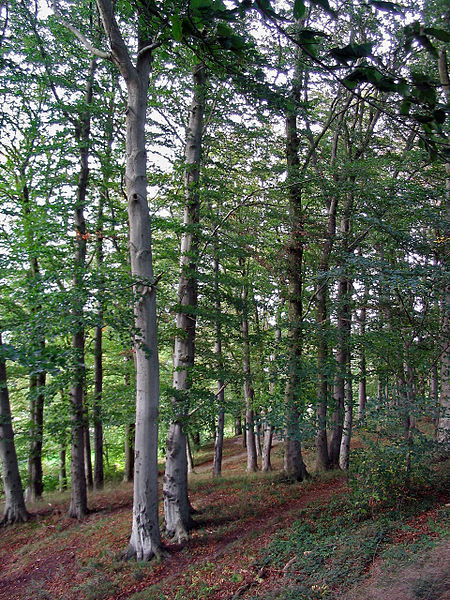

Fagales Fagus sylvatica Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Plantae (tanpa takson): Tracheophyta (tanpa takson): Angiospermae (tanpa takson): Eudikotil (tanpa takson): Rosid (tanpa takson): Fabid Ordo: Fagales Famili lihat teks. Fagales adalah salah satu ordo tumbuhan berbunga yang termasuk dalam klad euRosidae I, Rosidae, core Eudikotil, dan Eudikotil (Sistem klasifikasi APG II). Bangsa ini juga diakui sebagai takson dalam sistem klasifikasi Cronquist dan tercakup dalam anak kelas Hamamelidae, kelas M…

Video game series by Ninja Kiwi For the first game in the series, see § Bloons Tower Defense. Video game seriesBloons Tower DefenseThe logo of Bloons Tower Defense, the first game in the series.Genre(s)Tower defenseDeveloper(s) Ninja Kiwi Digital Goldfish Ltd. (iOS) Publisher(s)Ninja KiwiPlatform(s)Android, browser (Flash), iOS, macOS, Nintendo DSi, PlayStation Portable, Microsoft Windows, Xbox One, Nintendo SwitchFirst releaseBloons TDAugust 16, 2007Latest releaseBloons TD Battles 2Novemb…

Wali Kota BaubauPetahanaMuhammad Rasman ManafiPenjabatsejak 25 September 2023Pemerintah Kota BaubauKediamanRumah Jabatan Wali Kota BaubauMasa jabatan5 tahun dan dapat dipilih kembali untuk satu kali masa jabatanDibentuk21 Juni 2001; 22 tahun lalu (2001-06-21)Pejabat pertamaBelum diketahuiSitus webSitus web resmi Berikut adalah daftar wali kota Baubau dari masa ke masa. No. Wali Kota Potret Partai Awal Akhir Masa jabatan Periode Wakil Ref. 1 Mz. Amirul Tamim(lahir 1954) PPP 2003 2008 4�…

Une nouvelle amie Données clés Réalisation François Ozon Scénario François Ozond'après la nouvelle de Ruth Rendell Musique Philippe Rombi Acteurs principaux Romain DurisAnaïs DemoustierRaphaël Personnaz Sociétés de production Mandarin Cinéma Pays de production France Genre Film dramatique Durée 105 minutes Sortie 2014 Pour plus de détails, voir Fiche technique et Distribution. modifier Une nouvelle amie est un mélodrame français écrit et réalisé par François Ozon, sorti en 20…

Nuclear-powered cruise missile 9M730 Burevestnik TypeNuclear-powered cruise missilePlace of originRussiaService historyIn serviceUnder developmentSpecificationsLength12 m[1]Effective firing rangeEffectively unlimitedWarheadThermonuclear Satellite imagery of the launch site The 9M730 Burevestnik (Russian: Буревестник; Storm petrel, NATO reporting name: SSC-X-9 Skyfall)[2][3][4] is a Russian low-flying, nuclear-powered, nuclear-ar…
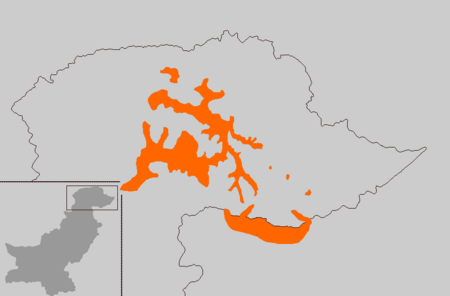
Indo-Aryan language primarily spoken in Gilgit-Baltistan and Gurez valley Not to be confused with Kohistani Shina. Shinaݜݨیاٗ زبان / ݜݨیاٗ گلیتوࣿ زبانṢiṇyaáThe word Ṣiṇyaá written in the Arabic script in Nastaliq style.Pronunciation[ʂiɳjá]Native toPakistan, IndiaRegionGilgit-Baltistan, Kohistan, Drass, GurezEthnicityShinaNative speakers720,200 Shina (2018)[1]and Shina, Kohistani 458,000 (2018)[2]Language familyIndo-European …

Intense dislike or fear of Eastern Orthodoxy, hostility or prejudice towards Orthodox Christians This article is about negative attitudes towards Eastern Orthodox Christians and acts which have been committed against them because of their faith. For Anti-Orthodox theological positions and various theoretical and philosophical disputes during Christian history, see History of Christian theology. Freedom of religion Concepts Laicism Religious discrimination Religious censorship Religious liberty R…
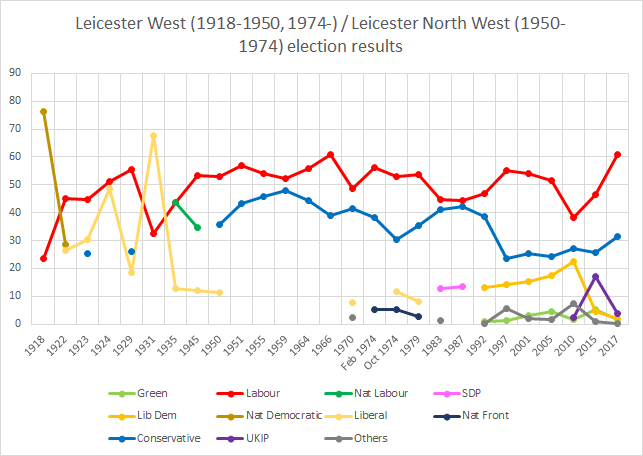
Parliamentary constituency in the United Kingdom, 1950–1974 Leicester North WestFormer Borough constituencyfor the House of Commons1950–February 1974SeatsoneCreated fromLeicester WestReplaced byLeicester West Leicester North West was a borough constituency in the city of Leicester. It returned one Member of Parliament (MP) to the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. The constituency was created for the 1950 general election, and abolished for the February 1974 general el…
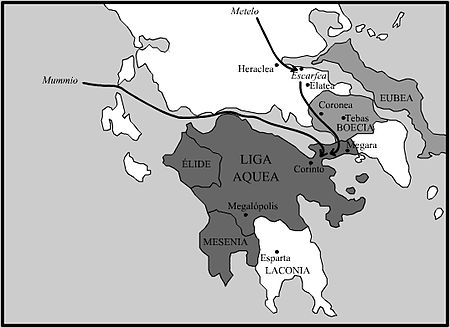
亞該亞戰爭《科林斯的最後一天》,由東尼·羅伯特-弗勒里(英语:Tony Robert-Fleury)於1870年所繪日期前146年地点希臘本土结果 羅馬獲得勝利领土变更 羅馬佔領希臘本土参战方 羅馬共和國 亞該亞同盟指挥官与领导者 昆圖斯·凱基利烏斯·梅特盧斯盧基烏斯·穆米烏斯 梅格洛玻利斯的克里圖勞斯迪亞厄斯 亞該亞戰爭,是前146年羅馬共和國與希臘亞該亞同盟之間所爆發的戰爭,亞…

Deaf sign language of Cuba Cuban Sign LanguageFingerspelling of LSCNative toCubaSigners34,000 (2021)[1]Language family(unclassified)[2]Language codesISO 639-3csfGlottologcuba1235 LSC Dactilema Cuban Sign Language, (Spanish: Lengua de señas cubana, LSC) is the language used by the Deaf community in Cuba. There are approximately 19,000 users of the language.[3] Cuban Sign Language is an important part of the culture of the Deaf community in Cuba.[4] Histo…

Old and stable part of the continental lithosphere Cratons of South America and Africa during the Triassic Period when the two continents were joined as part of the Pangea supercontinent A craton ( /ˈkreɪtɒn/ KRAYT-on, /ˈkrætɒn/ KRAT-on, or /ˈkreɪtən/ KRAY-tən;[1][2][3] from Greek: κράτος kratos strength) is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often …

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (يوليو 2017) حريما الإحداثيات 32°38′17.4″N 35°50′17.6″E / 32.638167°N 35.838222°E / 32.638167; 35.838222 تقسيم إداري البلد الأردن&#…

1288 treaty between England and Aragon The Treaty of Canfranc was an agreement, signed in October 1288, between Edward I of England and Alfonso III of Aragon about the release of Charles II of Naples,[1] who had been captured by the Admiral of Sicily, Roger of Lauria, in a naval battle on 5 June 1284.[2][3] References ^ Bárány 2010, p. 71. ^ Bárány 2010, p. 68. ^ Runciman 1958, p. 246. Sources Bárány, Attila (2010). The English relations of Charles II…

Tenis padaPekan Olahraga Nasional XIX Tunggal putra putri Ganda putra putri campuran Beregu putra putri Pertandingan tenis tunggal putra pada Pekan Olahraga Nasional XIX berlangsung di Lapang Tenis Siliwangi dan Taman Maluku, Kompleks olahraga Siliwangi, Kota Bandung, Jawa Barat dari tanggal 23 sampai 27 september 2016.[1] Jadwal Tanggal 22−23 Sep 23−24 Sep 25 Sep 26 Sep 27 Sep Tunggal putra Babak 32 besar Babak 16 besar Perempatfinal Semifinal Final Unggulan Arief Rahman (KTM) (Fina…

Letkol Tek (Purn.)Basir Surya Informasi pribadiLahir(1914-07-17)17 Juli 1914Garut, Jawa Barat, Hindia BelandaMeninggal20 Desember 1993(1993-12-20) (umur 79)Tasikmalaya, Jawa BaratKarier militerPihak IndonesiaDinas/cabang TNI Angkatan UdaraPangkat LetkolSatuanKorps TeknikSunting kotak info • L • B Letnan Kolonel Tek. (Purn.) Basir Surya (17 Juli 1914 – 20 Desember 1993) adalah seorang perwira Teknik TNI Angkatan Udara, komandan pertama Lanud Wiriadinata tah…

Armando MadonnaMadonna all'Atalanta nel 1988Nazionalità Italia Altezza180 cm Peso74 kg Calcio RuoloAllenatore (ex centrocampista, attaccante) Termine carriera2002 - giocatore CarrieraGiovanili 1980-1981 Atalanta Squadre di club1 1981-1983 Atalanta19 (1)1983-1988 Piacenza169 (43)1988-1990 Atalanta57 (12)1990-1991 Lazio25 (2)1991-1992→ Piacenza27 (5)1992-1993 SPAL21 (0)1993-2002 Alzano Virescit259 (29) Carriera da allenatore 2002-2003 Alzano Vi…

此條目没有列出任何参考或来源。 (2018年3月3日)維基百科所有的內容都應該可供查證。请协助補充可靠来源以改善这篇条目。无法查证的內容可能會因為異議提出而被移除。 河合曾良出生1649年??月??日 日本 信濃国下桑原村逝世1710年6月18日 日本 壱岐国勝本職業俳諧師體裁俳句代表作曾良旅日記 河合曾良(日语:河合 曾良/かわい そら Kawai Sora,1649年—1710年6月18�…

Quella strana ragazza che abita in fondo al vialeJodie Foster in una scena del filmTitolo originaleThe Little Girl Who Lives Down the Lane Paese di produzioneCanada, Francia Anno1976 Durata94 min e 96 min Rapporto16/9 Generedrammatico, thriller RegiaNicolas Gessner SoggettoLaird Koenig (racconto) SceneggiaturaLaird Koenig ProduttoreZev Braung FotografiaRené Verzier MontaggioYves Langlois MusicheChristian Gaubert Interpreti e personaggi Jodie Foster: Rynn Jacobs Martin Sheen: Frank Halle…

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Dimanche (homonymie) et Jour du Seigneur. Un dimanche, par Paul Signac, 1890. Le dimanche est le jour de la semaine privilégié pour le repos hebdomadaire dans plusieurs pays du monde, dont la France. La norme internationale ISO 8601 considère que le dimanche clôt la semaine[1], et le code avec le chiffre 7. Pour les religions bibliques, le dimanche est le premier jour de la semaine juive et chrétienne. Pour les chrétiens, le dimanche est le jour de la rés…