Manganese stearate
|
| Names
|
| Other names
Manganese(II) stearate, manganese distearate, manganese(2+) dioctadecanoate
|
| Identifiers
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ChemSpider
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard
|
100.020.110 
|
| EC Number
|
|
|
|
|
| UNII
|
|
|
|
|
InChI=1S/2C18H36O2.Mn/c2*1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18(19)20;/h2*2-17H2,1H3,(H,19,20);/q;;+2/p-2 Key: SZINCDDYCOIOJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-L
|
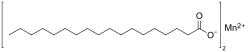
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)[O-].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)[O-].[Mn+2]
|
| Properties
|
|
|
C
36H
70MnO
4
|
| Molar mass
|
621.89
|
| Appearance
|
Pale pink powder
|
| Density
|
g/cm3
|
| Boiling point
|
359.4 °C (678.9 °F; 632.5 K)
|
|
|
insoluble
|
| Hazards
|
| GHS labelling:
|
|
|
Warning
|
|
|
H302, H312, H315, H319, H332, H335
|
| Flash point
|
162.4 °C (324.3 °F; 435.5 K)
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). |
Chemical compound
Manganese stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of manganese and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70MnO
4.[1][2] The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.[3]
Synthesis
Manganese stearate is synthesized by the reaction of stearic acid with sodium hydroxide, followed by reacting with manganese chloride.[4]
Also, the reaction of manganese(II) acetate with stearic acid.[5]
Physical properties
The compound forms pale pink powder.[6]
Insoluble in water.[6]
Uses
The compound is used in organic synthesis reactions.[6]
Also as an oxidant additive for oxo-biodegradable polymers (for example, high-density polyethylene).[7]
References
|
|---|
| Manganese(−I) | |
|---|
| Manganese(0) | |
|---|
| Manganese(I) | |
|---|
| Manganese(II) | |
|---|
| Manganese(II,III) | |
|---|
| Manganese(II,IV) | |
|---|
| Manganese(III) | |
|---|
| Manganese(IV) | |
|---|
| Manganese(V) | |
|---|
| Manganese(VI) | |
|---|
| Manganese(VII) | |
|---|
Salts and covalent derivatives of the stearate ion |
|---|
|
