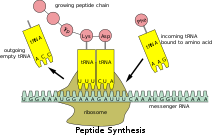
核糖體轉譯過程示意圖 核糖體停滯 (Ribosomal pause, Ribosomal stall)[ 1] 核糖體 轉譯 mRNA 時發生停滯的現象,在原核生物 與真核生物 細胞中皆會發生[ 2] [ 3] 核糖體分析 [ 4]
早在1980年代即有研究顯示核糖體轉譯mRNA不同區域的的速率不一致,當時認為轉譯較慢的位點是因含有罕見的密碼子 ,對應的tRNA 在細胞中含量較少,因此與mRNA結合所需的時間較長[ 5] [ 2] 脯氨酸 序列(polyproline)、tRNA未活化(未連接氨基酸)等[ 1] eIF5A [ 6] 蛋白質摺疊 有關(即在蛋白質的結構域 轉譯結束時發生停滯,讓其有時間完成折疊)[ 7] 核糖體移碼 發生[ 8] [ 9]
有時核糖體停滯為不可逆,原核生物與真核生物皆有將核糖體自mRNA釋出的機制。當真核細胞中mRNA上不具終止密碼子 時,核糖體轉譯後會停滯於mRNA的末端,此時細胞會啟動無終止密碼子媒介式分解 途徑(NSD)將核糖體釋出,並將該mRNA與轉譯的多肽產物降解;有時核糖體會遇到mRNA上較複雜的二級結構 而停滯,細胞則可啟動轉譯停滯分解 (no-go decay,NGD)途徑,亦可將核糖體釋出,並降解mRNA及多肽產物[ 8] 转运-信使RNA (tmRNA)啟動反式轉譯來處理停滯的核糖體[ 1] ArfA ArfB [ 1] [ 10]
^ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Buskirk, Allen R.; Green, Rachel. Ribosome pausing, arrest and rescue in bacteria and eukaryotes . Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2017, 372 (1716): 20160183. PMC 5311927 PMID 28138069 doi:10.1098/rstb.2016.0183 ^ 2.0 2.1 Li GW, Oh E, Weissman JS. The anti-Shine-Dalgarno sequence drives translational pausing and codon choice in bacteria . Nature. 2012, 484 (7395): 538–41 [2021-12-06 ] . Bibcode:2012Natur.484..538L PMC 3338875 PMID 22456704 doi:10.1038/nature10965 存档 于2021-12-06). ^ Lopinski JD, Dinman JD, Bruenn JA. Kinetics of ribosomal pausing during programmed -1 translational frameshifting . Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2000, 20 (4): 1095–103. PMC 85227 PMID 10648594 doi:10.1128/MCB.20.4.1095-1103.2000 ^ Brar GA, Yassour M, Friedman N, Regev A, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS. High-resolution view of the yeast meiotic program revealed by ribosome profiling . Science. 2012, 335 (6068): 552–7. Bibcode:2012Sci...335..552B PMC 3414261 PMID 22194413 doi:10.1126/science.1215110 ^ Kontos H, Napthine S, Brierley I. Ribosomal pausing at a frameshifter RNA pseudoknot is sensitive to reading phase but shows little correlation with frameshift efficiency . Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2001, 21 (24): 8657–70. PMC 100026 PMID 11713298 doi:10.1128/MCB.21.24.8657-8670.2001 ^ Darnell AM, Subramaniam AR, O'Shea EK. Translational Control through Differential Ribosome Pausing during Amino Acid Limitation in Mammalian Cells . Molecular Cell. 2018, 71 (2): 229–243.e11. PMC 6516488 PMID 30029003 doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.041 ^ Gawroński P, Jensen PE, Karpiński S, Leister D, Scharff LB. Pausing of Chloroplast Ribosomes Is Induced by Multiple Features and Is Linked to the Assembly of Photosynthetic Complexes . Plant Physiology. March 2018, 176 (3): 2557–2569. PMC 5841727 PMID 29298822 doi:10.1104/pp.17.01564 ^ 8.0 8.1 Buchan JR, Stansfield I. Halting a cellular production line: responses to ribosomal pausing during translation. Biology of the Cell. 2007, 99 (9): 475–87. PMID 17696878 doi:10.1042/BC20070037 ^ Manjunath H, Zhang H, Rehfeld F, Han J, Chang TC, Mendell JT. Suppression of Ribosomal Pausing by eIF5A Is Necessary to Maintain the Fidelity of Start Codon Selection . Cell Reports. 2019, 29 (10): 3134–3146.e6. PMC 6917043 PMID 31801078 doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2019.10.129 ^ Chan, KH; Petrychenko, V; Mueller, C; Maracci, C; Holtkamp, W; Wilson, DN; Fischer, N; Rodnina, MV. Mechanism of ribosome rescue by alternative ribosome-rescue factor B. . Nature Communications. 2020, 11 (1): 4106. PMC 7427801 PMID 32796827 doi:10.1038/s41467-020-17853-7