|
systemd是Linux電腦作業系統之下的一套中央化系統及設定管理程式(init),包括有守护进程、程式庫以及應用軟體,由Lennart Poettering带头开发。其开发目标是提供更优秀的框架以表示系统服务间的依赖关系,并依此实现系统初始化时服务的并行启动,同时达到降低Shell的系统开销的效果,最终代替现在常用的System V与BSD风格init程序。
目前絕大多數的Linux發行版都已採用systemd代替原來的System V。
systemd在LGPL 2.1及其后续版本许可证下开源发布[1][2]。
起源
systemd这一名字源于Unix中的一个惯例:在Unix中常以“d”作为系统守护进程(英語:daemon,亦称后台进程)的后缀标识。除此以外,systemd亦是借代英文术语D体系,而这一术语即是用于描述一个人具有快速地适应环境并解决困难的能力[3]。
设计
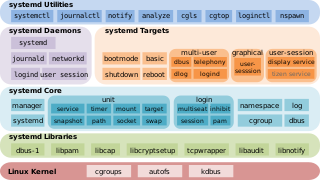 systemd組件 systemd組件
 專門由systemd所使用的統一層次結構控制組 專門由systemd所使用的統一層次結構控制組
与System V风格init相比,systemd采用了以下新技术:
- 將service(服務)、target(執行模式,類似於運行級別)、mount、timer、snapshot、path、socket、swap等稱為Unit。比如,一個auditd服務(就是auditd.service)就是一個Unit,一個multi-user.target執行模式也是一個Unit。
- 采用Socket激活式与D-Bus激活式服务,以提高相互依赖的各服务的并行运行性能;
- 用cgroups代替进程ID来追踪进程,因此即使是两次fork之后生成的守护进程也不会脱离systemd的控制。
- 用target代替System V的運行級別(Runlevel),比如,SystemD的graphical.target相當於System V的init 5,multi-user.target相當於System V的init 3。
- 內建journald 日誌管理系統。
- 內建resolved、timesyncd、networkd等元件。
- 引入localectl、timedatectl、hostnamectl等新命令,系統配置更方便。
从设计构思上说,由于systemd使用了cgroup与fanotify等组件以实现其特性,所以只适用于Linux[4]。有鉴于此,考虑到kFreeBSD分支的软件源无法纳入systemd,为与其他分支保持一致,Debian开发者尽力避免纳入systemd[5]。但Lennart Poettering本人对此并不在意,并称「Debian GNU/kFreeBSD不过是玩具系统」[6]。但Debain 8.0 Jessie開始以systemd取代sysvinit。[7]。
应用
systemd已纳入众多Linux发行版的软件源中,以下简表:
- 默认init程序为systemd的发行版
- 可以使用systemd的发行版
 systemd-manager systemd-manager
除此以外,systemd已由Lennart Poettering提请纳入GNOME 3.2的外部依赖关系列表[21],而这意味着所有使用GNOME的发行版都应该使用systemd,最低限度来说也必须将其作为配置选项之一。
注释
参考文献
- ^ 1.0 1.1 Lennart Poettering, systemd Status Update, 2012-04-21 [2012-04-28], (原始内容存档于2015-08-27)
- ^ Lennart Poettering, FAQs, systemd (0pointer), [2011-06-16], (原始内容存档于2017-01-15)
- ^ Lennart Poettering, Kay Sievers, Thorsten Leemhuis, Control Centre: The systemd Linux init system, 2012-05-08 [2012-06-10], (原始内容存档于2012-06-14)
- ^ Lennart Poettering, systemd FAQ, 2010-04-30 [2011-12-14], (原始内容存档于2017-01-15)
- ^ Jake Edge, Debian debates systemd, 2011-07-27 [2011-12-14], (原始内容存档于2012-05-15)
- ^ Un entretien avec Lennart Poettering), 2011-07-05 [2011-12-14], (原始内容存档于2014-08-05)
- ^ Richard Chirgwin, Debian ships new 'Jessie' release with systemd AND sysvinit, 2015-04-27 [2016-05-23], (原始内容存档于2016-04-25)
- ^ Dj Walker-Morgan, Fedora 15's Lovelock released, The H, 2011-05-24 [2011-05-26], (原始内容存档于2012-07-12)
- ^ Jake Edge, systemd and Fedora 14, LWN, 2010-08-25 [2011-02-03], (原始内容存档于2010-12-27)
- ^ Fabian Scherschel, Mageia 2 arrives with GNOME 3 and systemd, The H, 2012-05-23 [2012-05-26], (原始内容存档于2013-12-08)
- ^ Dj Walker-Morgan, Mandriva 2011 arrives with systemd, The H, 2011-08-29 [2011-08-29], (原始内容存档于2012-07-09)
- ^ Chris von Eitzen, openSUSE 12.1 arrives with systemd and Btrfs, The H, 2011-11-16 [2011-11-16], (原始内容存档于2012-04-20)
- ^ Bächler, Thomas. systemd is now the default on new installations. Arch Linux Official. [2012-10-16]. (原始内容存档于2012-10-15).
- ^ systemd, Archlinux Wiki, [2011-03-09], (原始内容存档于2011-05-23)
- ^ Full switch to Systemd with Claire-2012.10 ISO released today, [2012-10-28], (原始内容存档于2013-03-15)
- ^ Bdale Garbee. The Debian technical committee vote concludes. LWN.net. [2014-02-12]. (原始内容存档于2014-02-22).
- ^ seb128, VividVervet/ReleaseNotes, Ubuntu Wiki, 2015-04-24 [2015-04-29], (原始内容存档于2015-06-11)
- ^ Comment #210, systemd – bug #318365 (Gentoo's Bugzilla), [2011-07-05], (原始内容存档于2015-02-16)
- ^ systemd, Gentoo's Documentation, [2011-07-05], (原始内容存档于2011-06-26)
- ^ systemd, Gentoo wiki, [2012-08-26], (原始内容存档于2012-10-12)
- ^ Lennart Poettering, systemd as an external dependency, desktop-devel mailing list (GNOME), 2011-05-18 [2011-05-26], (原始内容存档于2014-10-10)
外部链接
- 官方网站
- systemd, 0pointer, [2012-06-10], (原始内容存档于2017-01-15)
- systemd project, Fedora, [2012-06-10], (原始内容存档于2012-05-21)
- The road forward for systemd, LWN, [2012-06-10], (原始内容存档于2012-10-21)
- cgit, freedesktop, [2012-06-10], (原始内容存档于2012-06-20)
参见
|